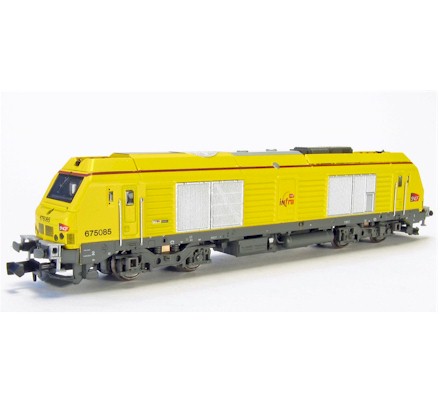
Model Information: This model was first released by Life-Like in 1988. It was later made by Life-Like for Bev-Bel in the early 1990's. It was overhauled in 2006. After the acquisition by Walthers, it was again updated in 2015 and sold under the Walthers N brand. This has always been an economy model that runs well and doesn't cost as much as the Kato and Atlas equivalents.
The original design was a simple open-sided 5-pole motor with weights and truck-mounted rapido couplers. The 2006 version went to a split frame design with flywheels, LED lights and body mounted Accumate couplers. The motor is NOT isolated from the frame so this version is not DCC-Ready. The 2015 version does accept a drop-in decoder and is DCC-Ready. This most recent Walthers version has Micro-Trains couplers.
The original design was a simple open-sided 5-pole motor with weights and truck-mounted rapido couplers. The 2006 version went to a split frame design with flywheels, LED lights and body mounted Accumate couplers. The motor is NOT isolated from the frame so this version is not DCC-Ready. The 2015 version does accept a drop-in decoder and is DCC-Ready. This most recent Walthers version has Micro-Trains couplers.
DCC Information: The early 1988 version is not DCC anything.
The 2006 redo is marginally DCC-Friendly. A DCC decoder installation for this version can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog and in this article. Using a drop-in decoder for Atlas locos is also possible, pending some modification of the chassis and some soldering, as shown on the same article.
The 2015 version is fully DCC-Ready, and will accept the following drop-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163L0A: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Walthers/life-Like Proto GP20 and similar locos
- TCS L1D4 (Installation in Life-Like GP20, very similar to this GP38-2)
The 2006 redo is marginally DCC-Friendly. A DCC decoder installation for this version can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog and in this article. Using a drop-in decoder for Atlas locos is also possible, pending some modification of the chassis and some soldering, as shown on the same article.
The 2015 version is fully DCC-Ready, and will accept the following drop-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163L0A: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Walthers/life-Like Proto GP20 and similar locos
- TCS L1D4 (Installation in Life-Like GP20, very similar to this GP38-2)
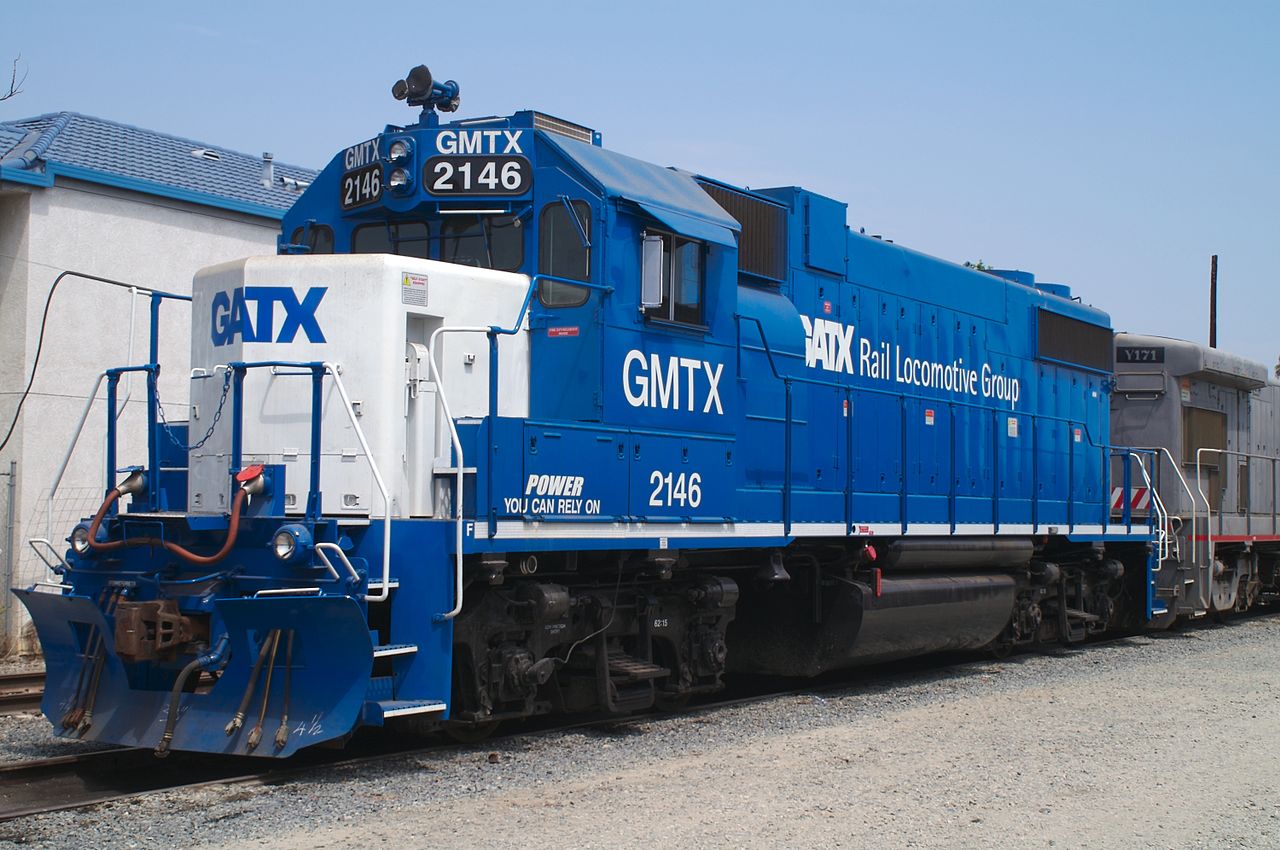
Prototype History: The EMD GP38-2 is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive of the road switcher type built by General Motors, Electro-Motive Division. Part of the EMD Dash 2 line, the GP38-2 was an upgraded version of the earlier GP38. Power is provided by an EMD 645E 16-cylinder engine, which generates 2000 horsepower (1.5 MW). Most built still remain in service in the modern era due to ease of maintenance and exceptional reliability.
The GP38-2 differs externally from the earlier GP38 only in minor details. Its most distinctive identifying feature is the cooling water level sight glass on the right side of the long hood. The battery box covers of the Dash 2s are bolted down instead of hinged. It can be distinguished from the contemporary GP39-2 and GP40-2 in that its Roots blown engine had two exhaust stacks, one on each side of the dynamic brake fan, if equipped, while the turbocharged GP39-2 and GP40-2 has a single stack. The GP39-2 has two radiator fans on the rear of the long hood like the GP38-2, while the GP40-2 has three. It was also available with either a high-short-hood, common on Norfolk Southern units, or a low-short-hood, which is found on most other railroads.
From Wikipedia
The GP38-2 differs externally from the earlier GP38 only in minor details. Its most distinctive identifying feature is the cooling water level sight glass on the right side of the long hood. The battery box covers of the Dash 2s are bolted down instead of hinged. It can be distinguished from the contemporary GP39-2 and GP40-2 in that its Roots blown engine had two exhaust stacks, one on each side of the dynamic brake fan, if equipped, while the turbocharged GP39-2 and GP40-2 has a single stack. The GP39-2 has two radiator fans on the rear of the long hood like the GP38-2, while the GP40-2 has three. It was also available with either a high-short-hood, common on Norfolk Southern units, or a low-short-hood, which is found on most other railroads.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The BNSF Railway (reporting mark BNSF) is one of the largest freight railroad networks in North America, second to the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) (its primary competitor for Western U.S. freight), and is one of seven North American Class I railroads. It has 48,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide high-speed links between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.[2] The BNSF and UP have a duopoly on all transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western U.S. and share trackage rights over thousands of miles of track.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
Brand/Importer Information:  Life-Like Products LLC (now Life-Like Toy and Hobby division of Wm. K. Walthers) was a manufacturer of model railroad products and was based in Baltimore, Maryland.
Life-Like Products LLC (now Life-Like Toy and Hobby division of Wm. K. Walthers) was a manufacturer of model railroad products and was based in Baltimore, Maryland.
It was founded in the 1950s by a company that pioneered extruded foam ice chests under the Lifoam trademark. Because ice chests are a summer seasonal item, the company needed a way to keep the factory operating year round. As model railroading was becoming popular in the post-war years, they saw this as an opportunity and so manufactured extruded foam tunnels for model trains. Over the years, Life-Like expanded into other scenery items, finally manufacturing rolling stock beginning in the late 1960s. At some point in the early 1970s, Life-Like purchased Varney Inc. and began to produce the former Varney line as its own.
The Canadian distributor for Life-Like products, Canadian Hobbycraft, saw a missing segment in market for Canadian model prototypes, and started producing a few Canadian models that were later, with a few modifications, offered in the US market with US roadnames.
In 2005, the company, now known as Lifoam Industries, LLC, decided to concentrate on their core products of extruded foam and sold their model railroad operations to Wm. K. Walthers.
In June 2018, Atlas and Walthers announced to have reached an agreement under which all Walthers N scale rolling stock tooling, including the former Life-Like tooling, will be purchased by Atlas.
Read more on Wikipedia and The Train Collectors Association.

It was founded in the 1950s by a company that pioneered extruded foam ice chests under the Lifoam trademark. Because ice chests are a summer seasonal item, the company needed a way to keep the factory operating year round. As model railroading was becoming popular in the post-war years, they saw this as an opportunity and so manufactured extruded foam tunnels for model trains. Over the years, Life-Like expanded into other scenery items, finally manufacturing rolling stock beginning in the late 1960s. At some point in the early 1970s, Life-Like purchased Varney Inc. and began to produce the former Varney line as its own.
The Canadian distributor for Life-Like products, Canadian Hobbycraft, saw a missing segment in market for Canadian model prototypes, and started producing a few Canadian models that were later, with a few modifications, offered in the US market with US roadnames.
In 2005, the company, now known as Lifoam Industries, LLC, decided to concentrate on their core products of extruded foam and sold their model railroad operations to Wm. K. Walthers.
In June 2018, Atlas and Walthers announced to have reached an agreement under which all Walthers N scale rolling stock tooling, including the former Life-Like tooling, will be purchased by Atlas.
Read more on Wikipedia and The Train Collectors Association.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2017-05-23 17:50:32. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-10-04 02:49:33
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.