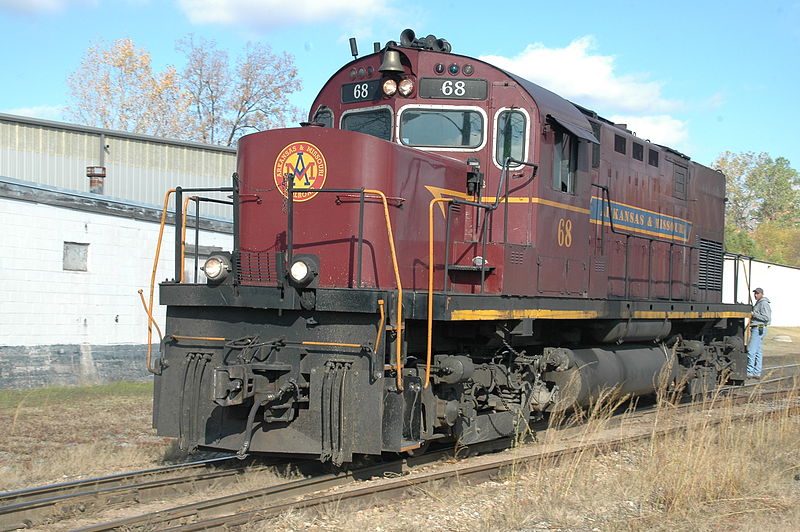
Model Information: Atlas first released this model of the Century 420 (C420) in 2007. The first release of the C420 was a low-nose “phase 1” model. The combination of stanchions mounted into the top of the walkway deck and a high-mounted engine air intake (located ahead of the radiator area) identifies this C420 variant. Phase 1 models were produced between June 1963 and October 1964 and this first production run covers all original owners of the low nose version.
Atlas’ 2008 second release of the C420 is a low-nose “phase 2” model. All Phase 2 versions feature the low/vertical mounted engine air intake located ahead of the radiator area on the long hood. Early phase 2 locomotives feature phase 1-style walkways/sills with stanchions mounted into the top walkway deck (referred to as “Phase 2a” models). Later phase 2 locomotives feature a revised configuration where the stanchions are mounted to the sides of the sill (referred to as “Phase 2b” models). Phase 2a production ran from December 1964 through September 1965. Phase 2b units were produced from December 1965 through the end of C420 locomotive production in August 1968.
The C-420 has the standard attributes of modern Atlas models. The chassis is fully DCC-Ready (and, in fact, available with factory-installed decoder). These models perform excellently; they are quiet, responsive and powerful.
Standard Features: Flat or "step" pilots used where appropriate; Long hood with or without dynamic brake detail used where appropriate; 3,100 gallon fuel tank; Separately-applied coupler cut levers; Painted safety rails; Dual flywheels; Directional lighting and a Scale Speed motor.
Atlas’ 2008 second release of the C420 is a low-nose “phase 2” model. All Phase 2 versions feature the low/vertical mounted engine air intake located ahead of the radiator area on the long hood. Early phase 2 locomotives feature phase 1-style walkways/sills with stanchions mounted into the top walkway deck (referred to as “Phase 2a” models). Later phase 2 locomotives feature a revised configuration where the stanchions are mounted to the sides of the sill (referred to as “Phase 2b” models). Phase 2a production ran from December 1964 through September 1965. Phase 2b units were produced from December 1965 through the end of C420 locomotive production in August 1968.
The C-420 has the standard attributes of modern Atlas models. The chassis is fully DCC-Ready (and, in fact, available with factory-installed decoder). These models perform excellently; they are quiet, responsive and powerful.
Standard Features: Flat or "step" pilots used where appropriate; Long hood with or without dynamic brake detail used where appropriate; 3,100 gallon fuel tank; Separately-applied coupler cut levers; Painted safety rails; Dual flywheels; Directional lighting and a Scale Speed motor.
Prototype History: ALCo built a total of 131 Century 420 locomotives between 1963 and 1969, when the builder ceased all new locomotive production. Powered by a 12-cylinder, turbocharged, 2,000-hp 251-series prime mover, the C420’s direct competitor in 1963 was the EMD GP18. In fact, EMD did not offer a 12-cylinder, 2,000-hp prime mover until the GP39 model was produced in 1969. The shorter 12-cylinder engine block allowed the C420 to have its distinctive set-back cab and extended short hood.
The first road to purchase the C420 was the Lehigh & Hudson River, with its first two units built in 1963. The largest fleet was purchased by the Long Island Railroad, with 30 units built between 1963 and 1968. All were equipped with a high short hood which housed a steam generator for passenger service. Over time, the largest fleet of C420s was amassed by the Louisville & Nashville. While only 26 units were purchased new, their total fleet grew to well over 60 units through mergers and acquisitions. The C420 can still be found in daily service today in the US. Currently the largest fleet of C420s is operated by the Arkansas & Missouri Railroad.
The first road to purchase the C420 was the Lehigh & Hudson River, with its first two units built in 1963. The largest fleet was purchased by the Long Island Railroad, with 30 units built between 1963 and 1968. All were equipped with a high short hood which housed a steam generator for passenger service. Over time, the largest fleet of C420s was amassed by the Louisville & Nashville. While only 26 units were purchased new, their total fleet grew to well over 60 units through mergers and acquisitions. The C420 can still be found in daily service today in the US. Currently the largest fleet of C420s is operated by the Arkansas & Missouri Railroad.
Road Name History: The LIRR was established in 1834 as part of a ferry-rail-ferry-rail route linking New York City with Boston. Within a few years, an all-rail route (later becoming the New Haven) was completed and LIRR’s through traffic evaporated. In the 1880s, the LIRR absorbed all of the other railroads on the island and settled in to a life of dependable local service. This included what may have been the first WOFC (wagon on flat car) service.
In 1900, Pennsylvania Railroad bought control of the LIRR and began incorporating it into their plans for Penn Station in Manhattan. This included electrifying certain routes on the west end of the LIRR with 600 volt DC third rail. The steam locomotive fleet began to take on a distinctly Pennsy look. Over the next 20 years, Long Island began to develop into a bedroom community for New York City and the LIRR stepped in to become the transport of choice for tens of thousands of daily commuters.
However, running commuter trains is an inherently dodgy business. It requires large investments in equipment and facilities that are used for two brief windows of time during the day, then sit idle for the rest of the time. The problem was made worse by the state of New York who froze ticket prices at the end of the First World War and left them there until after the Second World War. The LIRR slipped into bankruptcy. Parent PRR and the state came to an agreement. New York’s onerous property taxes were relaxed, ticket fares were allowed to rise and PRR began modernizing the LIRR. Steam was replaced with diesels primarily from Alco and Fairbanks-Morse. EMD’s joined the party in 1976.
In 1966, a state agency (later called the Metropolitan Transportation Authority) bought control of the LIRR from the Pennsylvania Railroad. Under state control, the LIRR gradually lost interest in their freight service and in 1997 freight operations were turned over to the New York & Atlantic Railway. The LIRR remains today America’s largest passenger hauler, moving over a third of a million passengers on a typical weekday.
In 1900, Pennsylvania Railroad bought control of the LIRR and began incorporating it into their plans for Penn Station in Manhattan. This included electrifying certain routes on the west end of the LIRR with 600 volt DC third rail. The steam locomotive fleet began to take on a distinctly Pennsy look. Over the next 20 years, Long Island began to develop into a bedroom community for New York City and the LIRR stepped in to become the transport of choice for tens of thousands of daily commuters.
However, running commuter trains is an inherently dodgy business. It requires large investments in equipment and facilities that are used for two brief windows of time during the day, then sit idle for the rest of the time. The problem was made worse by the state of New York who froze ticket prices at the end of the First World War and left them there until after the Second World War. The LIRR slipped into bankruptcy. Parent PRR and the state came to an agreement. New York’s onerous property taxes were relaxed, ticket fares were allowed to rise and PRR began modernizing the LIRR. Steam was replaced with diesels primarily from Alco and Fairbanks-Morse. EMD’s joined the party in 1976.
In 1966, a state agency (later called the Metropolitan Transportation Authority) bought control of the LIRR from the Pennsylvania Railroad. Under state control, the LIRR gradually lost interest in their freight service and in 1997 freight operations were turned over to the New York & Atlantic Railway. The LIRR remains today America’s largest passenger hauler, moving over a third of a million passengers on a typical weekday.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: gdm on 2016-06-27 13:14:33. Last edited by gdm on 2018-03-29 11:22:43
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.