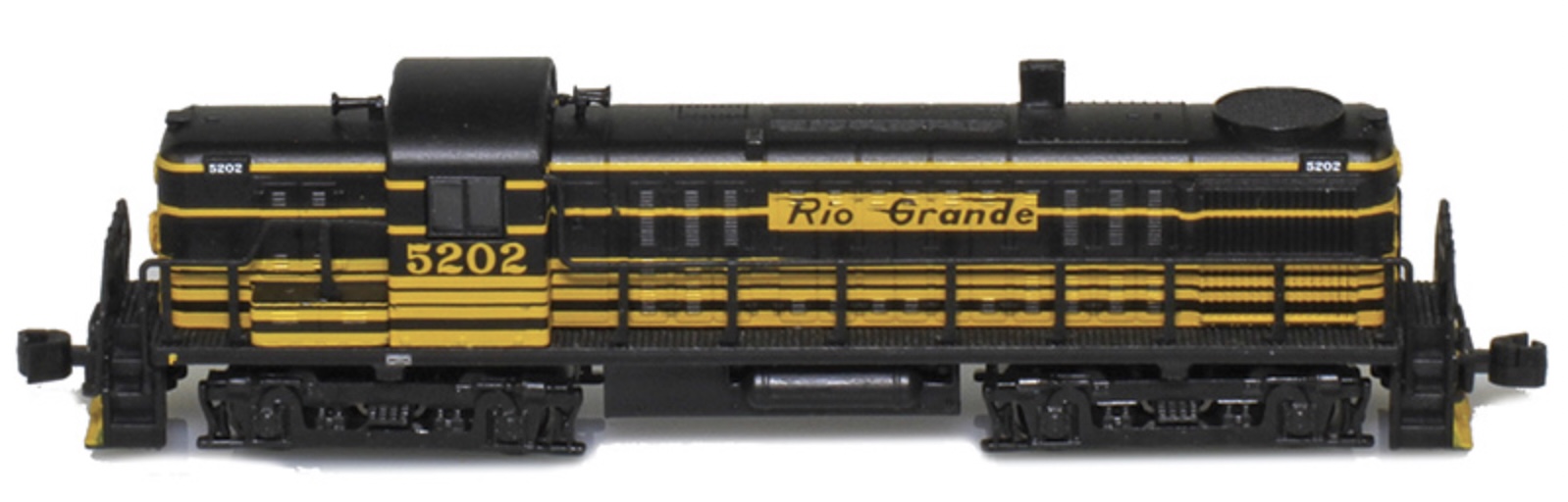
Prototype History: Introduced in 1950, the all-purpose, 1600-HSP RS-3 diesel locomotive had the stamina and strength for freight and passenger service yet was agile enough for yard work. With its rugged, dependable design, it's no wonder that many of these versatile RS-3 locomotives are still working today on short lines, tourist lines, and hauling freight. The ALCO RS-3 is a 1,600 hp (1.2 MW), B-B road switcher diesel-electric locomotive. It was manufactured by American Locomotive Company (ALCO) and Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) from May 1950 to August 1956, and 1,418 were produced - 1,265 for American railroads, 98 for Canadian railroads, 48 for Brazilian and 7 for Mexican railroads. It has a single, 12 cylinder, model 244 engine.
Well over 1,300 RS-3 road-switcher locomotives were built by ALCO between 1950 and 1956. It can be considered one of the most successful four-axle diesel road-switchers ever produced by the builder. These 1,600hp locomotives were powered by an ALCO 244 V-12 engine which was complimented by rugged GE electrical components. The RS-3 was truly a versatile locomotive. It could be found in virtually every type of service from passenger and commuter runs to heavy-haul and local freight assignments. Original owners of the RS-3 tended to be in the eastern and central regions of the US (with heavier concentrations in the northeast and southeast).
During this same time-period, ALCO offered a six-axle road-switcher which was more commonly found in the west. The RSD-4/5 was externally very similar to the RS-3, having six-axle trucks as an obvious spotting feature. They produced the same 1,600hp as an RS-3, but offered increased tractive effort due to the use of a larger generator. Many RSD-4/5s were assigned to operate in mountainous territory (with varying degrees of success) on the Southern Pacific, Santa Fe and the Utah Railway.
Well over 1,300 RS-3 road-switcher locomotives were built by ALCO between 1950 and 1956. It can be considered one of the most successful four-axle diesel road-switchers ever produced by the builder. These 1,600hp locomotives were powered by an ALCO 244 V-12 engine which was complimented by rugged GE electrical components. The RS-3 was truly a versatile locomotive. It could be found in virtually every type of service from passenger and commuter runs to heavy-haul and local freight assignments. Original owners of the RS-3 tended to be in the eastern and central regions of the US (with heavier concentrations in the northeast and southeast).
During this same time-period, ALCO offered a six-axle road-switcher which was more commonly found in the west. The RSD-4/5 was externally very similar to the RS-3, having six-axle trucks as an obvious spotting feature. They produced the same 1,600hp as an RS-3, but offered increased tractive effort due to the use of a larger generator. Many RSD-4/5s were assigned to operate in mountainous territory (with varying degrees of success) on the Southern Pacific, Santa Fe and the Utah Railway.
Road Name History: The Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad (reporting mark DRGW), often shortened to Rio Grande, D&RG or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, was an American Class I railroad company. The railroad started as a 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge line running south from Denver, Colorado in 1870. It served mainly as a transcontinental bridge line between Denver, and Salt Lake City, Utah.
In 1988, the Rio Grande's parent corporation, Rio Grande Industries, purchased Southern Pacific Transportation Company, and as the result of a merger, the larger Southern Pacific Railroad name was chosen for identity. The Rio Grande operated as a separate division of the Southern Pacific, until that company was acquired by the Union Pacific Railroad. Today, most former D&RGW main lines are owned and operated by the Union Pacific while several branch lines are now operated as heritage railways by various companies.
In 1988, the Rio Grande's parent corporation, Rio Grande Industries, purchased Southern Pacific Transportation Company, and as the result of a merger, the larger Southern Pacific Railroad name was chosen for identity. The Rio Grande operated as a separate division of the Southern Pacific, until that company was acquired by the Union Pacific Railroad. Today, most former D&RGW main lines are owned and operated by the Union Pacific while several branch lines are now operated as heritage railways by various companies.
Brand/Importer Information:  AZL is the leader in North American Z scale locomotives and rolling stock. Since 2000, AZL has released a vast variety of freight, passenger and locomotives. AZL continues to push the boundaries of Z scale with amazing details and incredible performance. No matter if you are looking to run steam, or the most modern diesels, AZL has something for you.
AZL is the leader in North American Z scale locomotives and rolling stock. Since 2000, AZL has released a vast variety of freight, passenger and locomotives. AZL continues to push the boundaries of Z scale with amazing details and incredible performance. No matter if you are looking to run steam, or the most modern diesels, AZL has something for you.

Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-07-09 11:40:08
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.