Specific Item Information:
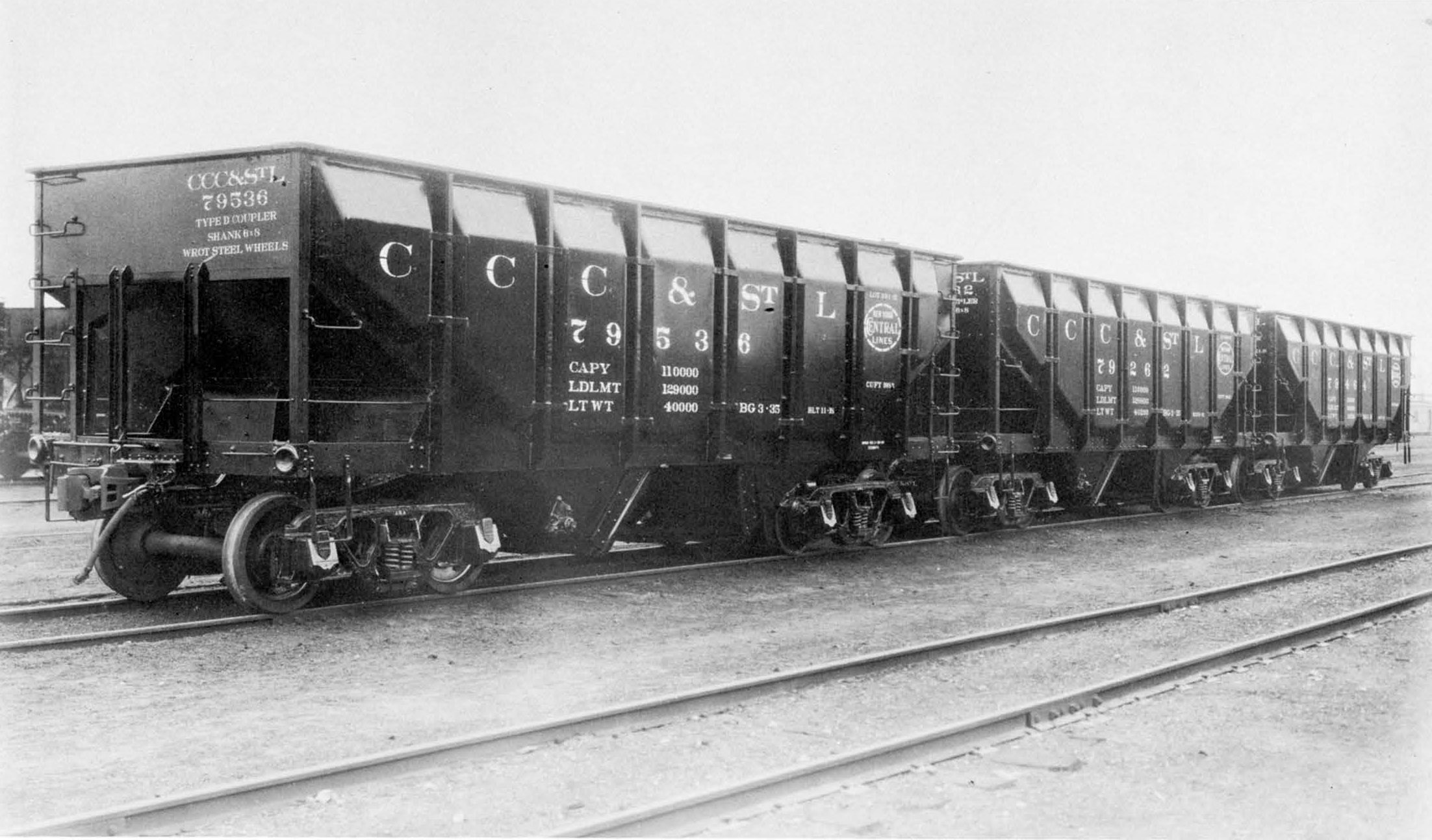
This group of Canadian National hoppers (originally built for Grand Trunk Railway) was rebuilt with panel sides in April of 1937. At that point, CN hoppers were painted black but in 1948, CN switched to brown for hopper cars and this paint scheme represents cars repainted after that time.
Model Information: These ready-to-run N scale models will feature: die cast slope sheet-hopper bay-center sill assembly; injection molded plastic sides, ends, and hopper doors; fully molded brake tank, valve and air lines; body mounted brake hose detail; coal load; lever-style hand brake; body mounted magnetically operating knuckle couplers; close coupling; and Fox Valley Models metal wheels.
Prototype History: The USRA 55-Ton hopper was designed by the United States Railway Administration during World War I as a standardized hopper to be used by all railroads in order to aid the war effort. After WWI many railroads continued to use the USRA 55-Ton hoppers, as well as build many thousands more clones. The USRA hopper was in use on North American railroads from 1918 until the 1970’s. Many of these hoppers were rebuilt between 1930 and 1970 with panel sides to increase capacity. Principally used for rebuilding, the concept of raised panel sides was originally developed out of a need to provide parts to repair heavily used and rusted hoppers and increase capacity at the same time.
Road Name History: The Canadian National Railway Company (reporting mark CN) is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec that serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad". CN is a public company with 24,000 employees. It had a market capitalization of 32 billion CAD in 2011. CN was government-owned, having been a Canadian Crown corporation from its founding to its privatization in 1995. Bill Gates was, in 2011, the largest single shareholder of CN stock.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Bluford Shops began in 2007 as a side project of two model railroad industry veterans, Craig Ross and Steve Rodgers. They saw a gap between road names available on N scale locomotives but not available on cabooses. They commissioned special runs of Atlas cabooses in Atlantic Coast Line, Central of Georgia, Monon, Boston & Maine and Southern plus runs on Grand Trunk Western and Central Vermont on the MDC wooden cabooses. While these were in process, they began to develop their first all new tooling project, 86' Auto Parts Boxcars in double door and quad door editions in N scale. By January of 2008, Bluford Shops became a full time venture. Along with additional N scale freight cars and their own tooling for new cabooses, they have brought their own caboose line to HO scale. They also have their popular Cornfields in both HO and N. The future looks bright as they continue to develop new products for your railroad.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-04-18 08:40:21
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.