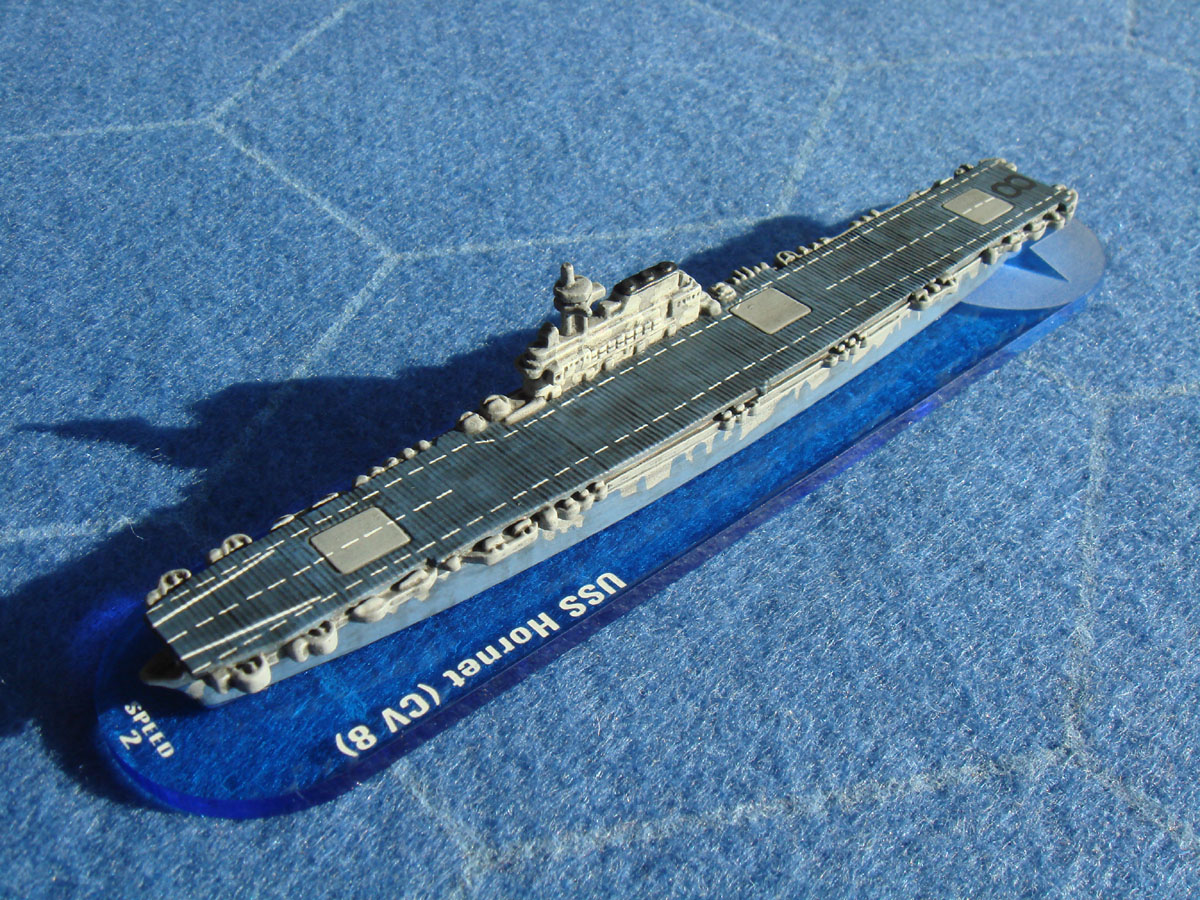
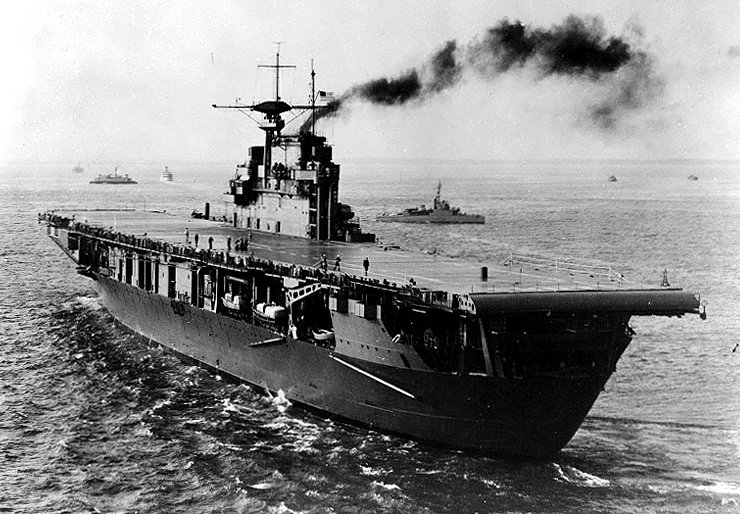
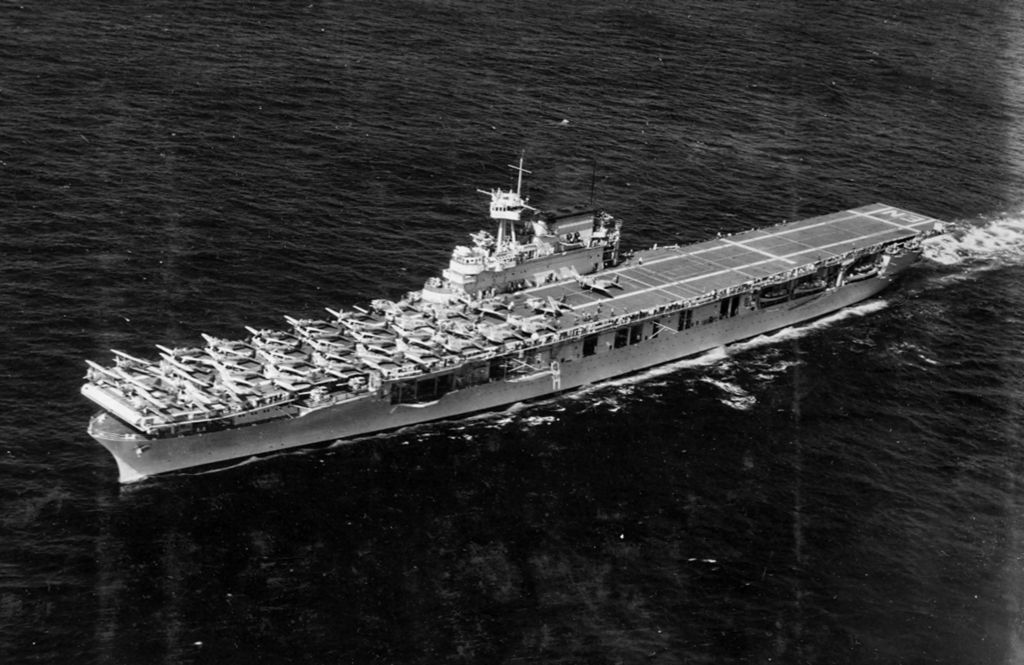
Prototype: USS Hornet (CV-8), the seventh ship to carry the name Hornet, was a Yorktown-class aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. During World War II in the Pacific Theater, she launched the Doolittle Raid on Tokyo and participated in the Battle of Midway and the Buin-Faisi-Tonolai Raid. In the Solomon Islands campaign, she was involved in the capture and defense of Guadalcanal and the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands where she was irreparably damaged by enemy torpedo and dive bombers. Faced with an approaching Japanese surface force, Hornet was abandoned and later torpedoed and sunk by approaching Japanese destroyers. Hornet was in service for a year and six days and was the last US fleet carrier ever sunk by enemy fire. For these actions, she was awarded four service stars, a citation for the Doolittle Raid in 1942, and her Torpedo Squadron 8 received a Presidential Unit Citation for extraordinary heroism for the Battle of Midway. Her wreck was located in late January 2019 near the Solomon Islands.
Class History: The Yorktown class was a class of three aircraft carriers built by the U.S. and completed shortly before World War II. They immediately followed the Ranger, the first U.S. aircraft carrier built as such, and benefited in design from experience with the Ranger and the earlier Lexington class. These ships bore the brunt of early action in the Pacific War, and two of the three were lost: Yorktown, sunk at the Battle of Midway, and Hornet, sunk in the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands. Enterprise, the sole survivor of the class, became the most decorated ship in the history of the U.S. Navy. After efforts to save her as a museum ship failed, she was scrapped in 1960
The lessons learned from operations with the large converted battlecruiser Lexington class in comparison with the smaller purpose-built Ranger had taught the Navy that large carriers were more flexible in operational terms and were more survivable than smaller ones. As the result of this experience, the U.S. Navy built Yorktown (CV-5) and Enterprise (CV-6), commissioned in 1937 and 1938 respectively. These were fast and versatile carriers able to carry and operate over 80 warplanes which was almost as many as the much larger Lexington class.
With the addition of the 14,700 ton USS Wasp (CV-7), a scaled down version of the class, the U.S. Navy used up its full 135,000 ton Washington Naval Treaty limit of aircraft carrier tonnage. The abandonment of the arms limitation treaties system in 1937 allowed the US to begin building more carriers, and the first of this new carrier program was Hornet (CV-8), another of the class, commissioned in 1941. Improvements to the Yorktown design and freedom from the Washington Treaty limitations brought about the Essex-class carriers.
Like the earlier ships of the Lexington-class, the Yorktowns carried a seldom used catapult on the hangar deck level. This catapult was subsequently eliminated from U.S. carriers as it was relatively useless in operation. The hangar deck catapult was removed from Enterprise and Hornet in late June 1942. All three ships of the Yorktown class were built at the Newport News Shipbuilding Company, Newport News, Virginia.
The lessons learned from operations with the large converted battlecruiser Lexington class in comparison with the smaller purpose-built Ranger had taught the Navy that large carriers were more flexible in operational terms and were more survivable than smaller ones. As the result of this experience, the U.S. Navy built Yorktown (CV-5) and Enterprise (CV-6), commissioned in 1937 and 1938 respectively. These were fast and versatile carriers able to carry and operate over 80 warplanes which was almost as many as the much larger Lexington class.
With the addition of the 14,700 ton USS Wasp (CV-7), a scaled down version of the class, the U.S. Navy used up its full 135,000 ton Washington Naval Treaty limit of aircraft carrier tonnage. The abandonment of the arms limitation treaties system in 1937 allowed the US to begin building more carriers, and the first of this new carrier program was Hornet (CV-8), another of the class, commissioned in 1941. Improvements to the Yorktown design and freedom from the Washington Treaty limitations brought about the Essex-class carriers.
Like the earlier ships of the Lexington-class, the Yorktowns carried a seldom used catapult on the hangar deck level. This catapult was subsequently eliminated from U.S. carriers as it was relatively useless in operation. The hangar deck catapult was removed from Enterprise and Hornet in late June 1942. All three ships of the Yorktown class were built at the Newport News Shipbuilding Company, Newport News, Virginia.
Country: The U.S. is a country of 50 states covering a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. Major Atlantic Coast cities are New York, a global finance and culture center, and capital Washington, DC. Midwestern metropolis Chicago is known for influential architecture and on the west coast, Los Angeles' Hollywood is famed for filmmaking.
Item created by: Lethe on 2015-05-31 17:46:30. Last edited by gdm on 2019-04-19 17:56:44
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.