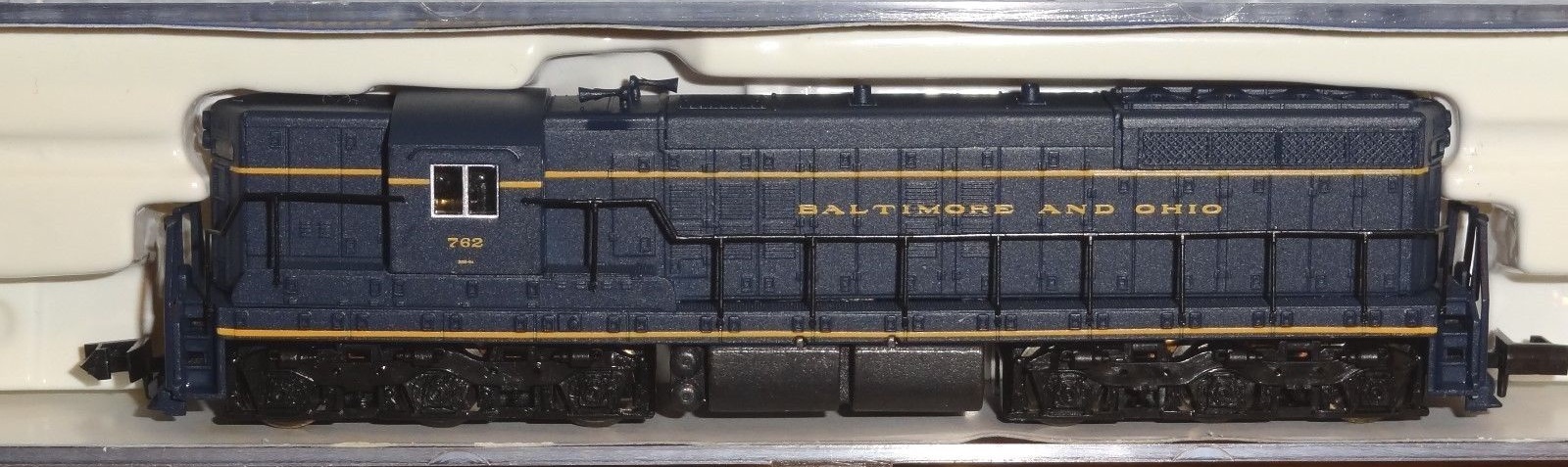
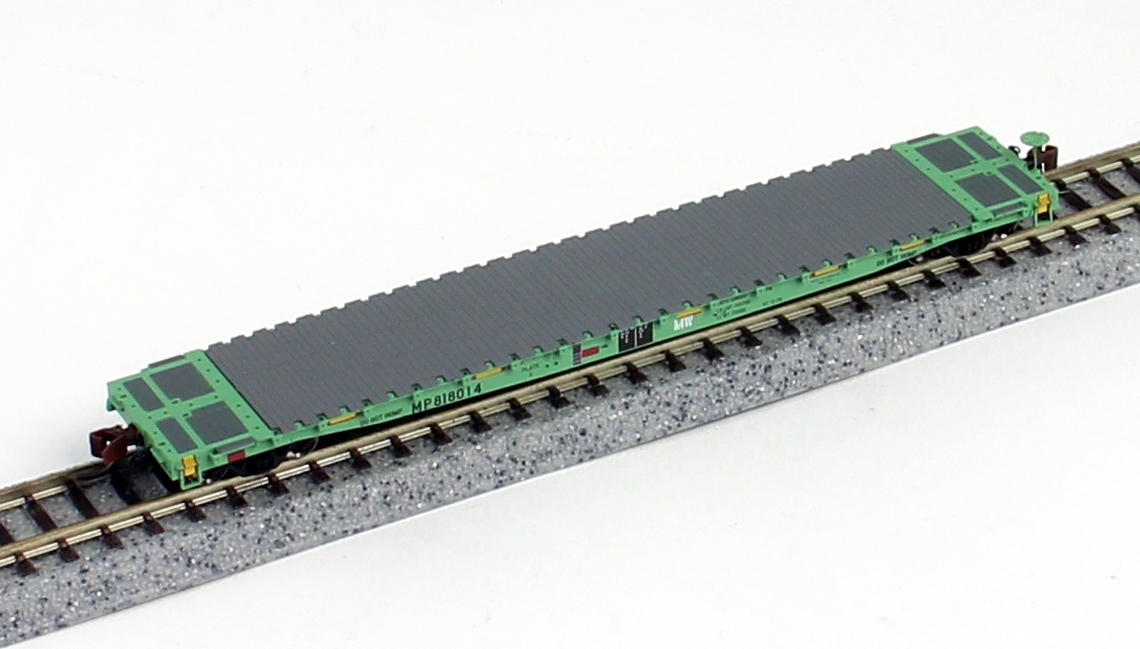
Model Information: Like many BLMA projects, their research began with builder drawings, actual dimensions, and thousands of photographs. Designed to be intricate yet durable, and highly detailed but not highly expensive, these models provide a great value for their exceptional execution of detail, paint and varied schemes. Along with the fine-scale attention to detail you've come to know from BLMA Models, these models ride on our 70-Ton ASF Ride Control trucks and 33" Low-Profile, Metal Wheels! Furthermore, these models feature body-mounted knuckle couplers for superb operation!
Prototype History: A flatcar (US) (also flat car (US) or flat wagon (UIC)) is a piece of railroad (US) or railway (non-US) rolling stock that consists of an open, flat deck mounted on a pair of trucks (US) or bogies (UK), one at each end containing four or six wheels. Occasionally, flat cars designed to carry extra heavy or extra large loads are mounted on a pair (or rarely, more) of bogeys under each end . The deck of the car can be wood or steel, and the sides of the deck can include pockets for stakes or tie-down points to secure loads. Flatcars designed for carrying machinery have sliding chain assemblies recessed in the deck.
Flatcars are used for loads that are too large or cumbersome to load in enclosed cars such as boxcars. They are also often used to transport intermodal containers (shipping containers) or trailers as part of intermodal freight transport shipping.
From Wikipedia
Flatcars are used for loads that are too large or cumbersome to load in enclosed cars such as boxcars. They are also often used to transport intermodal containers (shipping containers) or trailers as part of intermodal freight transport shipping.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: Wabash was the product of an 1889 restructuring (under the leadership of Jay Gould) of several railroads centered around the Wabash St. Louis & Pacific. Wabash was unusual in that it evenly straddled the border between “eastern railroads” and railroads west of the Chicago-St.Louis-Memphis-New Orleans border. In the west, Wabash connected Kansas City, Omaha and Des Moines. Heading east from those points, Wabash reached St. Louis, Decatur, and Chicago. Then, clearly in the eastern territory, Wabash reached Fort Wayne, Detroit, Toledo and finally Buffalo. Total length was about 2500 miles. The Detroit to Buffalo line cut though southern Ontario, Canada on Canadian National trackage rights. That route also required a car float operation across the Detroit River. As a result, Wabash’s Buffalo traffic was a fraction of that of competitors Nickel Plate and New York Central. However, Wabash’s Detroit-Kansas City and Detroit-St. Louis service was a force to be reckoned with and well patronized by Michigan’s automakers. The Wabash Cannonball was the name of the daytime passenger run between Detroit and St. Louis. The song of the same name was a hit long before it was ever applied to the train itself. Wabash bought control of the Ann Arbor in 1925 and soon after, Wabash and Delaware & Hudson jointly bought control of the Lehigh Valley (Wabash’s principle connection in Buffalo.) This got the attention of the Pennsylvania Railroad who bought control of Wabash under the auspices of their “Pennsylvania Company” subsidiary in 1928.
As PRR planned their merger with New York Central, it became obvious that they could not take Wabash with them. The first step was to transfer control of Ann Arbor from Wabash to Detroit Toledo & Ironton (also in the Pennsylvania Company family.) Up to that point, Ann Arbor was routinely included in the official Wabash system map. Then PRR arranged for Wabash to be included in the Norfolk & Western-Nickel Plate-Pittsburgh & West Virginia merger that was being planned. PRR didn’t overtly control the N&W but they did have considerable influence over them. The deal was made and the new, larger Norfolk & Western leased the Wabash for 50 years in October of 1964. At that point, Wabash became a paper railroad. They were finally merged out of existence by N&W successor Norfolk Southern in the 1990s.
As PRR planned their merger with New York Central, it became obvious that they could not take Wabash with them. The first step was to transfer control of Ann Arbor from Wabash to Detroit Toledo & Ironton (also in the Pennsylvania Company family.) Up to that point, Ann Arbor was routinely included in the official Wabash system map. Then PRR arranged for Wabash to be included in the Norfolk & Western-Nickel Plate-Pittsburgh & West Virginia merger that was being planned. PRR didn’t overtly control the N&W but they did have considerable influence over them. The deal was made and the new, larger Norfolk & Western leased the Wabash for 50 years in October of 1964. At that point, Wabash became a paper railroad. They were finally merged out of existence by N&W successor Norfolk Southern in the 1990s.
Brand/Importer Information: BLMA Models was founded in July of 2000 to bring Z, N, and HO Scale products of superior quality and originality to the model train community. At BLMA Models, we understand that quality and accuracy count in producing realistic scale models. Our passion revolves around accuracy, diversity, innovation and satisfaction to prototype model railroaders by providing exceptional products and service that goes beyond your expectations.
BLMA was acquired by Atlas Model Railroad in January of 2016.
BLMA was acquired by Atlas Model Railroad in January of 2016.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-05-01 13:08:23
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.