Company History: BC Rail (reporting mark BCOL, BCIT), known as the British Columbia Railway between 1972 and 1984 and as the Pacific Great Eastern Railway (PGE) before 1972, was a railway that operated in the Canadian province of British Columbia between 1912 and 2004. It was a class II regional railway and the third-largest in Canada, operating 2,320 km (1,440 mi) of mainline track. Its operations were owned by the public as a crown corporation from 1918 until 2004, when the provincial government leased operations for 999 years to CN. The track and other assets, including a marine division and stevedoring subsidiary as well as large tracts of real estate, remain under public ownership. 40 km of track serving the Roberts Bank Superport that were scheduled to be sold to OmniTRAX remain under BC Rail management due to that sale being cancelled because of the transaction being tainted by an influence-peddling and bribery scandal resulting in convictions in 2010. The provincial government, which promised when originally elected to never sell the railway, has announced that the crown corporation and its remaining operations and assets would be "wound down" and taken over by various departments of the Ministry of Transportation The details of the sale/lease to CN, which are related to the OmniTRAX affair, have become the subject of protracted public inquiry as part of the proceedings of the trial surrounding a scandal known as the British Columbia Legislature Raids Affair, or "Railgate". Government leaders and civil servants involved with the arrangements to CN have refused to comment on the deal because the matter "is before the courts".
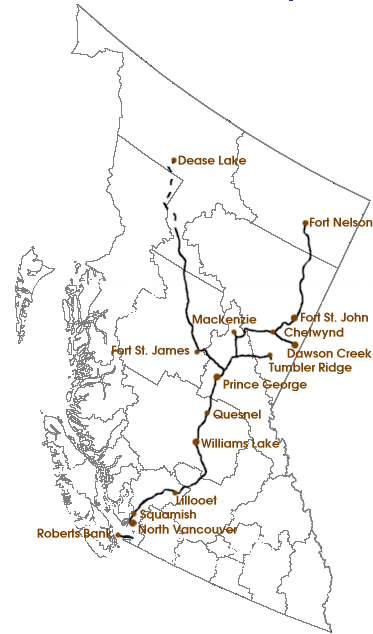
Chartered in 1912, the railway was acquired by the provincial government in 1918 after running into financial difficulties. A railway that ran "from nowhere, to nowhere" for over 30 years, neither passing through any major city nor interchanging with any other railway, its southern terminus was at Squamish and its northern terminus at Quesnel during that period. It expanded significantly between 1949 and 1984. Primarily a freight railway, it also offered passenger service, as well as some excursion services, most notably the Royal Hudson excursion train. The railway's operations only reached profitability in 1980, due to large capital and operating debts, which were intended as subsidies to develop and sustain mining and timber economies and employment in the regions it accessed, though during the 1980s it regularly posted significant profits, contributing to the public treasury significantly, and maintained a lower operating debt than any of the continent's other major railways. The railway's operations and management, as one of the province's largest crown corporations, have necessarily been at the centre of public debate since its takeover. Notably, as example, the Social Credit governments of WAC Bennett and his son Bill Bennett forgave the railways' capital debts in 1954 and 1979, respectively, with bookkeeping matters related to that bringing much criticism. The current provincial government has been accused of fabricating falsehoods about the state of its debts and viability in order to justify the deal with CN, claiming the railway was in disarray. Other participants in the bidding process withdrew their bids, saying that CN had unfair access to confidential information about their own operations, provided by the government, and at least one bidder (Canadian Pacific) privately stated in since-released communications that the bid was "rigged". Controversy over CN's management of the line has focused on layoffs, toxic spills and other safety concerns, and cuts in service to some regions. The line has generated profits for CN in the range of $25 million per year since its takeover of the railway's operations.
Chartered in 1912, the railway was acquired by the provincial government in 1918 after running into financial difficulties. A railway that ran "from nowhere, to nowhere" for over 30 years, neither passing through any major city nor interchanging with any other railway, its southern terminus was at Squamish and its northern terminus at Quesnel during that period. It expanded significantly between 1949 and 1984. Primarily a freight railway, it also offered passenger service, as well as some excursion services, most notably the Royal Hudson excursion train. The railway's operations only reached profitability in 1980, due to large capital and operating debts, which were intended as subsidies to develop and sustain mining and timber economies and employment in the regions it accessed, though during the 1980s it regularly posted significant profits, contributing to the public treasury significantly, and maintained a lower operating debt than any of the continent's other major railways. The railway's operations and management, as one of the province's largest crown corporations, have necessarily been at the centre of public debate since its takeover. Notably, as example, the Social Credit governments of WAC Bennett and his son Bill Bennett forgave the railways' capital debts in 1954 and 1979, respectively, with bookkeeping matters related to that bringing much criticism. The current provincial government has been accused of fabricating falsehoods about the state of its debts and viability in order to justify the deal with CN, claiming the railway was in disarray. Other participants in the bidding process withdrew their bids, saying that CN had unfair access to confidential information about their own operations, provided by the government, and at least one bidder (Canadian Pacific) privately stated in since-released communications that the bid was "rigged". Controversy over CN's management of the line has focused on layoffs, toxic spills and other safety concerns, and cuts in service to some regions. The line has generated profits for CN in the range of $25 million per year since its takeover of the railway's operations.
Successor/Parent History: The Canadian National Railway Company (reporting mark CN) is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec that serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad". CN is a public company with 24,000 employees. It had a market capitalization of 32 billion CAD in 2011. CN was government-owned, having been a Canadian Crown corporation from its founding to its privatization in 1995. Bill Gates was, in 2011, the largest single shareholder of CN stock.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brief History: Canada is a North American country stretching from the U.S. in the south to the Arctic Circle in the north. Major cities include massive Toronto, west coast film centre Vancouver, French-speaking Montréal and Québec City, and capital city Ottawa. Canada's vast swaths of wilderness include lake-filled Banff National Park in the Rocky Mountains. It's also home to Niagara Falls, a famous group of massive waterfalls.
Item Links: We found: 4 different collections associated with BC Rail - Railroad
- Collection N Scale Model Trains: 383 different items.
- Collection Transportation Companies: 2 different items.
- Collection Z Scale Trains: 20 different items.
- Collection HO Scale Model Trains: 21 different items.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-10-10 09:54:23. Last edited by Powderman on 2024-01-10 14:15:42
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.