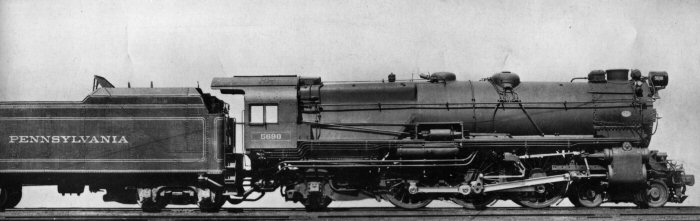
Model Information: Model Power introduced this model in 2002 in standard version. Additional versions have been introduced subsequently: semi-streamlined version in 2004, Vandy tender version in 2005, a revised semi-streamlined version in 2010, and lastly a revised MRC version in 2015. There has been several runs with different road numbers, but using the same stock number.
They are manufactured in Korea and feature die-cast bodies. This makes them fairly solid. Unlike many steam engines they also are very DCC-Friendly. The fall short of being fully DCC-Ready because they do not support drop-in decoders and instead require some manipulation of wiring. They run very well and can pull a lot of cars. The shell details are excellent. They were delivered in a jewelry-like plastic chest.
Unfortunately, the design is not great for running and parts of the lower shell can get mangled when they hit rough patches of track (especially turnouts). This can effectively put one of these out of commission. For this reason we advise buying these from a certified dealer because if you have to return them for repairs you will need the documentation.
They are manufactured in Korea and feature die-cast bodies. This makes them fairly solid. Unlike many steam engines they also are very DCC-Friendly. The fall short of being fully DCC-Ready because they do not support drop-in decoders and instead require some manipulation of wiring. They run very well and can pull a lot of cars. The shell details are excellent. They were delivered in a jewelry-like plastic chest.
Unfortunately, the design is not great for running and parts of the lower shell can get mangled when they hit rough patches of track (especially turnouts). This can effectively put one of these out of commission. For this reason we advise buying these from a certified dealer because if you have to return them for repairs you will need the documentation.
DCC Information: It is pretty easy to add DCC to this engine. However, it is not DCC-Ready as you need to splice in a decoder inside the tender. Not a lot of work, but not as nice as a drop-in decoder swap.
Prototype History: Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The 4-6-2 locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type. The type is well-suited to high speed running. The world speed record for steam traction of 126 miles per hour (203 kilometres per hour) has been held by a British Pacific locomotive, the Mallard, since 3 July 1938.
The introduction of the 4-6-2 design in 1901 has been described as "a veritable milestone in locomotive progress". On many railways worldwide, Pacific steam locomotives provided the motive power for express passenger trains throughout much of the early to mid-20th century, before either being superseded by larger types in the late 1940s and 1950s, or replaced by electric or diesel-electric locomotives during the 1950s and 1960s. Nevertheless, new Pacific designs continued to be built until the mid-1950s.
The type is generally considered to be an enlargement of the 4-4-2 Atlantic type, although its prototype had a direct relationship to the 4-6-0 Ten-wheeler and 2-6-2 Prairie, effectively being a combination of the two types. The success of the type can be attributed to a combination of its four-wheel leading truck which provided better stability at speed than a 2-6-2 Prairie, the six driving wheels which allowed for a larger boiler and the application of more tractive effort than the earlier 4-4-2 Atlantic, and the two-wheel trailing truck, first used on the New Zealand 2-6-2 Prairie of 1885. This permitted the firebox to be located behind the high driving wheels and thereby allowed it to be both wide and deep, unlike the 4-6-0 Ten-wheeler which had either a narrow and deep firebox between the driving wheels or a wide and shallow one above.
From Wikipedia
The introduction of the 4-6-2 design in 1901 has been described as "a veritable milestone in locomotive progress". On many railways worldwide, Pacific steam locomotives provided the motive power for express passenger trains throughout much of the early to mid-20th century, before either being superseded by larger types in the late 1940s and 1950s, or replaced by electric or diesel-electric locomotives during the 1950s and 1960s. Nevertheless, new Pacific designs continued to be built until the mid-1950s.
The type is generally considered to be an enlargement of the 4-4-2 Atlantic type, although its prototype had a direct relationship to the 4-6-0 Ten-wheeler and 2-6-2 Prairie, effectively being a combination of the two types. The success of the type can be attributed to a combination of its four-wheel leading truck which provided better stability at speed than a 2-6-2 Prairie, the six driving wheels which allowed for a larger boiler and the application of more tractive effort than the earlier 4-4-2 Atlantic, and the two-wheel trailing truck, first used on the New Zealand 2-6-2 Prairie of 1885. This permitted the firebox to be located behind the high driving wheels and thereby allowed it to be both wide and deep, unlike the 4-6-0 Ten-wheeler which had either a narrow and deep firebox between the driving wheels or a wide and shallow one above.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR) was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy," the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
The PRR was the largest railroad by traffic and revenue in the U.S. for the first half of the twentieth century. Over the years, it acquired, merged with or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1925, it operated 10,515 miles of rail line; in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific or Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Central (NYC), which carried around three-quarters of PRR's ton-miles.
At one time, the PRR was the largest publicly traded corporation in the world, with a budget larger than that of the U.S. government and a workforce of about 250,000 people. The corporation still holds the record for the longest continuous dividend history: it paid out annual dividends to shareholders for more than 100 years in a row.
In 1968, PRR merged with rival NYC to form the Penn Central Transportation Company, which filed for bankruptcy within two years. The viable parts were transferred in 1976 to Conrail, which was itself broken up in 1999, with 58 percent of the system going to the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), including nearly all of the former PRR. Amtrak received the electrified segment east of Harrisburg.
The PRR was the largest railroad by traffic and revenue in the U.S. for the first half of the twentieth century. Over the years, it acquired, merged with or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1925, it operated 10,515 miles of rail line; in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific or Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Central (NYC), which carried around three-quarters of PRR's ton-miles.
At one time, the PRR was the largest publicly traded corporation in the world, with a budget larger than that of the U.S. government and a workforce of about 250,000 people. The corporation still holds the record for the longest continuous dividend history: it paid out annual dividends to shareholders for more than 100 years in a row.
In 1968, PRR merged with rival NYC to form the Penn Central Transportation Company, which filed for bankruptcy within two years. The viable parts were transferred in 1976 to Conrail, which was itself broken up in 1999, with 58 percent of the system going to the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), including nearly all of the former PRR. Amtrak received the electrified segment east of Harrisburg.
Brand/Importer Information: Founded in the late 1960's by Michael Tager, the 3rd generation business specializes in quality hobby products serving the toy and hobby markets worldwide. During its 50 years of operation, Model Power has developed a full line of model railroading products, die-cast metal aircraft, and die-cast metal cars and trucks.
In early 2014, Model Power ceased its business operations. Its extensive portfolio of intellectual property and physical assets are now exclusively produced, marketed, sold, and distributed by MRC (Model Power, MetalTrain and Mantua) and by Daron (Postage Stamp Airplanes and Airliner Collection).
In early 2014, Model Power ceased its business operations. Its extensive portfolio of intellectual property and physical assets are now exclusively produced, marketed, sold, and distributed by MRC (Model Power, MetalTrain and Mantua) and by Daron (Postage Stamp Airplanes and Airliner Collection).
Item created by: gdm on 2016-12-10 18:04:28. Last edited by Alain LM on 2021-06-13 04:05:29
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.