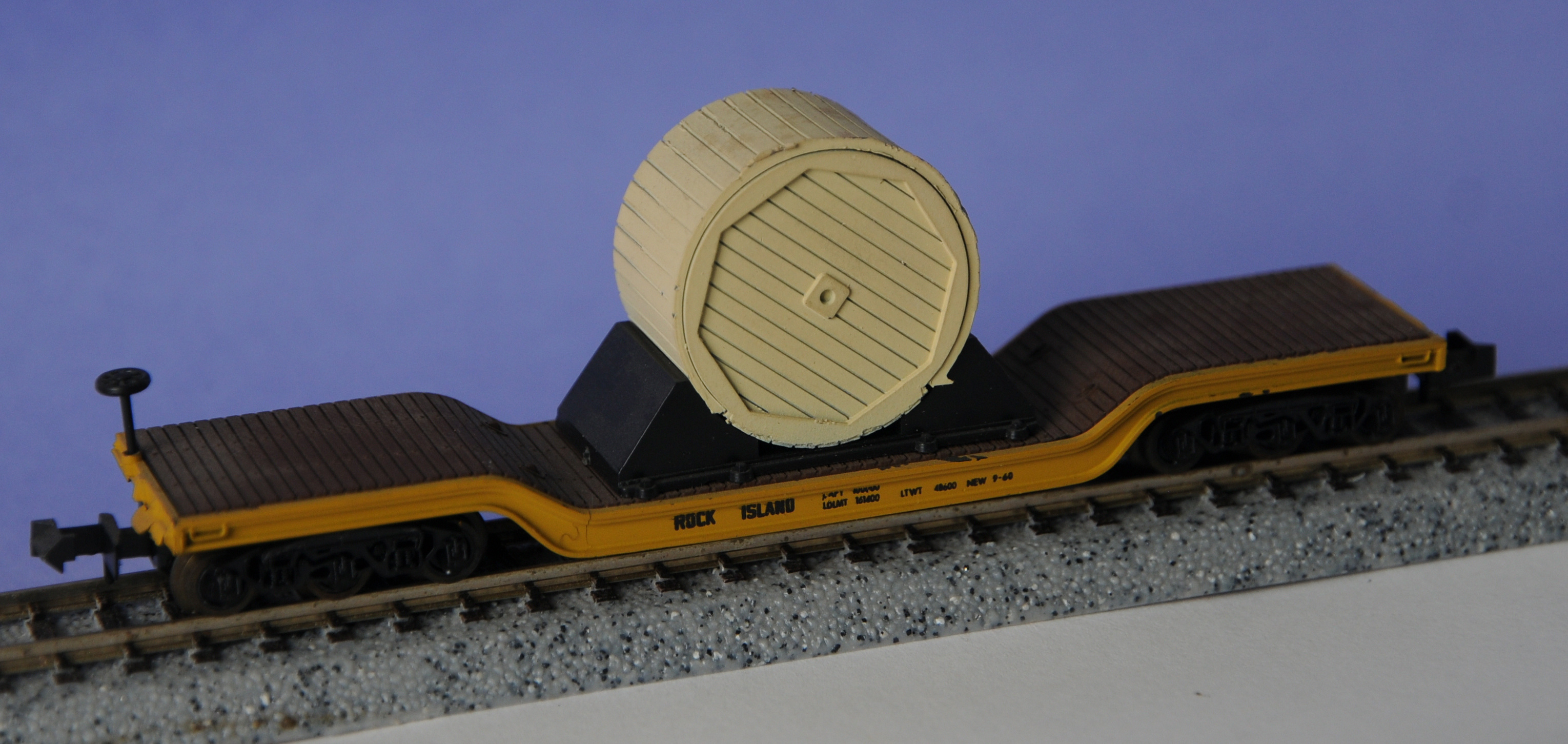
Model Information: Roco first produced this model for Minitrix. It appears in the Minitrix 1970 catalog priced at $2.50 each in four road names. It has also been imported by Aurora (Postage Stamp) , ER-Models and Model Power
Prototype History: A flatcar (US) (also flat car (US) or flat wagon (UIC)) is a piece of railroad (US) or railway (non-US) rolling stock that consists of an open, flat deck mounted on a pair of trucks (US) or bogies (UK), one at each end containing four or six wheels. Occasionally, flat cars designed to carry extra heavy or extra large loads are mounted on a pair (or rarely, more) of bogeys under each end . The deck of the car can be wood or steel, and the sides of the deck can include pockets for stakes or tie-down points to secure loads. Flatcars designed for carrying machinery have sliding chain assemblies recessed in the deck.
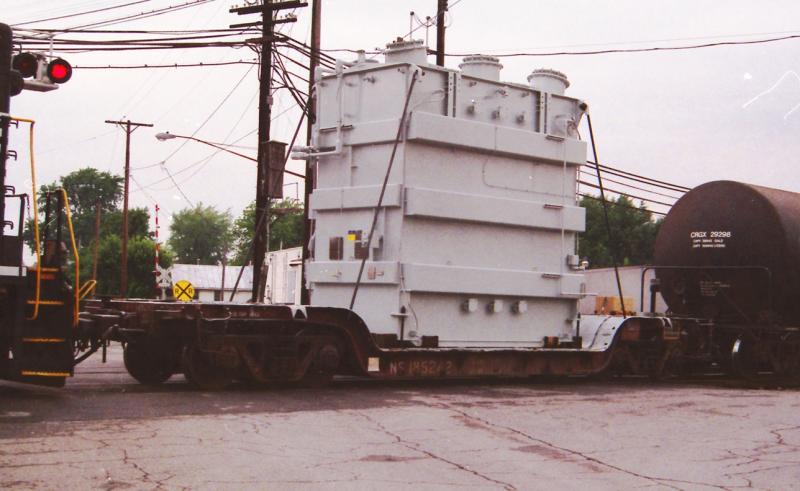
Depressed center flat cars are of a special construction having the portion of floor extending between trucks depressed to provide necessary overhead clearance for lading. When large and heavy loads need to be moved long distances railroads are often the best choice for the job. These loads are often tall enough that they wouldn't pass safely under bridges or other obstacles if carried on conventional flat cars. To provide extra clearance, railroads use heavy-duty, depressed center flat cars. The lower center deck provides several inches of extra clearance, and since the cargo does not have to be lifted as high, loading and unloading is easier.
Depressed center flat cars are of a special construction having the portion of floor extending between trucks depressed to provide necessary overhead clearance for lading. When large and heavy loads need to be moved long distances railroads are often the best choice for the job. These loads are often tall enough that they wouldn't pass safely under bridges or other obstacles if carried on conventional flat cars. To provide extra clearance, railroads use heavy-duty, depressed center flat cars. The lower center deck provides several inches of extra clearance, and since the cargo does not have to be lifted as high, loading and unloading is easier.
Road Name History: The Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad (CRI&P RR) (reporting marks RI, ROCK) was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was better known as the Rock Island Line, or, in its final years, The Rock. At the end of 1970 it operated 7183 miles of road on 10669 miles of track; that year it reported 20557 million ton-miles of revenue freight and 118 million passenger-miles. (Those totals may or may not include the former Burlington-Rock Island Railroad.)
Its predecessor, the Rock Island and La Salle Railroad Company, was incorporated in Illinois on February 27, 1847, and an amended charter was approved on February 7, 1851, as the Chicago and Rock Island Railroad. Construction began October 1, 1851, in Chicago, and the first train was operated on October 10, 1852, between Chicago and Joliet. Construction continued on through La Salle, and Rock Island was reached on February 22, 1854, becoming the first railroad to connect Chicago with the Mississippi River.
In 1980 Rock Island was liquidated. The railroad's locomotives, rail cars, equipment, tracks, and real estate were sold to other railroads or to scrappers. William Gibbons (the trustee) was able to raise more than $500 million in the liquidation, paying off all the railroad's creditors, bondholders and all other debts in full at face value with interest. Henry Crown was ultimately proven correct, as both he and other bondholders who had purchased Rock Island debt for cents on the dollar during the low ebb in prices did especially well.
Read more on Wikipedia and Rock Island Technical Society.
Its predecessor, the Rock Island and La Salle Railroad Company, was incorporated in Illinois on February 27, 1847, and an amended charter was approved on February 7, 1851, as the Chicago and Rock Island Railroad. Construction began October 1, 1851, in Chicago, and the first train was operated on October 10, 1852, between Chicago and Joliet. Construction continued on through La Salle, and Rock Island was reached on February 22, 1854, becoming the first railroad to connect Chicago with the Mississippi River.
In 1980 Rock Island was liquidated. The railroad's locomotives, rail cars, equipment, tracks, and real estate were sold to other railroads or to scrappers. William Gibbons (the trustee) was able to raise more than $500 million in the liquidation, paying off all the railroad's creditors, bondholders and all other debts in full at face value with interest. Henry Crown was ultimately proven correct, as both he and other bondholders who had purchased Rock Island debt for cents on the dollar during the low ebb in prices did especially well.
Read more on Wikipedia and Rock Island Technical Society.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1967, Aurora Plastics Corporation started importing the Minitrix N Scale product line. These trains were marketed as Postage Stamp Trains. It was a bold entry into what would become a very active market in the new N-Scale model train market. The basic starter set took advantage of N-Scale’s small size by packaging everything necessary for a small model railroad in a book-like box. The larger starter sets were packaged in more conventional boxes. Aurora went out of business in 1977.
The Body styles of this product line were made in Austria by Roco, imported into the United States by Minitrix and then rebranded by Aurora. Some of the exact same molds were also produced by Roco for Atlas who branded them using their own name.
A lot of information can be found on All about Aurora Postage Stamp Trains web site by David K. Smith.
The Body styles of this product line were made in Austria by Roco, imported into the United States by Minitrix and then rebranded by Aurora. Some of the exact same molds were also produced by Roco for Atlas who branded them using their own name.
A lot of information can be found on All about Aurora Postage Stamp Trains web site by David K. Smith.
Manufacturer Information:  The company was founded in 1960 by Ing. Heinz Rössler and started with a plastic Minitanks series of military vehicles. After export to the USA became successful, the model line was expanded with model trains in HO scale and the smaller N scale. TT scale was also subsequently added to the product line. The model rail product line covers many European countries including Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Spain, Austria, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden and the Netherlands, and also the USA.
The company was founded in 1960 by Ing. Heinz Rössler and started with a plastic Minitanks series of military vehicles. After export to the USA became successful, the model line was expanded with model trains in HO scale and the smaller N scale. TT scale was also subsequently added to the product line. The model rail product line covers many European countries including Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Spain, Austria, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden and the Netherlands, and also the USA.
On July 15, 2005 ROCO Modellspielwaren GmbH was declared bankrupt. From July 25 the company continues as Modelleisenbahn GmbH, but still uses the Roco brand and associated logo. On October 1, 2007, distribution of the 'Minitank' product series was assigned to the German model car manufacturer Herpa.
Since February 2008 Modelleisenbahn also owns Fleischmann, which like Roco had gone bankrupt. The two companies continue as separate brands under Modelleisenbahn GmbH, while benefiting from economies of scale through joined development projects, marketing and procurement.
From Wikipedia

On July 15, 2005 ROCO Modellspielwaren GmbH was declared bankrupt. From July 25 the company continues as Modelleisenbahn GmbH, but still uses the Roco brand and associated logo. On October 1, 2007, distribution of the 'Minitank' product series was assigned to the German model car manufacturer Herpa.
Since February 2008 Modelleisenbahn also owns Fleischmann, which like Roco had gone bankrupt. The two companies continue as separate brands under Modelleisenbahn GmbH, while benefiting from economies of scale through joined development projects, marketing and procurement.
From Wikipedia
Item created by: gdm on 2017-03-23 08:20:48. Last edited by gdm on 2021-02-06 16:47:58
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.