Specific Item Information: The Tennessee Central linked the city of Nashville with the Illinois Central to the northwest and with the Southern Railway to the east, breaking the stranglehold of the L&N and the NC&St.L (which was controlled by L&N) had on rail service to the city. The TC mainline was strewn with 3% grades, big bridges and tight curves. Coal made up a large portion of their originated traffic. In 1968, the TC was divided up between IC, L&N and Southern.
Model Information: These ready-to-run cars feature: die cast slope sheet-hopper bay-center sill assembly; injection molded plastic sides, ends, and hopper doors; fully molded brake tank, valve and air lines; body mounted brake hose detail; coal load; lever-style hand brake; body mounted magnetically operating knuckle couplers; close coupling; and Fox Valley Models metal wheels.
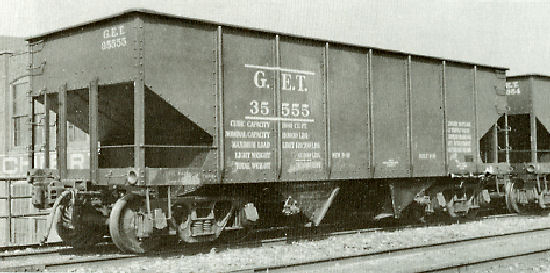
Prototype History: The USRA 55-Ton hopper was designed by the United States Railway Administration during World War I as a standardized hopper to be used by all railroads in order to aid the war effort. After WWI many railroads continued to use the USRA 55-Ton hoppers, as well as build many thousands more clones. The USRA hopper was in use on North American railroads from 1918 until the 1970’s
Road Name History: The Tennessee Central Railway was founded in 1884 as the Nashville and Knoxville Railroad by Alexander S. Crawford. It was an attempt to open up a rail route from the coal and minerals of East Tennessee to the markets of the midstate, a service which many businessmen felt was not being adequately provided by the existing railroad companies. They also wanted to ship coal and iron ore to the Northeastern US over the Cincinnati Southern Railway, which was leased to the Southern and operated as the Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway [CNOTP], through their Cincinnati gateway. The N&K was only completed between Lebanon, where it connected to a Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway branch from Nashville, and Standing Stone (now Monterey).
Wartime traffic in the early 1940s brightened the financial picture, but after that hard times returned. Despite losses in 1946, a group of investors led by J. L. Armstrong bought out the Davis group. The last of the steam engines were pulled from service in 1952 due to the arrival of four diesel locomotives (along with 200 coal hoppers) financed by a Reconstruction Finance Corporation loan in the amount of $2.2 million. 1954 saw the opening of the first unit of the Tennessee Valley Authority's Kingston coal-fired power generating plant, which was largely fed coal from TC's own on-line coal mines operators. The company dropped money-losing passenger service on July 31, 1955, also in that year, the TC ended operations of their steam locomotives. 1956 saw the TC purchase more diesel locomotives and coal hoppers with another RFC loan. Brief profitability was restored from 1949 through 1956. In 1957 the TVA began awarding contracts to non-TC coal mine operators and their traffic boom went bust. Although the program of right-of-way improvement and new equipment acquisition had been carried out, the firm at length was unable to repay the RFC loans and fell into its third and final receivership in 1968. Its assets were sold off. Much of the Nashville beltline south of Nashville had already been sold to the state to build I-440. The Western Division from the western end of the I-440 right of way in Nashville to Hopkinsville, KY was purchased by the Illinois Central Railroad. The eastern end of the line from Harriman to the siding just west of Crossville went to the Southern Railway. The remaining middle portion from Crossville to Nashville went to its old and not at all friendly rival, the Louisville & Nashville.
From Wikipedia
Wartime traffic in the early 1940s brightened the financial picture, but after that hard times returned. Despite losses in 1946, a group of investors led by J. L. Armstrong bought out the Davis group. The last of the steam engines were pulled from service in 1952 due to the arrival of four diesel locomotives (along with 200 coal hoppers) financed by a Reconstruction Finance Corporation loan in the amount of $2.2 million. 1954 saw the opening of the first unit of the Tennessee Valley Authority's Kingston coal-fired power generating plant, which was largely fed coal from TC's own on-line coal mines operators. The company dropped money-losing passenger service on July 31, 1955, also in that year, the TC ended operations of their steam locomotives. 1956 saw the TC purchase more diesel locomotives and coal hoppers with another RFC loan. Brief profitability was restored from 1949 through 1956. In 1957 the TVA began awarding contracts to non-TC coal mine operators and their traffic boom went bust. Although the program of right-of-way improvement and new equipment acquisition had been carried out, the firm at length was unable to repay the RFC loans and fell into its third and final receivership in 1968. Its assets were sold off. Much of the Nashville beltline south of Nashville had already been sold to the state to build I-440. The Western Division from the western end of the I-440 right of way in Nashville to Hopkinsville, KY was purchased by the Illinois Central Railroad. The eastern end of the line from Harriman to the siding just west of Crossville went to the Southern Railway. The remaining middle portion from Crossville to Nashville went to its old and not at all friendly rival, the Louisville & Nashville.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Bluford Shops began in 2007 as a side project of two model railroad industry veterans, Craig Ross and Steve Rodgers. They saw a gap between road names available on N scale locomotives but not available on cabooses. They commissioned special runs of Atlas cabooses in Atlantic Coast Line, Central of Georgia, Monon, Boston & Maine and Southern plus runs on Grand Trunk Western and Central Vermont on the MDC wooden cabooses. While these were in process, they began to develop their first all new tooling project, 86' Auto Parts Boxcars in double door and quad door editions in N scale. By January of 2008, Bluford Shops became a full time venture. Along with additional N scale freight cars and their own tooling for new cabooses, they have brought their own caboose line to HO scale. They also have their popular Cornfields in both HO and N. The future looks bright as they continue to develop new products for your railroad.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
The town of Bluford in southern Illinois featured a small yard on Illinois Central's Edgewood Cutoff (currently part of CN.) The yard included a roundhouse, concrete coaling tower (which still stands) and large ice house. Reefer trains running between the Gulf Coast and Chicago were re-iced in Bluford. Things are more quiet now in Bluford with the remaining tracks in the yard used to stage hoppers for mines to the south and store covered hoppers. Intersecting the IC line in Bluford is Southern Railway's (currently NS) line between Louisville and St. Louis. Traffic on this single track line remains relatively heavy.
Item created by: gdm on 2016-06-24 16:58:46. Last edited by gdm on 2018-01-24 07:35:53
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.