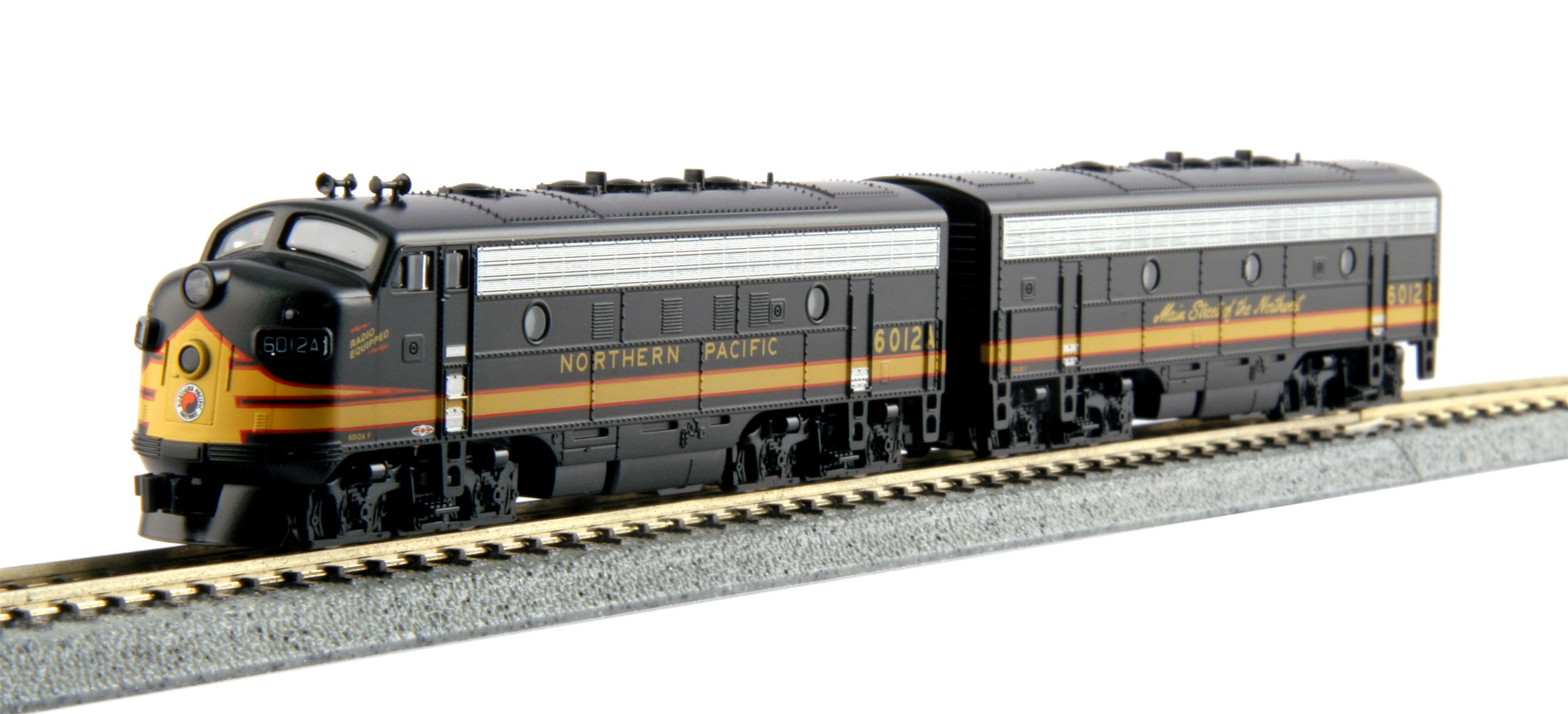
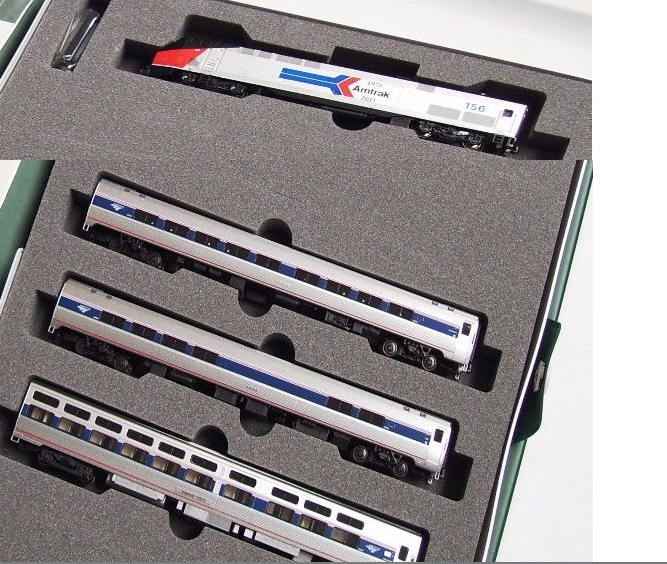
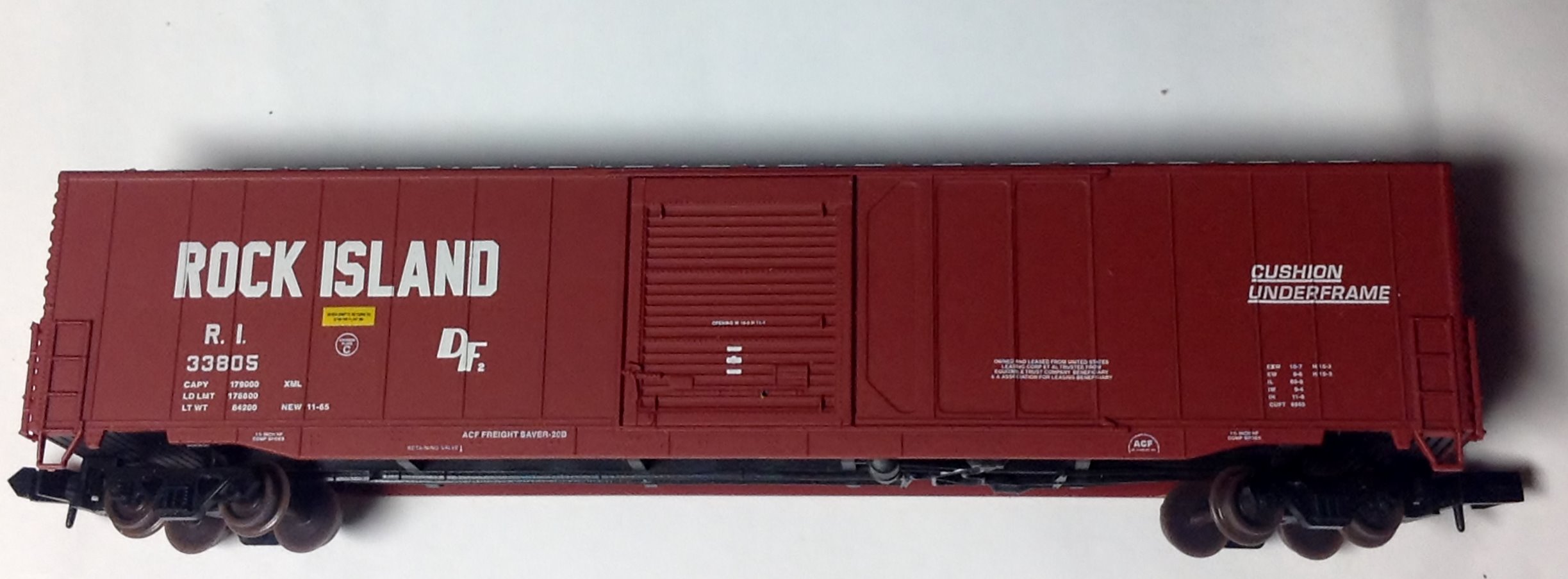
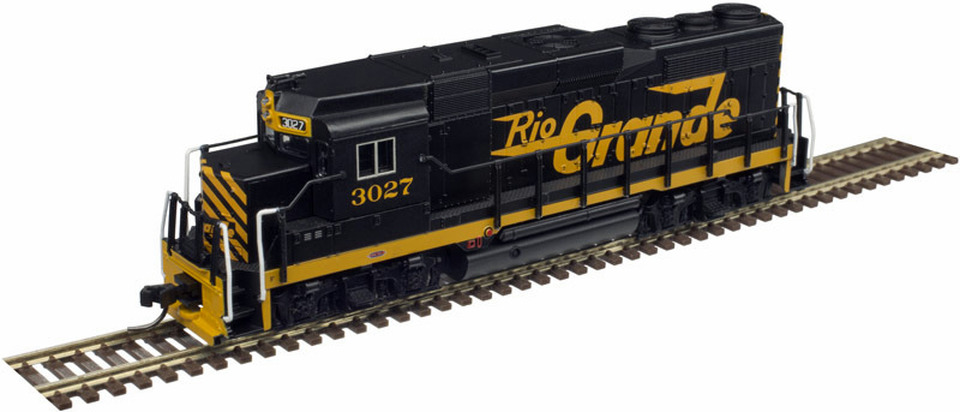
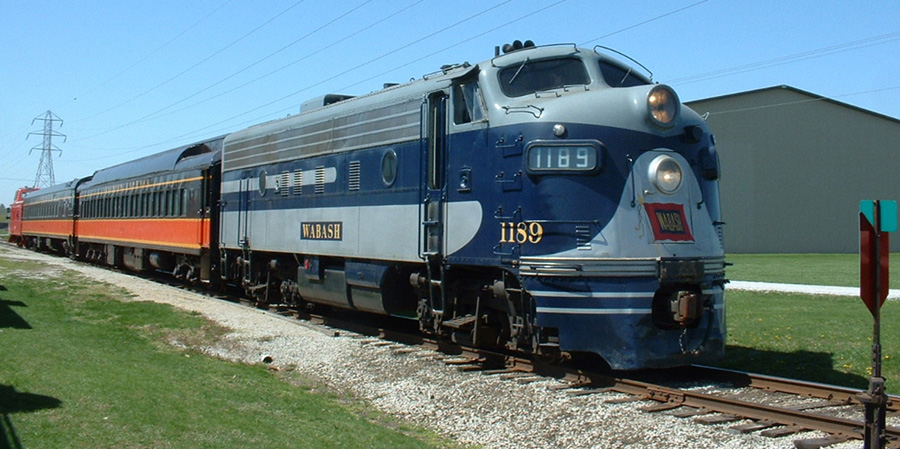
Specific Item Information: Dual headlight, no steam generator.
Model Information: The Kato F2, F3 and F7 all share the same mechanism. They differ only in shell details. Kato introduced the F3 model in 1988 and then followed up with the F7 in 1992. In 2003 a major overhaul introduced a DCC-Ready mechanism to the F3 and then in 2006 a similar update was performed for the F7. In 2014, a DCC-Ready version of the F2 was added to the roster.
Like the Atlas Geeps, these models have been a staple of Kato engine production for decades. They have undergone numerous revisions, each offering significant upgrades in features in performance. They have always been good runners (I have an older B&O AB pair I love to operate) but they get better with each update. Even the earliest models featured a modern split-frame design and are very heavy for their size. This probably aids in their excellent smooth operation.
Like the Atlas Geeps, these models have been a staple of Kato engine production for decades. They have undergone numerous revisions, each offering significant upgrades in features in performance. They have always been good runners (I have an older B&O AB pair I love to operate) but they get better with each update. Even the earliest models featured a modern split-frame design and are very heavy for their size. This probably aids in their excellent smooth operation.
DCC Information: Later releases permit easy DCC-installation (though they remain 'Friendly' rather than 'Ready'), Kato knuckle couplers and low-profile wheels. All versions run quietly.
Prototype History: The F7 was the fourth model in GM-EMD's successful line of F unit locomotives, and by far the best-selling cab unit of all time. In fact, more F7's were built than all other F units combined. It succeeded the F3 model in GM-EMD's F unit sequence, and was replaced in turn by the F9. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois, plant or GMD's London, Ontario, facility.
The F7 differed from the F3 primarily in internal equipment (mostly electrical) and some external features. Its continuous tractive effort rating was 20% higher (e.g. 40,000 lb (18,000 kg) for an F7 with 65 mph (105 km/h) gearing, compared to 32,500 lb (14,700 kg) for an F3 with the same gearing.
A total of 2,366 cab-equipped lead A units and 1,483 cabless-booster or B units were built. (Note: the B unit is often referred to as an "F7B", whereas the A unit is simply an "F7".)
Many F7s remained in service for decades, as railroads found them economical to operate and maintain. However, the locomotive was not very popular with yard crews who operated them in switching service because they were difficult to mount and dismount, and it was also nearly impossible for the engineer to see hand signals from a ground crew without leaning way outside the window. As most of these engines were bought and operated before two-way radio became standard on most American railroads, this was a major point of contention. In later years, with the advent of the "road switchers" such as the EMD GP7, F units were primarily used in "through freight" and "unit train" service where there was very little or no switching to be done on line of road.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
The F7 differed from the F3 primarily in internal equipment (mostly electrical) and some external features. Its continuous tractive effort rating was 20% higher (e.g. 40,000 lb (18,000 kg) for an F7 with 65 mph (105 km/h) gearing, compared to 32,500 lb (14,700 kg) for an F3 with the same gearing.
A total of 2,366 cab-equipped lead A units and 1,483 cabless-booster or B units were built. (Note: the B unit is often referred to as an "F7B", whereas the A unit is simply an "F7".)
Many F7s remained in service for decades, as railroads found them economical to operate and maintain. However, the locomotive was not very popular with yard crews who operated them in switching service because they were difficult to mount and dismount, and it was also nearly impossible for the engineer to see hand signals from a ground crew without leaning way outside the window. As most of these engines were bought and operated before two-way radio became standard on most American railroads, this was a major point of contention. In later years, with the advent of the "road switchers" such as the EMD GP7, F units were primarily used in "through freight" and "unit train" service where there was very little or no switching to be done on line of road.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
Road Name History:  The Northern Pacific Railway (reporting mark NP) was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States from Minnesota to the Pacific Coast. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly 40 million acres (160,000 km2) of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on Sept. 8, 1883.
The Northern Pacific Railway (reporting mark NP) was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States from Minnesota to the Pacific Coast. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly 40 million acres (160,000 km2) of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on Sept. 8, 1883.
The railroad had about 6800 miles of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington and Wisconsin. In addition the company had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land.
The company was headquartered first in Brainerd, Minnesota, then in Saint Paul, Minnesota. It had a tumultuous financial history, and in 1970 it merged with other lines to form the Burlington Northern Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The railroad had about 6800 miles of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington and Wisconsin. In addition the company had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land.
The company was headquartered first in Brainerd, Minnesota, then in Saint Paul, Minnesota. It had a tumultuous financial history, and in 1970 it merged with other lines to form the Burlington Northern Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: KATO U.S.A. was established in 1986, with the first U.S. locomotive model (the GP38-2, in N-Scale) released in 1987. Since that time, KATO has come to be known as one of the leading manufacturers of precision railroad products for the modeling community. KATO's parent company, Sekisui Kinzoku Co., Ltd., is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan.
In addition to producing ready-to-run HO and N scale models that are universally hailed for their high level of detail, craftsmanship and operation, KATO also manufactures UNITRACK. UNITRACK is the finest rail & roadbed modular track system available to modelers today. With the track and roadbed integrated into a single piece, UNITRACK features a nickel-silver rail and a realistic-looking roadbed. Patented UNIJOINERS allow sections to be snapped together quickly and securely, time after time if necessary.
The Kato U.S.A. office and warehouse facility is located in Schaumburg, Illinois, approximately 30 miles northwest of Chicago. All research & development of new North American products is performed here, in addition to the sales and distribution of merchandise to a vast network of wholesale representatives and retail dealers. Models requiring service sent in by hobbyists are usually attended to at this location as well. The manufacturing of all KATO products is performed in Japan.
Supporters of KATO should note that there is currently no showroom or operating exhibit of models at the Schaumburg facility. Furthermore, model parts are the only merchandise sold directly to consumers. (Please view the Parts Catalog of this website for more specific information.)
In addition to producing ready-to-run HO and N scale models that are universally hailed for their high level of detail, craftsmanship and operation, KATO also manufactures UNITRACK. UNITRACK is the finest rail & roadbed modular track system available to modelers today. With the track and roadbed integrated into a single piece, UNITRACK features a nickel-silver rail and a realistic-looking roadbed. Patented UNIJOINERS allow sections to be snapped together quickly and securely, time after time if necessary.
The Kato U.S.A. office and warehouse facility is located in Schaumburg, Illinois, approximately 30 miles northwest of Chicago. All research & development of new North American products is performed here, in addition to the sales and distribution of merchandise to a vast network of wholesale representatives and retail dealers. Models requiring service sent in by hobbyists are usually attended to at this location as well. The manufacturing of all KATO products is performed in Japan.
Supporters of KATO should note that there is currently no showroom or operating exhibit of models at the Schaumburg facility. Furthermore, model parts are the only merchandise sold directly to consumers. (Please view the Parts Catalog of this website for more specific information.)
Item created by: gdm on 2016-07-26 11:22:22. Last edited by gdm on 2018-02-26 12:01:19
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.