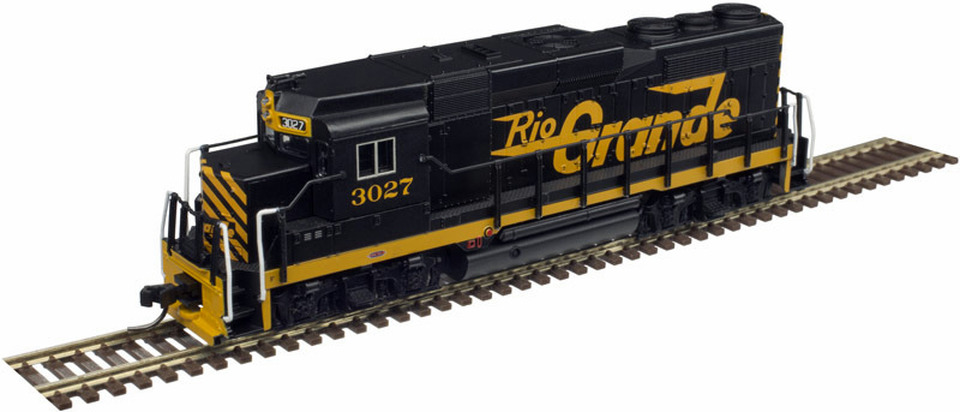
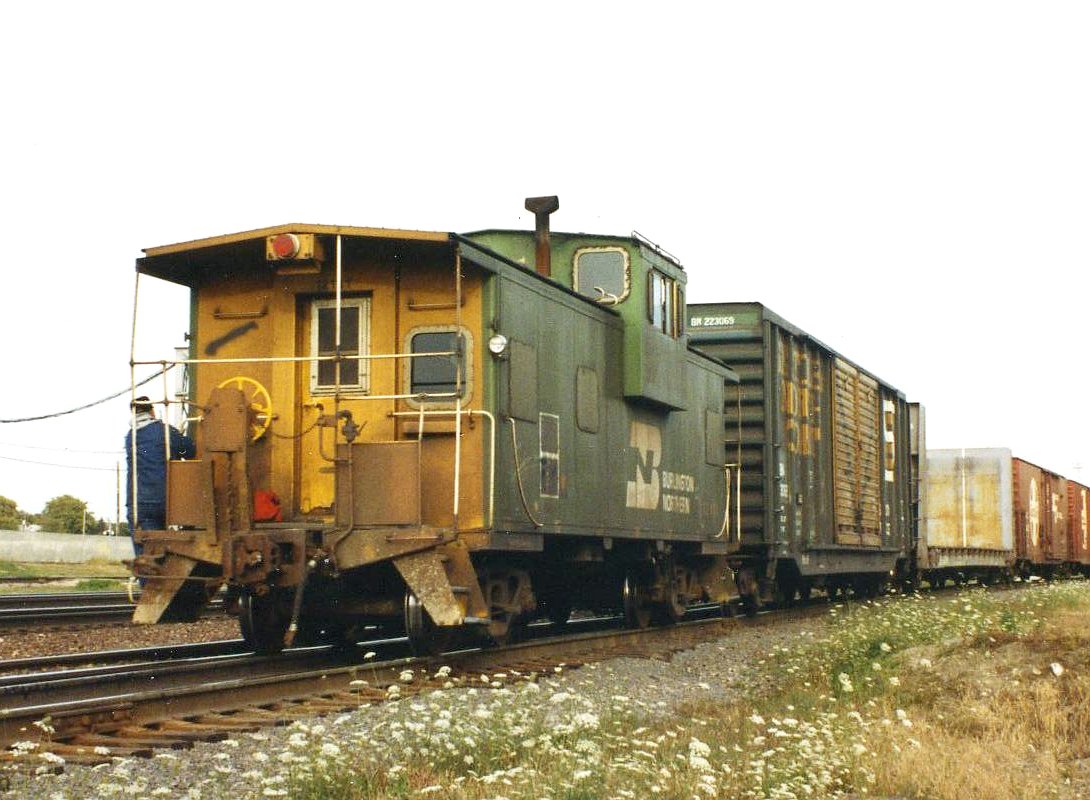
Specific Item Information: This model is depicted here with Micro-Trains couplers. This particular model was actually produced with Rapido couplers.
Model Information: Atlas released the "30" series extended vision caboose in 1996. This model is very similar to the "43" series cupola caboose in most respects. It can be easily distinguished from the standard cupola caboose in that the cupola is wider than the body on the "30" series - hence the name "Extended Vision". This model may or may not have "loop-over" ladders.
It is re-released every other year (approximately). The original releases sported Rapido hook couplers, but interestingly the 1999 release had versions with Rapido as well as versions with real (licensed) Magnematic couplers. As of the 2009 run, it comes with Accumate couplers (only).
The current release from Atlas features:
It is re-released every other year (approximately). The original releases sported Rapido hook couplers, but interestingly the 1999 release had versions with Rapido as well as versions with real (licensed) Magnematic couplers. As of the 2009 run, it comes with Accumate couplers (only).
The current release from Atlas features:
- Thin endrails
- Window glazing
- Separate brake cylinder
- Open smoke stack
- Triple valve and air reservoir
- Roller-bearing caboose trucks
- Roofwalk where appropriate
- Accurate painting and lettering
- Now with AccuMate couplers
Prototype History: In the extended-vision or wide-vision caboose, the sides of the cupola project beyond the side of the car body. Rock Island created some of these by rebuilding some standard cupola cabooses with windowed extensions applied to the sides of the cupola itself, but by far, the greatest number have the entire cupola compartment enlarged. This model was introduced by the International Car Company and saw service on most U.S. railroads. The expanded cupola allowed the crew to see past the top of the taller cars that began to appear after World War II, and also increased the roominess of the cupola area.
Additionally, Monon Railroad had a unique change to the extended-vision cabooses. They added a miniature bay to the sides of the cupola to enhance the views further. This created a unique look for their small fleet. Seven of the eight Monon-built cabooses have been saved. One was scrapped after an accident in Kentucky. The surviving cars are at the Indiana Transportation Museum (operational), the Indiana Railway Museum (operational), the Kentucky Railway Museum (fire damaged), and the Bluegrass Railroad Museum (unrestored but servicable). The remaining three are in private collections.
Additionally, Monon Railroad had a unique change to the extended-vision cabooses. They added a miniature bay to the sides of the cupola to enhance the views further. This created a unique look for their small fleet. Seven of the eight Monon-built cabooses have been saved. One was scrapped after an accident in Kentucky. The surviving cars are at the Indiana Transportation Museum (operational), the Indiana Railway Museum (operational), the Kentucky Railway Museum (fire damaged), and the Bluegrass Railroad Museum (unrestored but servicable). The remaining three are in private collections.
Road Name History: The D&TS was built just after the turn of the 20th Century, originally as a fast interurban line connecting Toledo with Detroit. With construction well underway (about 3/4 of the way to Detroit) and some of the trolley wire up, the backers started to run out of money and sold the line to Grand Trunk Western and The Clover Leaf Route, with each getting half. This would give GTW (which blanketed southern Michigan) a friendly connection to the rail hubs at Toledo. The Clover Leaf (officially the Toledo St. Louis & Western) got a friendly connection to Detroit. The trolley wire came down and the track was upgraded to GTW standards. From then on, Detroit & Toledo Shore Line was a multi-track 59 mile speedway for freight. Ironically for a line conceived as an interurban, the D&TS never offered passenger service. Later, they would adopt the motto, “Expressway for Industry.” In 1923, the Nickel Plate Road merged the Clover Leaf and took over their half of the D&TS.
In the steam era, about 30 locomotives were required to run the line. 2-8-2’s and 2-8-0’s handled the road traffic while USRA 0-8-0’s and some smaller switchers worked the yards. The D&TS dieselized in the early 50s with just three EMD models, SW7s and SW9s for switching and GP7s for road service. The 1953 batch of geeps was the last locomotives bought by the railroad! These were delivered in a yellow-over-blue paint scheme. The narrowly focused roster made the shop crews experts at getting the most from the fleet and keeping them running for the next three decades.
The crooked square logo is a nod to Grand Trunk Western while the black and yellow paint scheme adopted around 1959 is a nod to the Nickel Plate. In 1964, the Nickel Plate was merged into Norfolk & Western so they took the 50% stake in the D&TS. The Shore Line kept the Nickel Plate-esque paint scheme until the end however.
D&TS trains routinely ran north past Detroit and into Flint on GTW tracks, while GTW trains ran south all the way to the Toledo Terminal loop. After the 1964 N&W-Nickel Plate-Wabash merger, N&W had a better line west out of Detroit on the former Wabash rather than using the D&TS and the old Clover Leaf (which had been built on the cheap.) From then on, the D&TS became much more important to the GTW than to the N&W. In 1981, N&W finally sold their half to the Grand Trunk Western and the Detroit & Toledo Shore Line was merged into the GTW.
In the steam era, about 30 locomotives were required to run the line. 2-8-2’s and 2-8-0’s handled the road traffic while USRA 0-8-0’s and some smaller switchers worked the yards. The D&TS dieselized in the early 50s with just three EMD models, SW7s and SW9s for switching and GP7s for road service. The 1953 batch of geeps was the last locomotives bought by the railroad! These were delivered in a yellow-over-blue paint scheme. The narrowly focused roster made the shop crews experts at getting the most from the fleet and keeping them running for the next three decades.
The crooked square logo is a nod to Grand Trunk Western while the black and yellow paint scheme adopted around 1959 is a nod to the Nickel Plate. In 1964, the Nickel Plate was merged into Norfolk & Western so they took the 50% stake in the D&TS. The Shore Line kept the Nickel Plate-esque paint scheme until the end however.
D&TS trains routinely ran north past Detroit and into Flint on GTW tracks, while GTW trains ran south all the way to the Toledo Terminal loop. After the 1964 N&W-Nickel Plate-Wabash merger, N&W had a better line west out of Detroit on the former Wabash rather than using the D&TS and the old Clover Leaf (which had been built on the cheap.) From then on, the D&TS became much more important to the GTW than to the N&W. In 1981, N&W finally sold their half to the Grand Trunk Western and the Detroit & Toledo Shore Line was merged into the GTW.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: James on 2017-01-11 17:49:04
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.