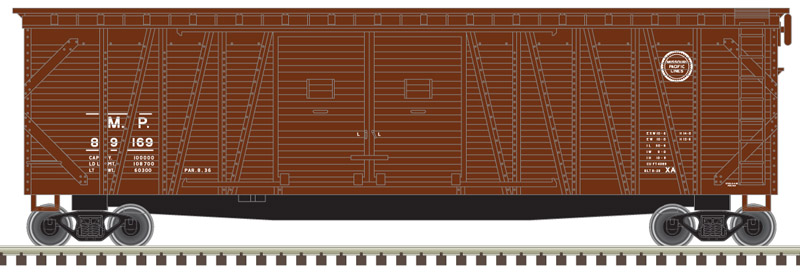
Specific Item Information: This group of hoppers was delivered in 1965 before Florida East Coast adopted the practice of applying very large road numbers in the middle of the car. FEC was in the second year of a harrowing strike. The strike finally ended in 1971 and FEC emerged as if from a time machine from 20 years in the future. They were installing concrete ties, trains ran with two-man crews and cabooses were a fond memory. FEC’s primary hopper commodity is gravel used in construction.
Prototype History: 70 ton 3-bay rib side hoppers were a common sight on most railroads in the 20th century, These cars were built by most of the major railcar manufacturers as well as by many of the Class I railroads themselves. They were used for non weather sensitive matrial such as coal and were designed to take a beating.
Road Name History: The Florida East Coast Railway (reporting mark FEC) is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida and since 2007 has been a subsidiary of Railroad Acquisition Holdings, LLC, itself a subsidiary of Fortress Investment Group, LLC.
The FEC was historically a Class I railroad owned by Florida East Coast Industries (FECI) from 2000-2006, FOXX Holdings from 1983-2000, and the St. Joseph Paper Company prior to 1983.
Built primarily in the last quarter of the 19th century and the first decade of the 20th century, the FEC was a project of Standard Oil principal Henry Morrison Flagler. Flagler originally visited Florida to aid with the health issues faced by his first wife, Mary. A key strategist who worked closely with John D. Rockefeller building the Standard Oil Trust, Henry Flagler noted both a lack of services and great potential during his stay at St. Augustine. He subsequently began what amounted to his second career developing resorts, industries, and communities all along Florida's shores abutting the Atlantic Ocean.
The FEC is possibly best known for building the railroad to Key West, completed in 1912. When the FEC's line from the mainland to Key West was heavily damaged by the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935, the State of Florida purchased the remaining right-of-way and bridges south of Dade County, and they were rebuilt into road bridges for vehicle traffic and became known as the Overseas Highway. However, a greater and lasting Flagler legacy was the developments along Florida's eastern coast.
During the Great Depression, control was purchased by heirs of the du Pont family. After 30 years of fragile financial condition, the FEC, under leadership of a new president, Ed Ball, took on the labor unions. Ball claimed the company could not afford the same costs as larger Class 1 railroads and needed to invest saved funds in its infrastructure, fast becoming a safety issue. Using replacement workers, the company and some of its employees engaged in one of the longest and more violent labor conflicts of the 20th century from 1963 until 1977. Ultimately, federal authorities had to intervene to stop the violence, which included bombings, shootings and vandalism. However, the courts ruled in the FEC's favor with regard to the right to employ strikebreakers. During this time, Ball invested heavily in numerous steps to improve its physical plant, installed various forms of automation,was the first US Railroad to operate two man train crews, eliminate cabooses and end all of its passenger services (which were unprofitable) by 1968.
In modern times, the company's primary rail revenues come from its intermodal and rock trains. Since 2007, it has been owned by Fortress Investment Group,[citation needed] which acquired it for over US$3 billion (including non-rail assets). Fortress previously owned conglomerate short line railroad operator RailAmerica, which for a time operated FEC but the two companies never merged; Fortress no longer owns RailAmerica and RailAmerica no longer operates FEC. A former CSX official, James Hertwig, was named as President and Chief Executive Officer of the company effective July 1, 2010.
From Wikipedia
The FEC was historically a Class I railroad owned by Florida East Coast Industries (FECI) from 2000-2006, FOXX Holdings from 1983-2000, and the St. Joseph Paper Company prior to 1983.
Built primarily in the last quarter of the 19th century and the first decade of the 20th century, the FEC was a project of Standard Oil principal Henry Morrison Flagler. Flagler originally visited Florida to aid with the health issues faced by his first wife, Mary. A key strategist who worked closely with John D. Rockefeller building the Standard Oil Trust, Henry Flagler noted both a lack of services and great potential during his stay at St. Augustine. He subsequently began what amounted to his second career developing resorts, industries, and communities all along Florida's shores abutting the Atlantic Ocean.
The FEC is possibly best known for building the railroad to Key West, completed in 1912. When the FEC's line from the mainland to Key West was heavily damaged by the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935, the State of Florida purchased the remaining right-of-way and bridges south of Dade County, and they were rebuilt into road bridges for vehicle traffic and became known as the Overseas Highway. However, a greater and lasting Flagler legacy was the developments along Florida's eastern coast.
During the Great Depression, control was purchased by heirs of the du Pont family. After 30 years of fragile financial condition, the FEC, under leadership of a new president, Ed Ball, took on the labor unions. Ball claimed the company could not afford the same costs as larger Class 1 railroads and needed to invest saved funds in its infrastructure, fast becoming a safety issue. Using replacement workers, the company and some of its employees engaged in one of the longest and more violent labor conflicts of the 20th century from 1963 until 1977. Ultimately, federal authorities had to intervene to stop the violence, which included bombings, shootings and vandalism. However, the courts ruled in the FEC's favor with regard to the right to employ strikebreakers. During this time, Ball invested heavily in numerous steps to improve its physical plant, installed various forms of automation,was the first US Railroad to operate two man train crews, eliminate cabooses and end all of its passenger services (which were unprofitable) by 1968.
In modern times, the company's primary rail revenues come from its intermodal and rock trains. Since 2007, it has been owned by Fortress Investment Group,[citation needed] which acquired it for over US$3 billion (including non-rail assets). Fortress previously owned conglomerate short line railroad operator RailAmerica, which for a time operated FEC but the two companies never merged; Fortress no longer owns RailAmerica and RailAmerica no longer operates FEC. A former CSX official, James Hertwig, was named as President and Chief Executive Officer of the company effective July 1, 2010.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Bluford Shops began in 2007 as a side project of two model railroad industry veterans, Craig Ross and Steve Rodgers. They saw a gap between road names available on N scale locomotives but not available on cabooses. They commissioned special runs of Atlas cabooses in Atlantic Coast Line, Central of Georgia, Monon, Boston & Maine and Southern plus runs on Grand Trunk Western and Central Vermont on the MDC wooden cabooses. While these were in process, they began to develop their first all new tooling project, 86' Auto Parts Boxcars in double door and quad door editions in N scale. By January of 2008, Bluford Shops became a full time venture. Along with additional N scale freight cars and their own tooling for new cabooses, they have brought their own caboose line to HO scale. They also have their popular Cornfields in both HO and N. The future looks bright as they continue to develop new products for your railroad.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-01-27 08:06:35
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.