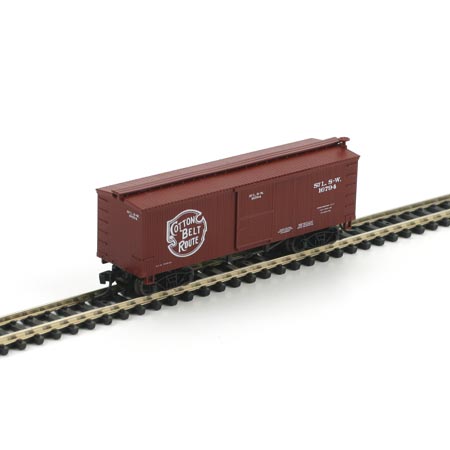
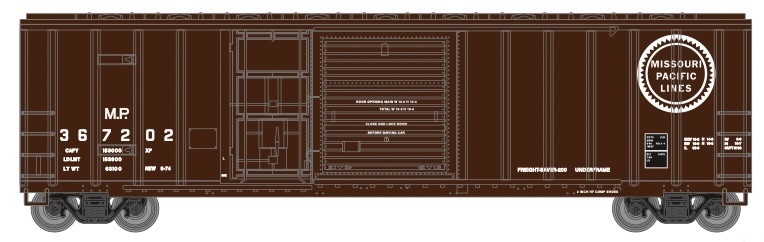
Specific Item Information: N RTR 36 foot Old Time Box, Cotton Belt #16794
Model Information: This MDC tooling models a pre-1900 boxcar with a truss-rod underframe. The MDC Truss-Rod underframe 36' Reefer and 36' Boxcar are very similar models. They were introduced in 1997 for the former and 1998 for the latter. The easiest way to tell the difference is that the reefers have plug doors and the boxcars have sliding doors. Like all of MDC N-Scale molds, this one was also acquired by Athearn in 2004 when they acquired MDC. The MDC releases were supplied in both 'kit' and RTR (Ready-To-Run) versions.
The Athearn (post 2004) releases come fully assembled and feature:
The Athearn (post 2004) releases come fully assembled and feature:
- Fully assembled and ready to operate
- Separately applied brake wheel and roof walk
- Molded truss rods with turnbuckles
- Molded plastic underframe with brake cylinder
- Screw mounted trucks for accurate tracking
- Truck mounted magnetically operated knuckle couplers
- Plastic wheels.
Prototype History: Boxcars in the early 20th century frequently featured a "Truss-Rod" design. The purpose of truss rods was to prevent the railcars from sagging in the middle by the use of turnbuckles in the center of the truss rods for tightening. Due to the limitations of the materials available at the time, there was a tendency for the railcars body to sag in the middle, between the trucks. Truss rods were designed to prevent this. They have the same purpose as I beams or channel beams do in more modern equipment; or, the unitized body of automobiles do today. They give strength in the direction needed to support the load placed on the car.
Road Name History: The St. Louis Southwestern Railway (reporting mark SSW), known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, is a former US Class I railroad which operated between St. Louis, Missouri, and various points in the states of Arkansas and Texas from 1891 to 1992.
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Athearn's history began in 1938, when its founder-to-be, Irvin Athearn, started an elaborate O scale layout in his mother's house. After placing an ad selling the layout, and receiving much response to it, Irv decided that selling model railroads would be a good living. He sold train products out of his mother's house through most of the 1940s. After becoming a full-time retailer in 1946, Irv opened a separate facility in Hawthorne, California in 1948, and that same year he branched into HO scale models for the first time.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Item created by: George on 2016-09-18 07:36:19. Last edited by Lethe on 2020-06-01 00:00:00
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.