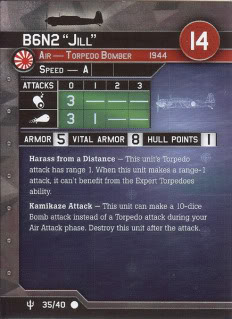
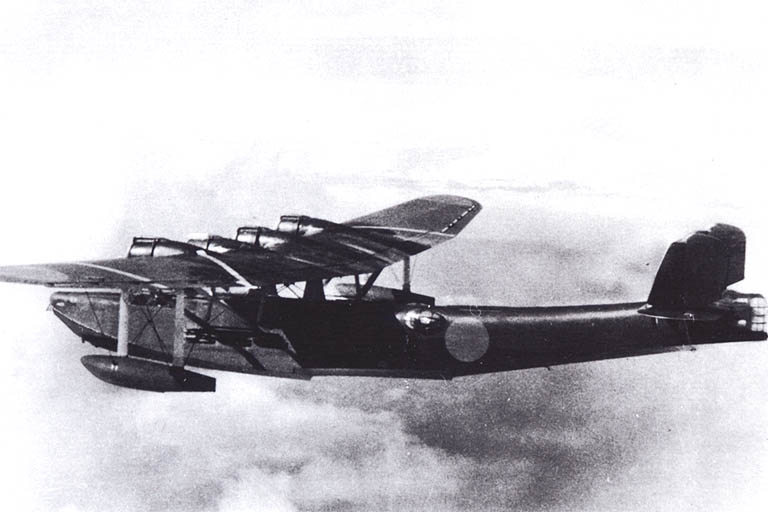
Aircraft History: The Kawanishi H6K was an Imperial Japanese Navy flying boat produced by the Kawanishi Aircraft Company and used during World War II for maritime patrol duties. The Allied reporting name for the type was Mavis; the Navy designation was "Type 97 Large Flying Boat" (九七式大型飛行艇).
H6Ks were deployed from 1938 onwards, first seeing service in the Sino-Japanese War and were in widespread use by the time the full-scale Pacific War erupted, in December 1941. At that time of the war, four Kōkūtai (air groups) operated a total of 66 H6K4s.
The type had some success over South East Asia and the South West Pacific. H6Ks had excellent endurance, being able to undertake 24-hour patrols, and were often used for long-range reconnaissance and bombing missions. From bases in the Dutch East Indies, they were able to undertake missions over a large portion of Australia.
However, the H6K became vulnerable to a newer generation of heavier armed and faster fighters. It continued in service throughout the war, in areas where the risk of interception was low. In front-line service, it was replaced by the Kawanishi H8K.
H6Ks were deployed from 1938 onwards, first seeing service in the Sino-Japanese War and were in widespread use by the time the full-scale Pacific War erupted, in December 1941. At that time of the war, four Kōkūtai (air groups) operated a total of 66 H6K4s.
The type had some success over South East Asia and the South West Pacific. H6Ks had excellent endurance, being able to undertake 24-hour patrols, and were often used for long-range reconnaissance and bombing missions. From bases in the Dutch East Indies, they were able to undertake missions over a large portion of Australia.
However, the H6K became vulnerable to a newer generation of heavier armed and faster fighters. It continued in service throughout the war, in areas where the risk of interception was low. In front-line service, it was replaced by the Kawanishi H8K.
Manufacturer: The Kawanishi Aircraft Company (川西航空機) was a Japanese aircraft manufacturer during World War II. It was founded as Kawanishi Engineering Works in 1920 in Hyōgo Prefecture as an outgrowth of the Kawanishi conglomerate, which had been funding the Nakajima Aircraft Company. Kawanishi built its first aircraft, the Kawanishi K-1 Mail-carrying Aircraft in 1921, and set up an airline, Nippon Koku K.K. (Japan Aviation Co. Ltd) in 1923, designing and building several aircraft for the airline's use. It was forced by the Japanese government to shut down Nippon Koku in 1929, however, with its routes being transferred to the government-owned Nippon Koku Yuso K.K. (Japan Air Transport Co. Ltd.) Kawanishi then split off the former Kawanishi Engineering Works, forming Kawanishi Kokuki KK in 1928, taking all of the Kawanishi Engineering Works' assets. While Kawanishi was best known for its seaplanes, such as the Kawanishi H6K and H8K flying boats, its N1K-J land-based fighter -derived from their Kawanishi N1K1 floatplane fighter- was considered one of the best in the war. After Japan's defeat, the company was reborn as Shin Meiwa Industries (later ShinMaywa), and continued to create flying boats such as the PS-1 and US-2.
Country: Japan is an island nation in the Pacific Ocean with dense cities, imperial palaces, mountainous national parks and thousands of shrines and temples. Shinkansen bullet trains connect the main islands of Kyushu (with Okinawa's subtropical beaches), Honshu (home to Tokyo and Hiroshima’s atomic-bomb memorial) and Hokkaido (famous for skiing). Tokyo, the capital, is known for skyscrapers, shopping and pop culture.
Although legend has it that Japan was founded in 660BC, archaeologists agree that settlement in the Japanese archpelago dates back as far as 100,000 years. The Jomon Period (8000-c.300BC) is the earliest that has been studied. It is named after the 'jomon' or cord-marked pattern style of pottery of the period.
Although legend has it that Japan was founded in 660BC, archaeologists agree that settlement in the Japanese archpelago dates back as far as 100,000 years. The Jomon Period (8000-c.300BC) is the earliest that has been studied. It is named after the 'jomon' or cord-marked pattern style of pottery of the period.
Item created by: gdm on 2015-08-29 11:03:49. Last edited by gdm on 2020-01-14 19:21:14
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.