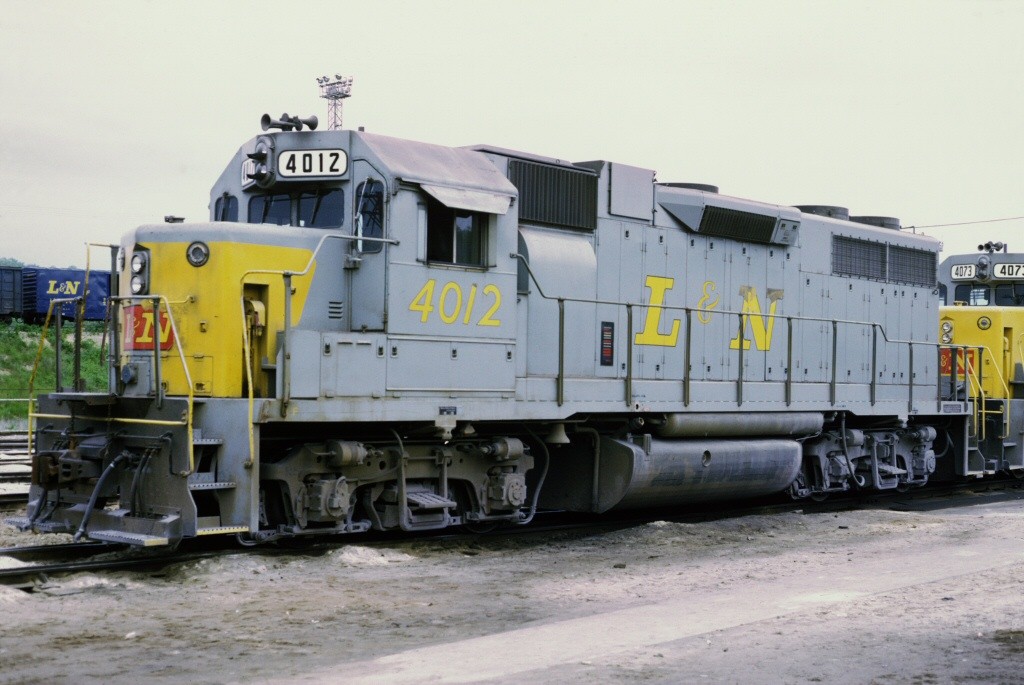
Model Information: The Atlas GP38 is made in China and has always been made in China. These mechanisms run fine but the first releases (1996) do not support drop in decoders. Both versions use a dual-flywheel, split frame chassis with a 5-Pole skew-wound motor.
DCC Information: Early Chinese versions are DCC-friendly requiring a complicated split-board DCC install. Later versions are DCC-Ready accepting a 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale GP40-2, U25B, SD35, Trainmaster, B23-7 and others (DN163A0) from digitrax.com. Unfortunately, the only way to tell which kind you have is to remove the shell and check the chassis. If it has two small lightboards, you have an old one in your hand. A single long lightboard indicates a DCC-Ready chassis.
As of the 2001 run, this model was also offered with factory-installed DCC decoder, first Lenz LE063XF and then (circa 2010s) a NCE decoder.
Since the 2018 run, it is only offered with ESU Loksound sound decoder without DCC no-sound option. So if you want a DCC no-sound, you'll need to install a decoder by yourself.
As of the 2001 run, this model was also offered with factory-installed DCC decoder, first Lenz LE063XF and then (circa 2010s) a NCE decoder.
Since the 2018 run, it is only offered with ESU Loksound sound decoder without DCC no-sound option. So if you want a DCC no-sound, you'll need to install a decoder by yourself.
Prototype History: The EMD GP38 is a 4-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between January 1966 and December 1971. The locomotive's power was provided by an EMD 645 16-cylinder engine which generated 2,000 horsepower (1.49 MW). The company built 706 GP38s for North American railroads. In 1972, it was replaced by an updated model, the GP38-2.
From Wikipedia
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Texas Mexican name first appeared in 1881 during a reorganization of a previous three foot gauge line linking the Gulf port of Corpus Christi, Texas and the city of Loredo on the Mexican border. The line was 157 miles long putting it between Spokane International and Duluth Winnipeg & Pacific in relative size. The TM was standard-gauged in 1902.
Since 1900, TM was owned by the Mexican government through a trust administered in New York. The TM acted as a funnel for traffic to and from Mexico, in fact the end of the line was half way across a bridge over the Rio Grande west of Loredo. The bridge, which was completed in 1883 was the first direct railroad connection between the U.S.A. and another country (the first connection to Canada that didn’t involve a ferry followed six years later!)
TM completely dieselized in 1939 with a fleet of 7 Whitcomb boxcabs. These strange little diesels had four axels set in a rigid frame. That sounds a little, well rigid, by diesel standards but think of it as a diesel powered 0-8-0. A few years later, TM built a few diesels themselves with 4 powered axels in a rigid frame plus a pair of un-powered leading wheels – essentially a diesel 2-8-0. They even built another diesel from an old baggage car.
TM did go on to buy more sensible locomotives including Baldwin switchers, EMD F7’s, and 7, 9, 18, 28, and 38 series geeps. By the 1980’s, there were 16 various geeps on the roster. For a while in the 1980s, TM provided passenger service under the name TexMex Express between Corpus Christi and Loredo with some success.
In 1982, the Mexican government sold their stake in TM to a Mexican company. As the privatization of the Mexican National Railways (FNM) loomed, Kansas City Southern was assembling a system to take advantage of new traffic moving north and south due to the passage of the NAFTA treaty. KCS was positioning itself to acquire a large stake in the “Northeast Concession” (that would become TFM) in the privatization of FNM. Over a period of several years, shares in Texas Mexican were traded back and forth between KCS and companies in Mexico. KCS officially took control of TM in 2005 when they also purchased all remaining shares of TFM. That left a gap between Corpus Christi and the end of the KCS at Beaumont, Texas. KCS had already leveraged trackage rights over Union Pacific to bridge that gap in exchange for not fighting UP’s acquisition of Southern Pacific. Today, TM is a wholly owned subsidiary of KCS and operations are largely integrated into those of KCS.
Since 1900, TM was owned by the Mexican government through a trust administered in New York. The TM acted as a funnel for traffic to and from Mexico, in fact the end of the line was half way across a bridge over the Rio Grande west of Loredo. The bridge, which was completed in 1883 was the first direct railroad connection between the U.S.A. and another country (the first connection to Canada that didn’t involve a ferry followed six years later!)
TM completely dieselized in 1939 with a fleet of 7 Whitcomb boxcabs. These strange little diesels had four axels set in a rigid frame. That sounds a little, well rigid, by diesel standards but think of it as a diesel powered 0-8-0. A few years later, TM built a few diesels themselves with 4 powered axels in a rigid frame plus a pair of un-powered leading wheels – essentially a diesel 2-8-0. They even built another diesel from an old baggage car.
TM did go on to buy more sensible locomotives including Baldwin switchers, EMD F7’s, and 7, 9, 18, 28, and 38 series geeps. By the 1980’s, there were 16 various geeps on the roster. For a while in the 1980s, TM provided passenger service under the name TexMex Express between Corpus Christi and Loredo with some success.
In 1982, the Mexican government sold their stake in TM to a Mexican company. As the privatization of the Mexican National Railways (FNM) loomed, Kansas City Southern was assembling a system to take advantage of new traffic moving north and south due to the passage of the NAFTA treaty. KCS was positioning itself to acquire a large stake in the “Northeast Concession” (that would become TFM) in the privatization of FNM. Over a period of several years, shares in Texas Mexican were traded back and forth between KCS and companies in Mexico. KCS officially took control of TM in 2005 when they also purchased all remaining shares of TFM. That left a gap between Corpus Christi and the end of the KCS at Beaumont, Texas. KCS had already leveraged trackage rights over Union Pacific to bridge that gap in exchange for not fighting UP’s acquisition of Southern Pacific. Today, TM is a wholly owned subsidiary of KCS and operations are largely integrated into those of KCS.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: George on 2016-09-05 16:22:36. Last edited by gdm on 2020-06-14 17:53:10
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.