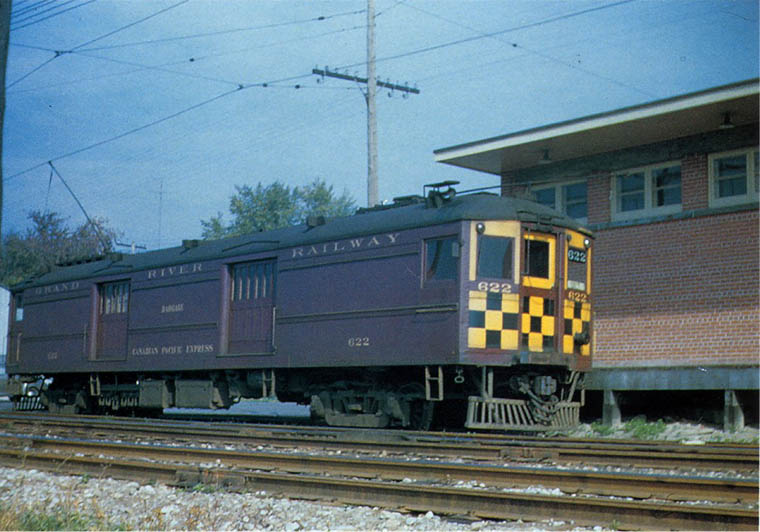
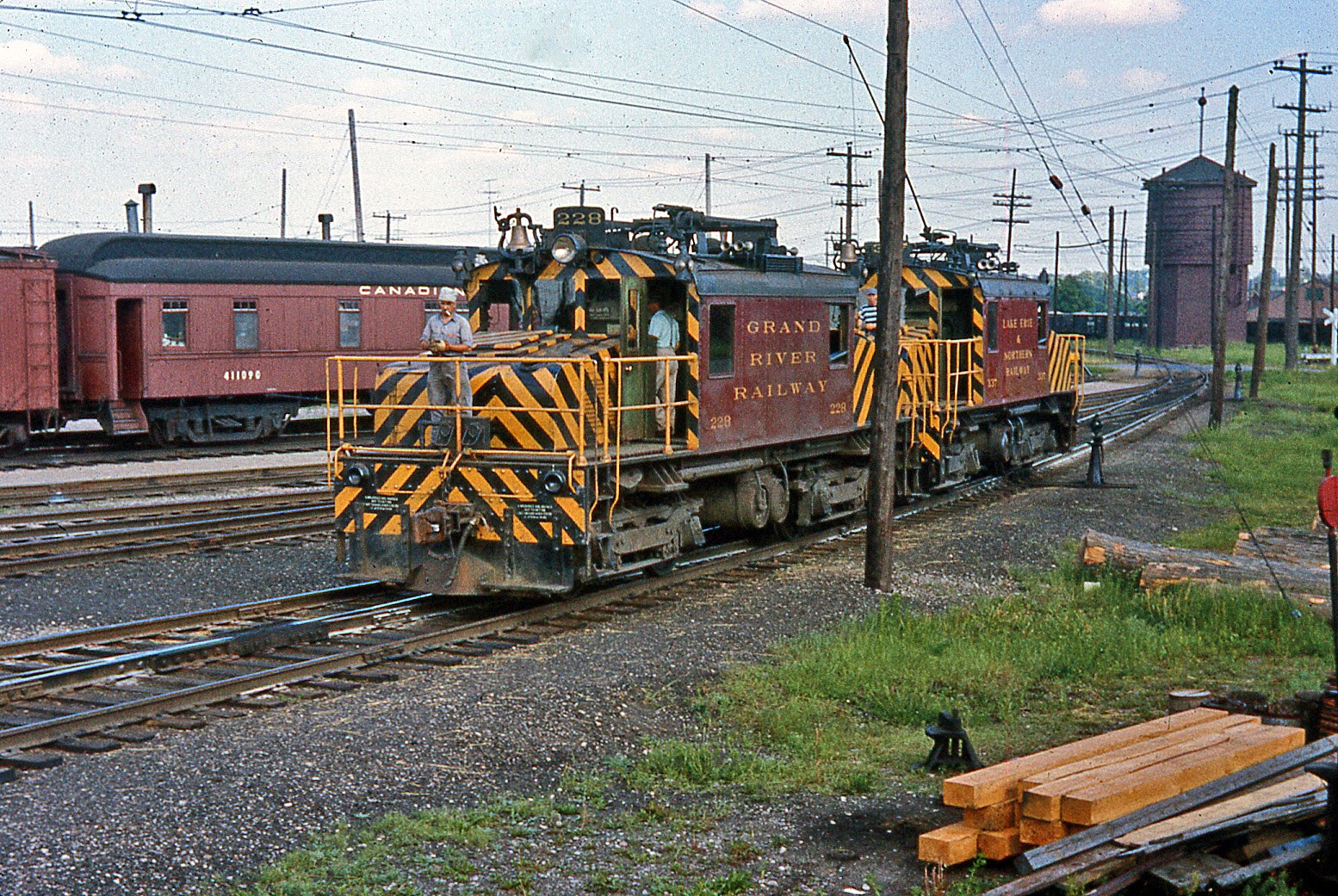Company History: The Grand River Railway was born in 1908 with the merger of the Galt Preston & Hespeler Street Railway and the Preston & Berlin Railway. At the time of the merger, the company was leased by Canadian Pacific for 99 years. For the first six years, the Grand River Railway was called the Berlin Waterloo Wellesley & Lake Huron Railway – quite a mouth full.
The Grand River was an electric interurban line (the Canadians tend to use the term “radial railway” for interurban) providing passenger and freight service to central Ontario. The line ran from Galt to Preston where it split with one leg serving Hespeler and the other going to the Kitchener/Waterloo area.
In 1921, the GRRwy was converted from 600 volt DC to 1500 volt DC to match the neighboring Lake Erie & Northern Railway (also a subsidiary of Canadian Pacific.) Equipment could then be shared as traffic dictated.
Passenger service ended in 1955. Freight traffic was significant, requiring seven freight motors to keep the traffic moving. Electric operation ended and the line was dieselized in 1961. The diesels were provided by Canadian Pacific, which became the first step in relegating the GRRwy to the status of paper railroad. Part of the GRRwy has been abandoned while the rest is operated as Canadian Pacific’s Waterloo Subdivision.
The Grand River was an electric interurban line (the Canadians tend to use the term “radial railway” for interurban) providing passenger and freight service to central Ontario. The line ran from Galt to Preston where it split with one leg serving Hespeler and the other going to the Kitchener/Waterloo area.
In 1921, the GRRwy was converted from 600 volt DC to 1500 volt DC to match the neighboring Lake Erie & Northern Railway (also a subsidiary of Canadian Pacific.) Equipment could then be shared as traffic dictated.
Passenger service ended in 1955. Freight traffic was significant, requiring seven freight motors to keep the traffic moving. Electric operation ended and the line was dieselized in 1961. The diesels were provided by Canadian Pacific, which became the first step in relegating the GRRwy to the status of paper railroad. Part of the GRRwy has been abandoned while the rest is operated as Canadian Pacific’s Waterloo Subdivision.
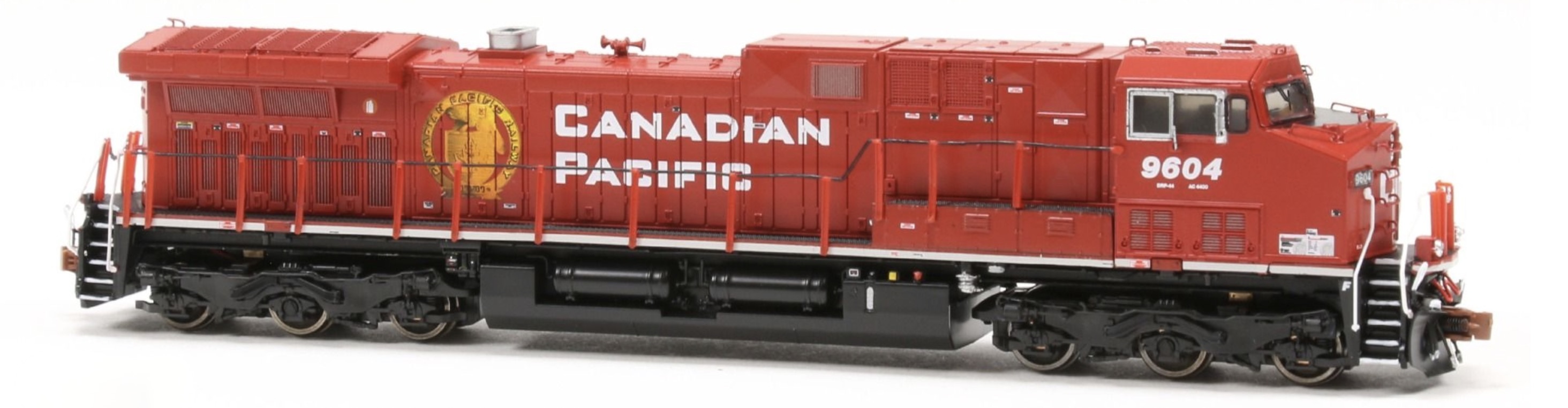
Successor/Parent History: The Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), formerly also known as CP Rail (reporting mark CP) between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railroad incorporated in 1881. The railroad is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited (TSX: CP, NYSE: CP), which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001.
Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, it owns approximately 23,000 kilometres (14,000 mi) of track all across Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves major cities in the United States, such as Minneapolis, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and New York City.
The railway was originally built between Eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a promise extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871. It was Canada's first transcontinental railway, but currently does not reach the Atlantic coast. Primarily a freight railway, the CPR was for decades the only practical means of long-distance passenger transport in most regions of Canada, and was instrumental in the settlement and development of Western Canada. The CP became one of the largest and most powerful companies in Canada, a position it held as late as 1975. Its primary passenger services were eliminated in 1986, after being assumed by Via Rail Canada in 1978. A beaver was chosen as the railway's logo because it is the national symbol of Canada and was seen as representing the hardworking character of the company.
The company acquired two American lines in 2009: the Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad and the Iowa, Chicago and Eastern Railroad. The trackage of the ICE was at one time part of CP subsidiary Soo Line and predecessor line The Milwaukee Road. The combined DME/ICE system spanned North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Nebraska and Iowa, as well as two short stretches into two other states, which included a line to Kansas City, Missouri, and a line to Chicago, Illinois, and regulatory approval to build a line into the Powder River Basin of Wyoming. It is publicly traded on both the Toronto Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker CP. Its U.S. headquarters are in Minneapolis.
After close of markets on November 17, 2015, CP announced an offer to purchase all outstanding shares of Norfolk Southern Railway, at a price in excess of the US$26 billion capitalization of the United States-based railway. If completed, this merger of the second and fourth oldest Class I railroads in North America would have formed the largest single railway company on that continent, reaching from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast to the Gulf Coast. The merger effort was abandoned by Canadian Pacific on April 11, 2016, after three offers were rejected by the Norfolk Southern board.
Read more on Wikipedia and on Canadian Pacific official website.
Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, it owns approximately 23,000 kilometres (14,000 mi) of track all across Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves major cities in the United States, such as Minneapolis, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and New York City.
The railway was originally built between Eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a promise extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871. It was Canada's first transcontinental railway, but currently does not reach the Atlantic coast. Primarily a freight railway, the CPR was for decades the only practical means of long-distance passenger transport in most regions of Canada, and was instrumental in the settlement and development of Western Canada. The CP became one of the largest and most powerful companies in Canada, a position it held as late as 1975. Its primary passenger services were eliminated in 1986, after being assumed by Via Rail Canada in 1978. A beaver was chosen as the railway's logo because it is the national symbol of Canada and was seen as representing the hardworking character of the company.
The company acquired two American lines in 2009: the Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad and the Iowa, Chicago and Eastern Railroad. The trackage of the ICE was at one time part of CP subsidiary Soo Line and predecessor line The Milwaukee Road. The combined DME/ICE system spanned North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Nebraska and Iowa, as well as two short stretches into two other states, which included a line to Kansas City, Missouri, and a line to Chicago, Illinois, and regulatory approval to build a line into the Powder River Basin of Wyoming. It is publicly traded on both the Toronto Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker CP. Its U.S. headquarters are in Minneapolis.
After close of markets on November 17, 2015, CP announced an offer to purchase all outstanding shares of Norfolk Southern Railway, at a price in excess of the US$26 billion capitalization of the United States-based railway. If completed, this merger of the second and fourth oldest Class I railroads in North America would have formed the largest single railway company on that continent, reaching from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast to the Gulf Coast. The merger effort was abandoned by Canadian Pacific on April 11, 2016, after three offers were rejected by the Norfolk Southern board.
Read more on Wikipedia and on Canadian Pacific official website.
Brief History: Canada is a North American country stretching from the U.S. in the south to the Arctic Circle in the north. Major cities include massive Toronto, west coast film centre Vancouver, French-speaking Montréal and Québec City, and capital city Ottawa. Canada's vast swaths of wilderness include lake-filled Banff National Park in the Rocky Mountains. It's also home to Niagara Falls, a famous group of massive waterfalls.
Item created by: gdm on 2020-02-12 07:01:38. Last edited by Lethe on 2020-05-07 00:00:00
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.