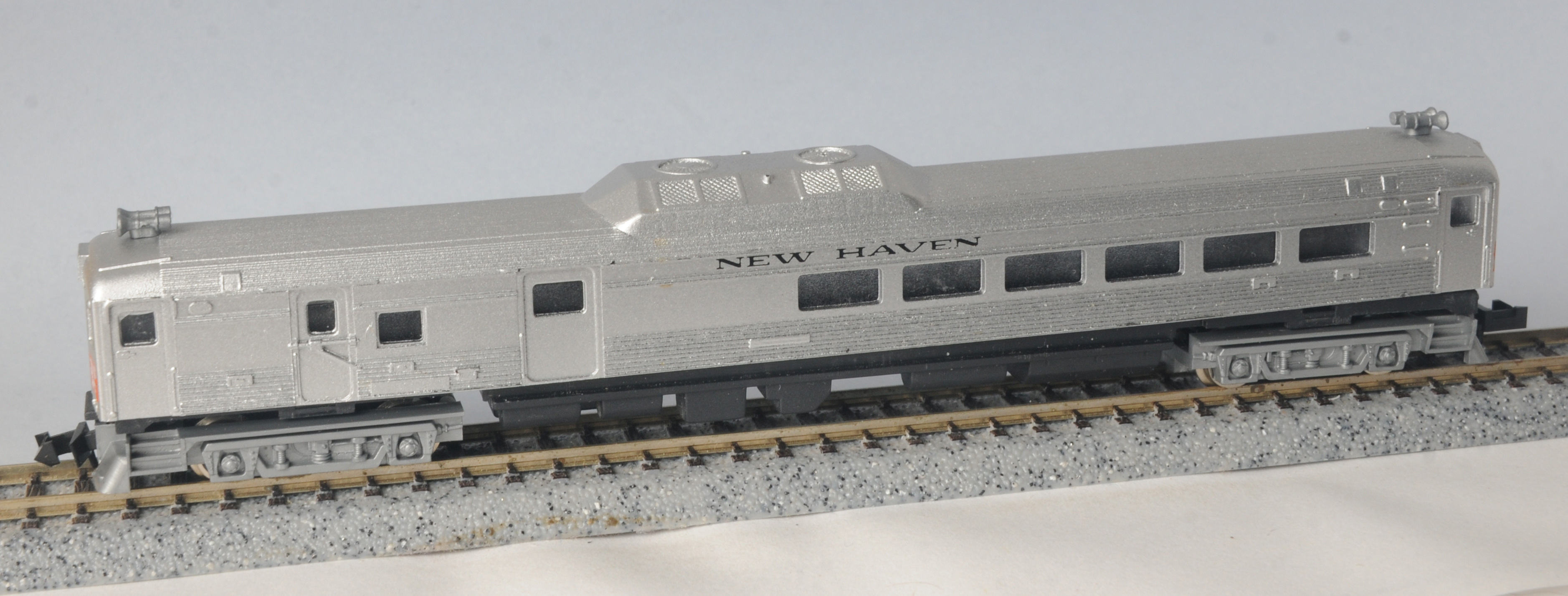
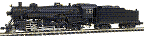Specific Item Information: Dummy. Price as per Con-Cor website 2017
Listed as new in the 1982-83 JMC Con-Cor Catalog for 14.98 for the Dummy.
Model Information: Con-Cor introduced this Roco made model of the Budd RDC-1 and the Budd RDC-2 in 1981. In 1982, they added the RDC-3 to the line-up. The same mechanism is used for all three railcars models: RDC-1's, 2's and 3's. The models come with both operating mechanisms as well as 'dummy' versions. For some strange reason, Con-Cor released more unpowered than powered units.
The chassis is huge and all-metal, making these units capable of serving as a make-shift doorstop, paperweight or club. They are driven with a 5-pole skew-wound motor. The Rapido couplers are truck-mounted and the wheels all have deep flanges, making Code-55 track a no-no. Fortunately, the heft of these puppies yields good pickup and nice slow-speed operation. Of course, the dummy units don't have the metal chassis and are quite light in comparison.
The chassis is huge and all-metal, making these units capable of serving as a make-shift doorstop, paperweight or club. They are driven with a 5-pole skew-wound motor. The Rapido couplers are truck-mounted and the wheels all have deep flanges, making Code-55 track a no-no. Fortunately, the heft of these puppies yields good pickup and nice slow-speed operation. Of course, the dummy units don't have the metal chassis and are quite light in comparison.
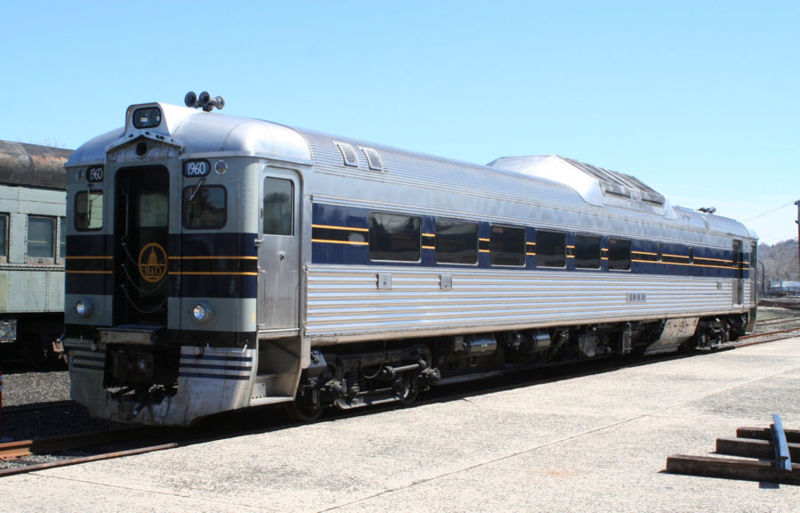
Prototype History: This Single-car DMU is commonly known as the "RDC," the motorized Rail Diesel Car generally operated in rural areas where ridership and mail/parcel transport were too low for regular passenger train service. When first introduced, the RDC was also proclaimed to be the savior of branch line and suburban service. It was heavily used as a commuter service workhorse (and still is currently in some locations!).
The Budd Company rolled out the first RDC in the fall of 1949, a single RDC-1 "Budd Demonstrator." Hundreds more would eventually follow for service to railroads throughout North America and around the world (including South America, Australia, Saudi Arabia and even Cuba!). Oddly enough, it was Budd's experience in the production of small yet powerful diesel engines for WWII tanks that eventually lead to the birth of the RDC.
A total of 398 units were built. The RDC utilized two compact motors mounted under the car's floor to drive one axle on each truck. Capable of being operated by a motorman from either end of the car, these units could be used independently or combined to create a two- or three-unit consist. These railcars cold achieve as top speed of 85mph
A review of the Budd roster reveals that many RDC cars were operated well into the 1970's and early 1980's, with a small number still in service today!
Four standardized designs were created to reduce the time and expense of custom production
- RDC-1 was strictly passenger-oriented, containing 90 coach seats.
- RDC-2 contained 71 seats and a separate baggage area.
- RDC-3 combined a Railway Post Office with a baggage compartment and 49 seats.
- RDC-4 was a self-contained RPO-Express car.
Read more on Wikipedia.
The Budd Company rolled out the first RDC in the fall of 1949, a single RDC-1 "Budd Demonstrator." Hundreds more would eventually follow for service to railroads throughout North America and around the world (including South America, Australia, Saudi Arabia and even Cuba!). Oddly enough, it was Budd's experience in the production of small yet powerful diesel engines for WWII tanks that eventually lead to the birth of the RDC.
A total of 398 units were built. The RDC utilized two compact motors mounted under the car's floor to drive one axle on each truck. Capable of being operated by a motorman from either end of the car, these units could be used independently or combined to create a two- or three-unit consist. These railcars cold achieve as top speed of 85mph
A review of the Budd roster reveals that many RDC cars were operated well into the 1970's and early 1980's, with a small number still in service today!
Four standardized designs were created to reduce the time and expense of custom production
- RDC-1 was strictly passenger-oriented, containing 90 coach seats.
- RDC-2 contained 71 seats and a separate baggage area.
- RDC-3 combined a Railway Post Office with a baggage compartment and 49 seats.
- RDC-4 was a self-contained RPO-Express car.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: Con-Cor has been in business since 1962. Many things have changed over time as originally they were a complete manufacturing operation in the USA and at one time had upwards of 45 employees. They not only designed the models,but they also built their own molds, did injection molding, painting, printing and packaging on their models.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Manufacturer Information:  The company was founded in 1960 by Ing. Heinz Rössler and started with a plastic Minitanks series of military vehicles. After export to the USA became successful, the model line was expanded with model trains in HO scale and the smaller N scale. TT scale was also subsequently added to the product line. The model rail product line covers many European countries including Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Spain, Austria, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden and the Netherlands, and also the USA.
The company was founded in 1960 by Ing. Heinz Rössler and started with a plastic Minitanks series of military vehicles. After export to the USA became successful, the model line was expanded with model trains in HO scale and the smaller N scale. TT scale was also subsequently added to the product line. The model rail product line covers many European countries including Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Spain, Austria, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden and the Netherlands, and also the USA.
On July 15, 2005 ROCO Modellspielwaren GmbH was declared bankrupt. From July 25 the company continues as Modelleisenbahn GmbH, but still uses the Roco brand and associated logo. On October 1, 2007, distribution of the 'Minitank' product series was assigned to the German model car manufacturer Herpa.
Since February 2008 Modelleisenbahn also owns Fleischmann, which like Roco had gone bankrupt. The two companies continue as separate brands under Modelleisenbahn GmbH, while benefiting from economies of scale through joined development projects, marketing and procurement.
From Wikipedia

On July 15, 2005 ROCO Modellspielwaren GmbH was declared bankrupt. From July 25 the company continues as Modelleisenbahn GmbH, but still uses the Roco brand and associated logo. On October 1, 2007, distribution of the 'Minitank' product series was assigned to the German model car manufacturer Herpa.
Since February 2008 Modelleisenbahn also owns Fleischmann, which like Roco had gone bankrupt. The two companies continue as separate brands under Modelleisenbahn GmbH, while benefiting from economies of scale through joined development projects, marketing and procurement.
From Wikipedia
Item created by: Alain LM on 2017-08-14 14:48:41. Last edited by meadowsn1956 on 2021-10-11 21:14:04
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.