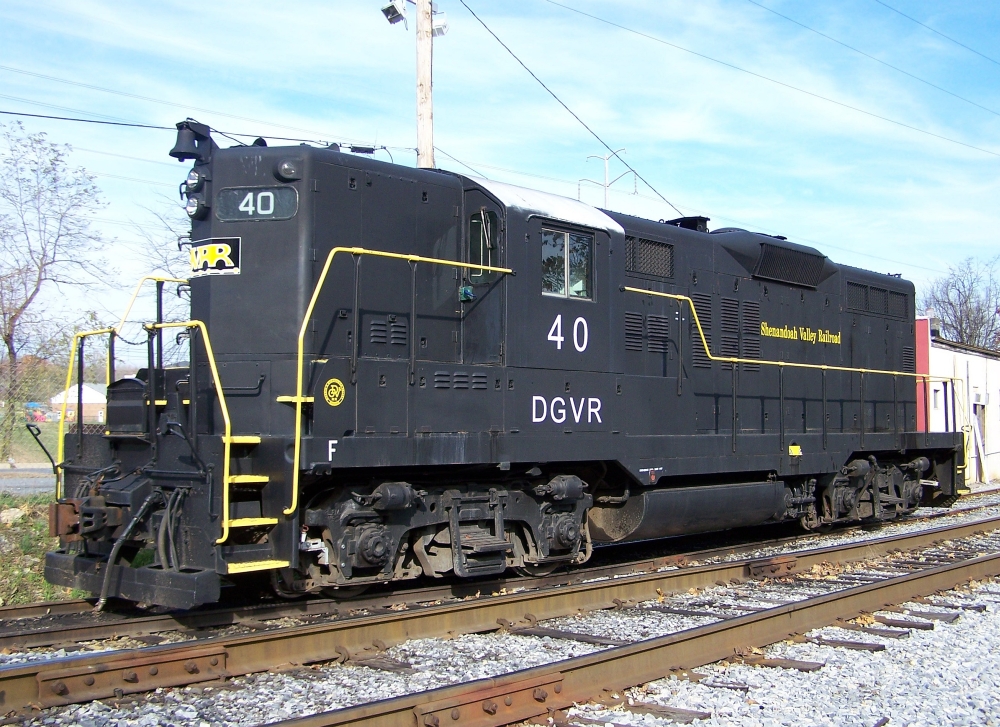
Model Information: The Atlas GP7, GP7-TT, GP9 and GP9-TT models are some of Atlas' oldest models. The four locomotives share the same internal mechanisms and differ only in their shell details. Unlike many of their other older body styles, these bodies have been updated several times and are still a regular part of the Atlas production cycle.
Given their long history of releases, these models come in a plethora of different versions. The first release of this body type was in 1974 and the models were produced by Roco in Austria. Production for these models ended in 1982. The next release started in 1987 and the models were re-tooled by Kato in Japan for Atlas. The Kato version re-used the same mechanism as was used in the earlier RS3. It doesn't work as well in the Geep. The third version was made in China for Atlas and these engines were essentially a redo of the Kato mechanism (with all the faults). Finally, in 2006, the mechanism was redone properly and this 4th version is a properly DCC-Ready split frame, slow-motor modern engine.
Assembly instructions from Atlas: GP9 (Japan version), GP9 Ph.2 (China version), GP9 Torpedo Tube.
Given their long history of releases, these models come in a plethora of different versions. The first release of this body type was in 1974 and the models were produced by Roco in Austria. Production for these models ended in 1982. The next release started in 1987 and the models were re-tooled by Kato in Japan for Atlas. The Kato version re-used the same mechanism as was used in the earlier RS3. It doesn't work as well in the Geep. The third version was made in China for Atlas and these engines were essentially a redo of the Kato mechanism (with all the faults). Finally, in 2006, the mechanism was redone properly and this 4th version is a properly DCC-Ready split frame, slow-motor modern engine.
Assembly instructions from Atlas: GP9 (Japan version), GP9 Ph.2 (China version), GP9 Torpedo Tube.
DCC Information: The first version of this engine (Roco) gets a solid "No" for DCC capability, but this is no surprise as these were made in 1974. The next two releases (Kato and China) are split-frame, but also split-board. They may be DCC-Friendly, but likely it will be a fair amount of work to upgrade these. The most recent version (China, 2006+) is eminently DCC-Ready. Furthermore, most road-names and numbers produced since 2006 are available in both a DCC-Ready and a Decoder-Equipped version. Earlier DCC factory-equipped versions were fitted with Lenz LE063XF decoders, whereas most recent versions are fitted with NCE N12A2 decoders. The Atlas version of these decoders will respond to manufacturer's address "127" (CV8) i.e. "Atlas Model Railroad Products", though being identical to their original manufacturer's specification.
For non-DCC-ready versions, a wired DCC decoder installation for this model can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog.
Models produced since 2006 accept the following plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A4: 1.5 Amp N Scale Board Replacement Mobile Decoder for Atlas GP30 and other short Atlas diesel locomotives.
- Digitrax DN163A2: Retired decoder, replaced by DN163A4.
- NCE N12A2: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas Classic Series GP7, GP9, GP30, GP35.
- TCS ASD4 (Installation for GP7, Installation for GP9)
- MRC 1955: N-Scale Sound Decoder for Atlas GP-7, GP-9, GP-30 or GP-35
For non-DCC-ready versions, a wired DCC decoder installation for this model can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog.
Models produced since 2006 accept the following plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A4: 1.5 Amp N Scale Board Replacement Mobile Decoder for Atlas GP30 and other short Atlas diesel locomotives.
- Digitrax DN163A2: Retired decoder, replaced by DN163A4.
- NCE N12A2: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas Classic Series GP7, GP9, GP30, GP35.
- TCS ASD4 (Installation for GP7, Installation for GP9)
- MRC 1955: N-Scale Sound Decoder for Atlas GP-7, GP-9, GP-30 or GP-35
Prototype History: An EMD GP9 is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division in the United States, and General Motors Diesel in Canada between January, 1954, and August, 1963. US production ended in December, 1959, while an additional thirteen units were built in Canada, including the last two in August, 1963. Power was provided by an EMD 567C sixteen-cylinder engine which generated 1,750 horsepower (1.30 MW). This locomotive type was offered both with and without control cabs; locomotives built without control cabs were called GP9B locomotives. All GP9B locomotives were built in the United States between February, 1954, and December, 1959.
One option available for locomotives without dynamic brakes, was to remove the two 22.5 in × 102 in (571.5 mm × 2,590.8 mm) air reservoir tanks from under the frame, and replace them with four 12 in × 150.25 in (304.80 mm × 3,816.35 mm) tanks that were installed on the roof of the locomotive, above the prime mover. These “torpedo tubes” as they were nicknamed, enabled the fuel and water tanks to be increased to 1,100 US gallons (4,200 l; 920 imp gal) each, although some railroads opted for roof-mounted air tanks and 2,200 US gallons (8,300 l; 1,800 imp gal) fuel tanks on their freight ‘Geeps’.
From Wikipedia
One option available for locomotives without dynamic brakes, was to remove the two 22.5 in × 102 in (571.5 mm × 2,590.8 mm) air reservoir tanks from under the frame, and replace them with four 12 in × 150.25 in (304.80 mm × 3,816.35 mm) tanks that were installed on the roof of the locomotive, above the prime mover. These “torpedo tubes” as they were nicknamed, enabled the fuel and water tanks to be increased to 1,100 US gallons (4,200 l; 920 imp gal) each, although some railroads opted for roof-mounted air tanks and 2,200 US gallons (8,300 l; 1,800 imp gal) fuel tanks on their freight ‘Geeps’.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  First of all, Milwaukee Road has only ever been a popular nickname. The real name from 1874 was Chicago Milwaukee & St. Paul. For the next 36 years, the CM&StP linked Chicago with Milwaukee, Green Bay, Madison, Wausau, the Twin Cities, Duluth, Kansas City and Omaha with a dense network of branches in Wisconsin, Iowa, southern Minnesota and eastern South Dakota. Essentially, the lines ended at the Missouri River.
First of all, Milwaukee Road has only ever been a popular nickname. The real name from 1874 was Chicago Milwaukee & St. Paul. For the next 36 years, the CM&StP linked Chicago with Milwaukee, Green Bay, Madison, Wausau, the Twin Cities, Duluth, Kansas City and Omaha with a dense network of branches in Wisconsin, Iowa, southern Minnesota and eastern South Dakota. Essentially, the lines ended at the Missouri River.
With a dearth of friendly western connections, CM&StP decided to build their own line to the Pacific. The original target was the bustling megalopolis of Eureka, California. However, they built toward Seattle instead. In 1909 the line opened. Along the way, they served Miles City, Lewiston, Great Falls, Harlowton and Butte, Montana; Avery, Idaho; and Spokane, Seattle and Tacoma, Washington. In 1912, they began to electrify two long segments, Harlowton, Montana to Avery, Idaho and Othello, Washington to Tacoma.
In 1921, they leased the Chicago Terre Haute & Southeastern and a bit later the Chicago Milwaukee & Gary to reach the coal fields of southern Indiana. Both roads were in trouble and dragged the CM&StP into receivership. In 1928, they emerged with a small name change. It was now the Chicago Milwaukee St. Paul & Pacific. Right after that, the nickname “Milwaukee Road” began to catch on.
The three Class One’s that already served the Pacific Northwest, Northern Pacific, Great Northern (along with their jointly owned minion Spokane Portland & Seattle) and Union Pacific were not pleased with their new neighbor and avoided building interchanges with them unless absolutely necessary. This left Milwaukee to haul whatever traffic they could originate or terminate on their own line or via a hand full of shortlines with which they interchanged. This is why when you see photos of Milwaukee Road trains west of the Dakotas, an exceptionally large majority of cars are lettered for Milwaukee Road.
Milwaukee’s steam fleet is generally quite handsome beginning with the period after WWI. Many locomotives were built in their own shops. The steam era came to an end on the Milwaukee in 1957.
The electrified lines were ruled by boxcabs and Bi-Polars for decades. In the 1950’s, Little Joe’s diverted from the Soviet Union arrived on the Milwaukee (and the South Shore.) By the late 60’s diesels began to regularly invade the electrified lines. Little Joes and diesels were MU’ed. The aging catenary could only handle so many electrics at a time so diesels filled the horsepower gap. By 1972, falling traffic, a declining fleet of serviceable electrics and the deteriorating catenary caused Milwaukee Road to de-energize the western lines lines with Avery to Harlowton lines following two years later.
Meanwhile on the east end, as a condition of the 1971 merger of Monon into L&N, Milwaukee Road received trackage rights from Chicago to Louisville. This gave Southern a friendly connection to Chicago it was losing with Monon.
In 1977, Milwaukee Road entered receivership again. This time, radical restructuring was needed. In 1980, everything west of Miles City, Montana was abandoned. Some lines were picked up by connections or spawned new shortlines but nearly 1,000 miles of track was pulled up. In 1982, Miles City to Ortonville, Minnesota was abandoned. Milwaukee was concentrating on their pre-1909 routes plus the new line to Louisville.
In an attempt to win back middle distance TOFC traffic, Milwaukee began running fast and short piggyback trains, usually behind a single SD40-2 and with a dozen or so 89’ flats. Unit coal trains added to the bottom line. By the mid-80s, the streamlined Milwaukee Road was up for sale and Grand Trunk Western, Chicago & North Western and Soo Line got into a bidding war. GTW had diverted 40,000 cars onto Milwaukee Road between Chicago and Duluth to help them turn a profit in 1983. Ironically, the ICC (which controlled mergers at the time) pushed GTW out of the contest leaving just C&NW and Soo. Furious, GTW diverted their 40,000 carloads off the Milwaukee. C&NW outbid Soo, but the ICC chose Soo Line anyway. Milwaukee Road merged into Soo Line in 1985. Almost immediately, Soo shops began painting big black rectangles over MILWAUKEE ROAD on the diesels, giving birth to the “bandit” paint scheme.

With a dearth of friendly western connections, CM&StP decided to build their own line to the Pacific. The original target was the bustling megalopolis of Eureka, California. However, they built toward Seattle instead. In 1909 the line opened. Along the way, they served Miles City, Lewiston, Great Falls, Harlowton and Butte, Montana; Avery, Idaho; and Spokane, Seattle and Tacoma, Washington. In 1912, they began to electrify two long segments, Harlowton, Montana to Avery, Idaho and Othello, Washington to Tacoma.
In 1921, they leased the Chicago Terre Haute & Southeastern and a bit later the Chicago Milwaukee & Gary to reach the coal fields of southern Indiana. Both roads were in trouble and dragged the CM&StP into receivership. In 1928, they emerged with a small name change. It was now the Chicago Milwaukee St. Paul & Pacific. Right after that, the nickname “Milwaukee Road” began to catch on.
The three Class One’s that already served the Pacific Northwest, Northern Pacific, Great Northern (along with their jointly owned minion Spokane Portland & Seattle) and Union Pacific were not pleased with their new neighbor and avoided building interchanges with them unless absolutely necessary. This left Milwaukee to haul whatever traffic they could originate or terminate on their own line or via a hand full of shortlines with which they interchanged. This is why when you see photos of Milwaukee Road trains west of the Dakotas, an exceptionally large majority of cars are lettered for Milwaukee Road.
Milwaukee’s steam fleet is generally quite handsome beginning with the period after WWI. Many locomotives were built in their own shops. The steam era came to an end on the Milwaukee in 1957.
The electrified lines were ruled by boxcabs and Bi-Polars for decades. In the 1950’s, Little Joe’s diverted from the Soviet Union arrived on the Milwaukee (and the South Shore.) By the late 60’s diesels began to regularly invade the electrified lines. Little Joes and diesels were MU’ed. The aging catenary could only handle so many electrics at a time so diesels filled the horsepower gap. By 1972, falling traffic, a declining fleet of serviceable electrics and the deteriorating catenary caused Milwaukee Road to de-energize the western lines lines with Avery to Harlowton lines following two years later.
Meanwhile on the east end, as a condition of the 1971 merger of Monon into L&N, Milwaukee Road received trackage rights from Chicago to Louisville. This gave Southern a friendly connection to Chicago it was losing with Monon.
In 1977, Milwaukee Road entered receivership again. This time, radical restructuring was needed. In 1980, everything west of Miles City, Montana was abandoned. Some lines were picked up by connections or spawned new shortlines but nearly 1,000 miles of track was pulled up. In 1982, Miles City to Ortonville, Minnesota was abandoned. Milwaukee was concentrating on their pre-1909 routes plus the new line to Louisville.
In an attempt to win back middle distance TOFC traffic, Milwaukee began running fast and short piggyback trains, usually behind a single SD40-2 and with a dozen or so 89’ flats. Unit coal trains added to the bottom line. By the mid-80s, the streamlined Milwaukee Road was up for sale and Grand Trunk Western, Chicago & North Western and Soo Line got into a bidding war. GTW had diverted 40,000 cars onto Milwaukee Road between Chicago and Duluth to help them turn a profit in 1983. Ironically, the ICC (which controlled mergers at the time) pushed GTW out of the contest leaving just C&NW and Soo. Furious, GTW diverted their 40,000 carloads off the Milwaukee. C&NW outbid Soo, but the ICC chose Soo Line anyway. Milwaukee Road merged into Soo Line in 1985. Almost immediately, Soo shops began painting big black rectangles over MILWAUKEE ROAD on the diesels, giving birth to the “bandit” paint scheme.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: trainnut3500 on 2017-06-21 14:41:06
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.