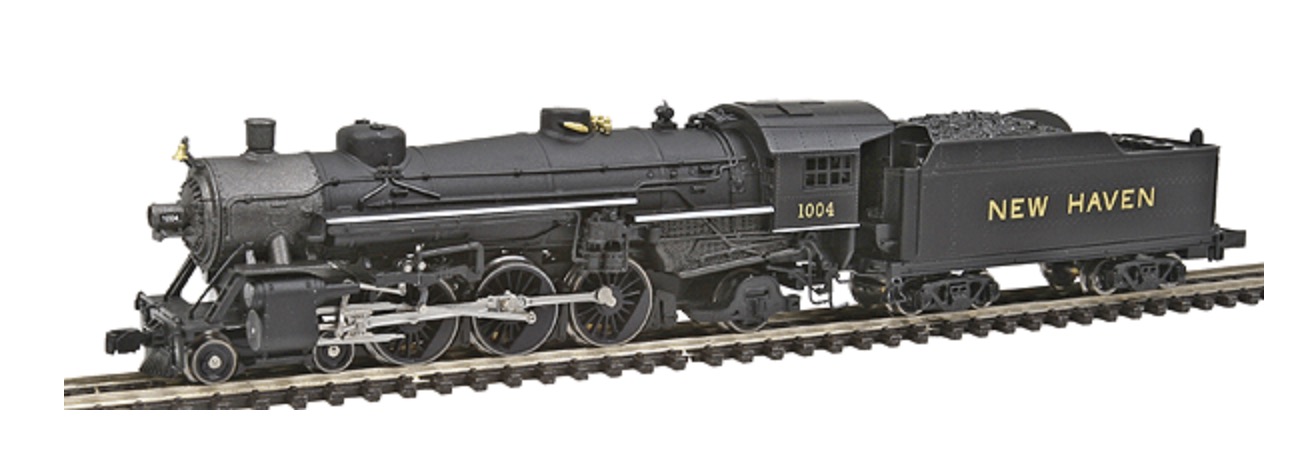
Model Information: This InterMountain model has some very nice details. Separately applied ladders brake wheels, platforms, placards roofwalk and stirrups all create a beautiful, albeit delicate, model. Some of the runs come with Micro-Trains trucks and couplers. The print quality is also excellent
Prototype History: During the mid-19th century, attempts were made to ship agricultural products by rail. As early as 1842, the Western Railroad of Massachusetts was reported in the June 15 edition of the Boston Traveler to be experimenting with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage. The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the Northern Railroad (New York) (or NRNY, which later became part of the Rutland Railroad). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success since it was only functional in cold weather. That same year, the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice for cooling.
The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stock yards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, proving to be impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.
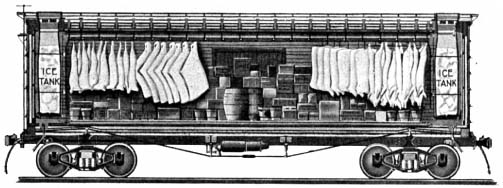
The use of ice to refrigerate and preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome stored ice and snow in caves, dugouts or ice houses lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 19th century, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required re-icing every 250 miles (400 km) to 400 miles (640 km).
From Wikipedia
The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stock yards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, proving to be impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.
The use of ice to refrigerate and preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome stored ice and snow in caves, dugouts or ice houses lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 19th century, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required re-icing every 250 miles (400 km) to 400 miles (640 km).
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  Fruit Growers Express (FGE) was a railroad refrigerator car leasing company that began as a produce-hauling subsidiary of Armour and Company's private refrigerator car line. Its customers complained they were overcharged. In 1919 the Federal Trade Commission ordered the company's sale for anti-trust reasons. The company is now controlled by the CSX Corporation.
Fruit Growers Express (FGE) was a railroad refrigerator car leasing company that began as a produce-hauling subsidiary of Armour and Company's private refrigerator car line. Its customers complained they were overcharged. In 1919 the Federal Trade Commission ordered the company's sale for anti-trust reasons. The company is now controlled by the CSX Corporation.
Incorporated on March 18, 1920 the firm took possession of 4,280 pieces of rolling stock, repairs shops at Alexandria, Virginia and Jacksonville, Florida, and numerous ice plants and other facilities scattered throughout the East Coast on May 1. By year's end, the Chicago and Eastern Illinois, New Haven, and Norfolk and Western railroads became major stockholders.
In order to compete with the Pacific Fruit Express and Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch in the west, FGE and the Great Northern Railway formed the Western Fruit Express (WFE) on July 18, 1923, a move that added 3,000 cars to the equipment pool. By 1926, FGE had expanded its service into the Pacific Northwest and the Midwest through the WFE and the Burlington Refrigerator Express (BREX), its other partly owned subsidiary (formed in partnership with the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CB&Q) on May 1). That same year, FGE purchased 2,676 36-foot-long (11 m) reefers from the Pennsylvania Railroad.
In February, 1928 FGE formed the National Car Company as a subsidiary to service the meat transportation market. Customers included Kahns, Oscar Mayer, and Rath Packing.
From Wikipedia

Incorporated on March 18, 1920 the firm took possession of 4,280 pieces of rolling stock, repairs shops at Alexandria, Virginia and Jacksonville, Florida, and numerous ice plants and other facilities scattered throughout the East Coast on May 1. By year's end, the Chicago and Eastern Illinois, New Haven, and Norfolk and Western railroads became major stockholders.
In order to compete with the Pacific Fruit Express and Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch in the west, FGE and the Great Northern Railway formed the Western Fruit Express (WFE) on July 18, 1923, a move that added 3,000 cars to the equipment pool. By 1926, FGE had expanded its service into the Pacific Northwest and the Midwest through the WFE and the Burlington Refrigerator Express (BREX), its other partly owned subsidiary (formed in partnership with the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad (CB&Q) on May 1). That same year, FGE purchased 2,676 36-foot-long (11 m) reefers from the Pennsylvania Railroad.
In February, 1928 FGE formed the National Car Company as a subsidiary to service the meat transportation market. Customers included Kahns, Oscar Mayer, and Rath Packing.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: InterMountain was founded in 1985 by Fred Brummet. They got started in the model railroad business by producing O-Scale model kits. They got started in the N Scale business almost a decade later when in 1994 they introduced the 40-23 reefer car in kit form. Later, in 1998, they started producing RTR (Ready-to-Run) models. By the early 2000s, InterMountain phased out kit production in favor of the RTR models.
The InterMountain Railway company is located at 1224 Boston Ave in Longmont, CO. They are a manufacturer of HO, N and Z scale model trains. They have produced kits as well as RTR (Ready-To-Run) models. Their N Scale products include locomotives as well as rolling stock. Their rolling stock lineup includes Boxcars, Hoppers, Tank Cars, Reefers, Gondolas, Stock Cars and Flatcars.
Their locomotive releases have primarily been diesel units, with the one major exception being their series of AC-12 Cab Forward steam locos. Their diesel lineup includes F3's, F7's, F9's, SD40's, SD45's and FT units. They are known for quality and detail. They also release their rolling stock in larger varieties of road numbers than most of the other manufacturers.
The InterMountain Railway company is located at 1224 Boston Ave in Longmont, CO. They are a manufacturer of HO, N and Z scale model trains. They have produced kits as well as RTR (Ready-To-Run) models. Their N Scale products include locomotives as well as rolling stock. Their rolling stock lineup includes Boxcars, Hoppers, Tank Cars, Reefers, Gondolas, Stock Cars and Flatcars.
Their locomotive releases have primarily been diesel units, with the one major exception being their series of AC-12 Cab Forward steam locos. Their diesel lineup includes F3's, F7's, F9's, SD40's, SD45's and FT units. They are known for quality and detail. They also release their rolling stock in larger varieties of road numbers than most of the other manufacturers.
Item created by: nscalestation on 2016-12-05 11:42:20
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.