Body Style Information: The Atlas model of the 20,700 gallon tank car was introduced in the mid-Sixties by General American Transportation Corporation, more commonly known simply as GATX. The design is a general-purpose, non-insulated, non-pressure tank car. The Atlas model recreates two major saddle variations (Type 10 and Type 20) and two top platform variations (one- and two-piece). The more common products carried in this tank car were tallow, animal fat, fuel oil, diesel fuel, vegetable oil, soybean oil, fertilizers, lubricating oil, waste oil, and glycol.
Features: Detailed five section non-insulated body Two saddle variations (Type 10 or 20) Detailed top platform with two options (one- or two-piece) With A-end pipe stubs (where applicable) See-through end walks Detailed brake gear and pipes Bottom outlet Safety vent Manway Control housing Stuffing box Safety rails Correct lettering to prototype cars
Features: Detailed five section non-insulated body Two saddle variations (Type 10 or 20) Detailed top platform with two options (one- or two-piece) With A-end pipe stubs (where applicable) See-through end walks Detailed brake gear and pipes Bottom outlet Safety vent Manway Control housing Stuffing box Safety rails Correct lettering to prototype cars
Prototype Information: Larger, 50' Tank cars replaced their smaller predecessors in the late 1960s and 1970s. The Richmond Tank Car Company was one of several manufacturers to produce these general purpose railcars. They generally had about 20,000 gallon capacity and were used to transport many different commodities.
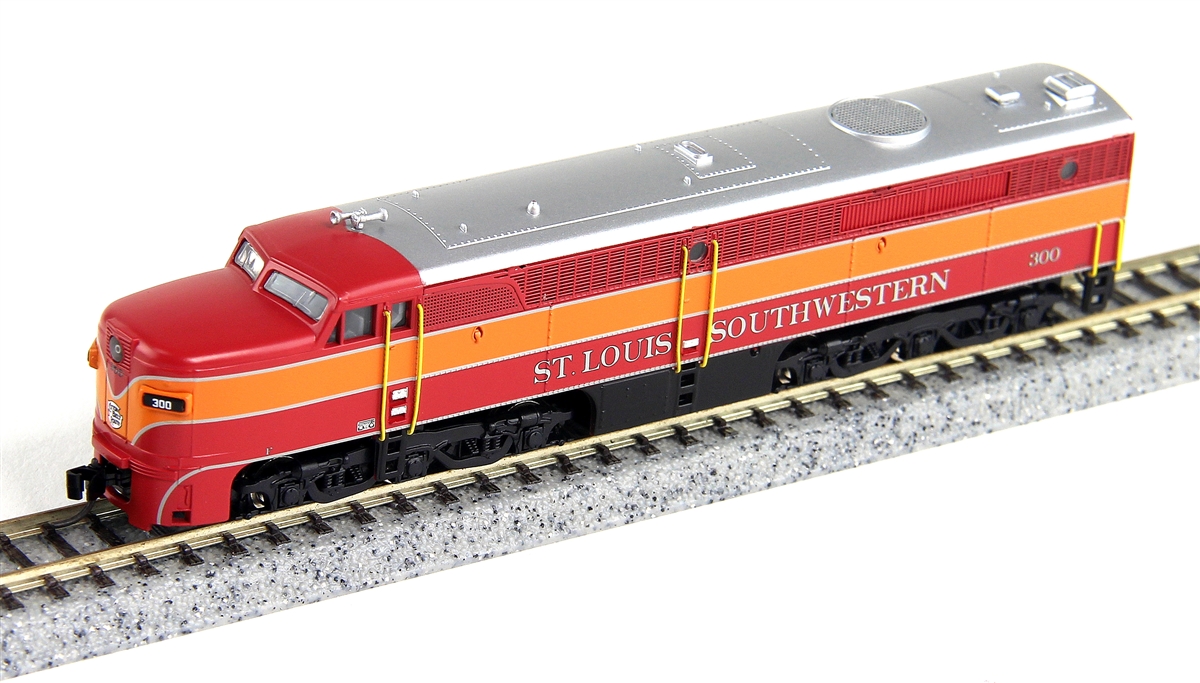
Road/Company Information: The St. Louis Southwestern Railway (reporting mark SSW), known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, is a former US Class I railroad which operated between St. Louis, Missouri, and various points in the states of Arkansas and Texas from 1891 to 1992.
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
Atlas has made a ton of wonderful products throughout the years and we often get questions one whether we have run a certain road name on a particular model. It should be noted that Atlas locomotives and rolling stock are greatly appreciated for their superior operating and running characteristics. Atlas products are also well known for their outstanding collectability not only due to their superior prototypical workmanship, details and decoration, but because there are relatively so few of them made. Each and every production run has been carefully built to market demand, meaning almost every piece in any given run is sold out by Atlas on arrival or shortly thereafter, thus creating a built in collectors market.
Atlas has made a ton of wonderful products throughout the years and we often get questions one whether we have run a certain road name on a particular model. It should be noted that Atlas locomotives and rolling stock are greatly appreciated for their superior operating and running characteristics. Atlas products are also well known for their outstanding collectability not only due to their superior prototypical workmanship, details and decoration, but because there are relatively so few of them made. Each and every production run has been carefully built to market demand, meaning almost every piece in any given run is sold out by Atlas on arrival or shortly thereafter, thus creating a built in collectors market.
Manufacturer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
Atlas has made a ton of wonderful products throughout the years and we often get questions one whether we have run a certain road name on a particular model. It should be noted that Atlas locomotives and rolling stock are greatly appreciated for their superior operating and running characteristics. Atlas products are also well known for their outstanding collectability not only due to their superior prototypical workmanship, details and decoration, but because there are relatively so few of them made. Each and every production run has been carefully built to market demand, meaning almost every piece in any given run is sold out by Atlas on arrival or shortly thereafter, thus creating a built in collectors market.
Atlas has made a ton of wonderful products throughout the years and we often get questions one whether we have run a certain road name on a particular model. It should be noted that Atlas locomotives and rolling stock are greatly appreciated for their superior operating and running characteristics. Atlas products are also well known for their outstanding collectability not only due to their superior prototypical workmanship, details and decoration, but because there are relatively so few of them made. Each and every production run has been carefully built to market demand, meaning almost every piece in any given run is sold out by Atlas on arrival or shortly thereafter, thus creating a built in collectors market.
Item created by: devsummers428 on 2020-07-24 15:52:11. Last edited by devsummers428 on 2020-07-24 15:52:12
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.