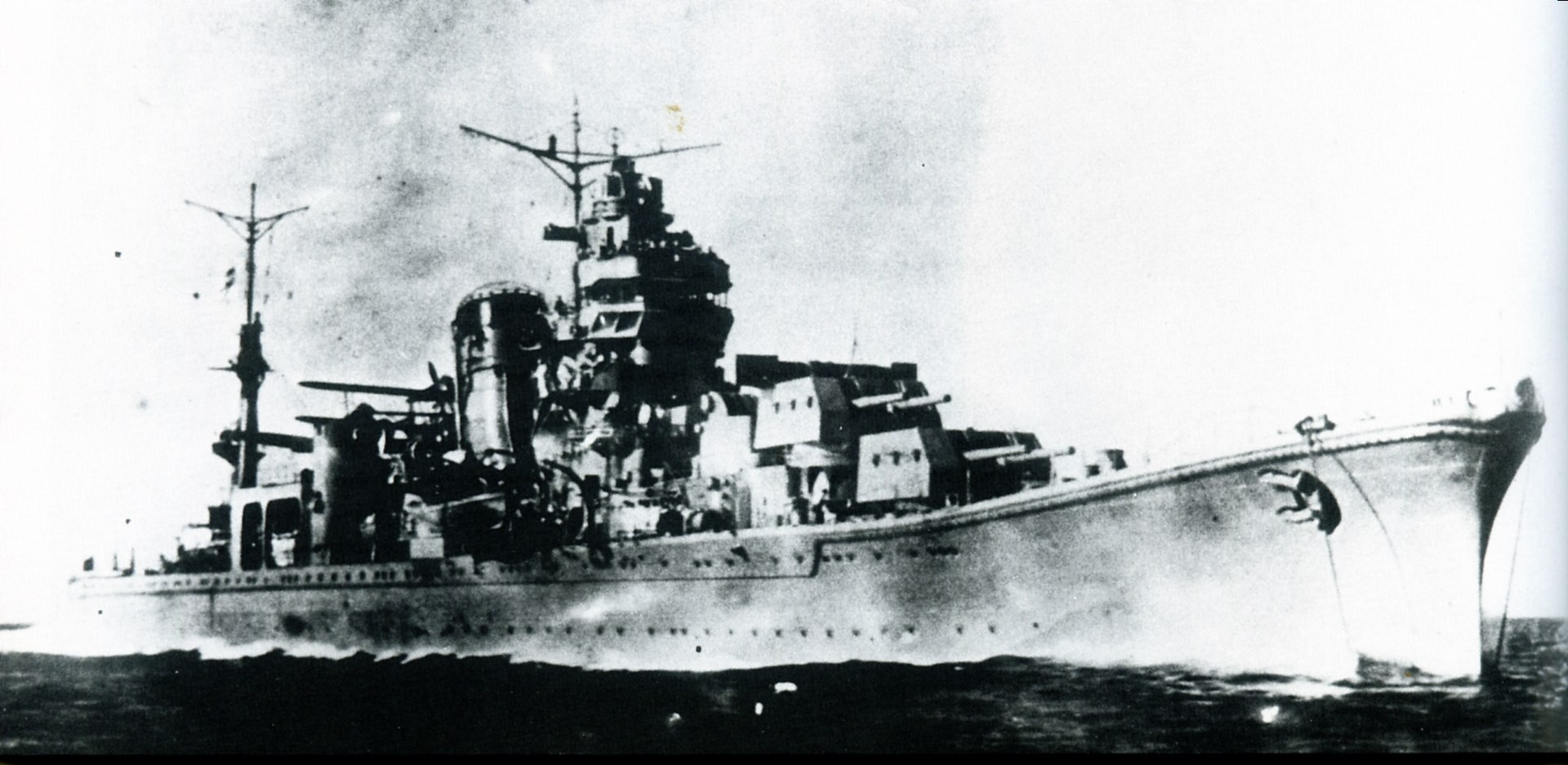
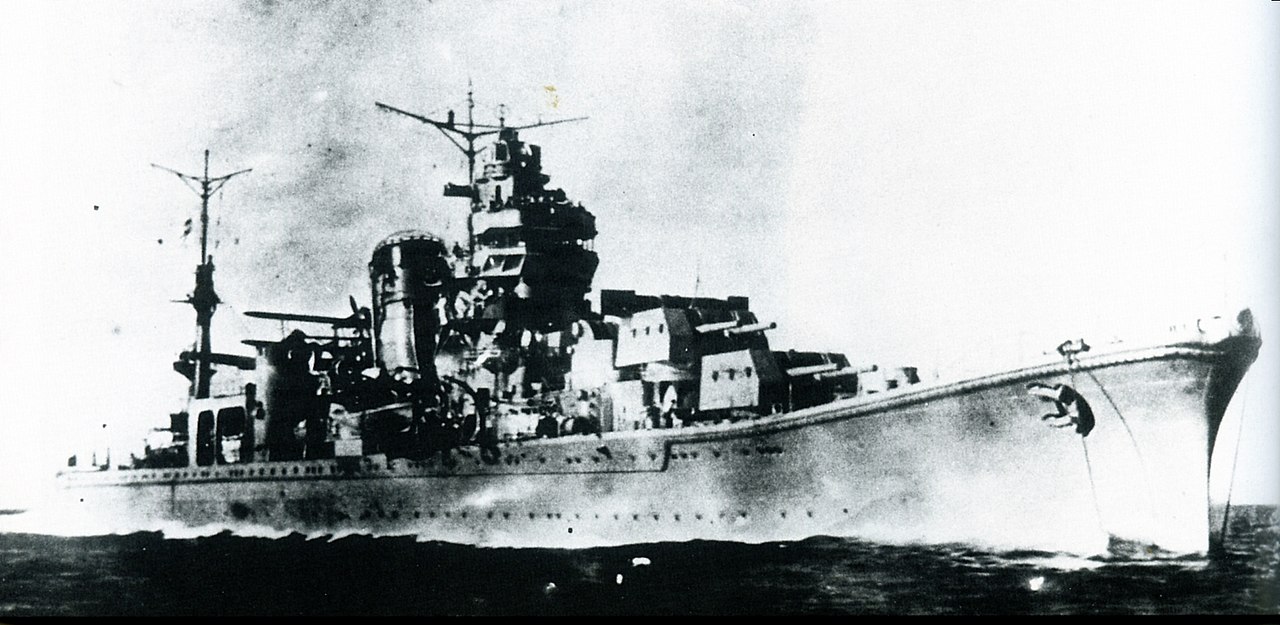
Prototype: Agano (阿賀野) was the lead ship of her class of four light cruisers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. Completed in 1942, she escorted a troop convoy to New Guinea in December. In early 1943 the ship participated in Operation Ke, the evacuation of Japanese troops from Guadalcanal. Six months later Agano transported troops and supplies to New Guinea and she played a minor role in the Battle of Empress Augusta Bay in early November. A few weeks later, the ship was badly damaged by American airstrikes and she sailed for Truk under her own power the following day. While en route, Agano was torpedoed by an American submarine and had to be towed to her destination. After several months of repairs, she left for Japan, but was intercepted and sunk by another American submarine in February 1944. Most of her crew was rescued by her escorting destroyer, but that ship was sunk with the loss of most of her crew and all of Agano's survivors by an American airstrike the following day.
Class History: The Agano class was a set of four light cruisers operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. All were named after Japanese rivers. Larger than these previous Japanese light cruisers, the Agano-class vessels were fast, but with little protection, and were under-gunned for their size. They participated in numerous actions during World War II.
The Imperial Japanese Navy had developed a standardized design for light cruisers as flagships for destroyer and submarine squadrons, based on a 5,500 ton displacement, shortly after World War I. However, by the 1930s these vessels were obsolete, as contemporary destroyers were faster, carried more powerful armament, and had greater endurance. As soon as the restrictions of the London Naval Treaty were removed, the Navy General Staff developed a plan within the Fourth Fleet Supplemental Budget to build 13 new 6000 ton cruisers between 1939 and 1945 to replace the Tenryu-class cruiser, Kuma-class cruiser, and Nagara-class cruiser. These vessels were intended to be the flagships for six destroyer squadrons and seven submarine squadrons. The new design was finalized in October 1937; however, construction was delayed due to overloading of the Japanese shipyards. Construction costs came to 16.4 million yen per vessel.
The Imperial Japanese Navy had developed a standardized design for light cruisers as flagships for destroyer and submarine squadrons, based on a 5,500 ton displacement, shortly after World War I. However, by the 1930s these vessels were obsolete, as contemporary destroyers were faster, carried more powerful armament, and had greater endurance. As soon as the restrictions of the London Naval Treaty were removed, the Navy General Staff developed a plan within the Fourth Fleet Supplemental Budget to build 13 new 6000 ton cruisers between 1939 and 1945 to replace the Tenryu-class cruiser, Kuma-class cruiser, and Nagara-class cruiser. These vessels were intended to be the flagships for six destroyer squadrons and seven submarine squadrons. The new design was finalized in October 1937; however, construction was delayed due to overloading of the Japanese shipyards. Construction costs came to 16.4 million yen per vessel.
Country: Japan is an island nation in the Pacific Ocean with dense cities, imperial palaces, mountainous national parks and thousands of shrines and temples. Shinkansen bullet trains connect the main islands of Kyushu (with Okinawa's subtropical beaches), Honshu (home to Tokyo and Hiroshima’s atomic-bomb memorial) and Hokkaido (famous for skiing). Tokyo, the capital, is known for skyscrapers, shopping and pop culture.
Although legend has it that Japan was founded in 660BC, archaeologists agree that settlement in the Japanese archpelago dates back as far as 100,000 years. The Jomon Period (8000-c.300BC) is the earliest that has been studied. It is named after the 'jomon' or cord-marked pattern style of pottery of the period.
Although legend has it that Japan was founded in 660BC, archaeologists agree that settlement in the Japanese archpelago dates back as far as 100,000 years. The Jomon Period (8000-c.300BC) is the earliest that has been studied. It is named after the 'jomon' or cord-marked pattern style of pottery of the period.
Item created by: Lethe on 2015-05-31 17:46:30. Last edited by gdm on 2020-01-25 17:13:02
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.