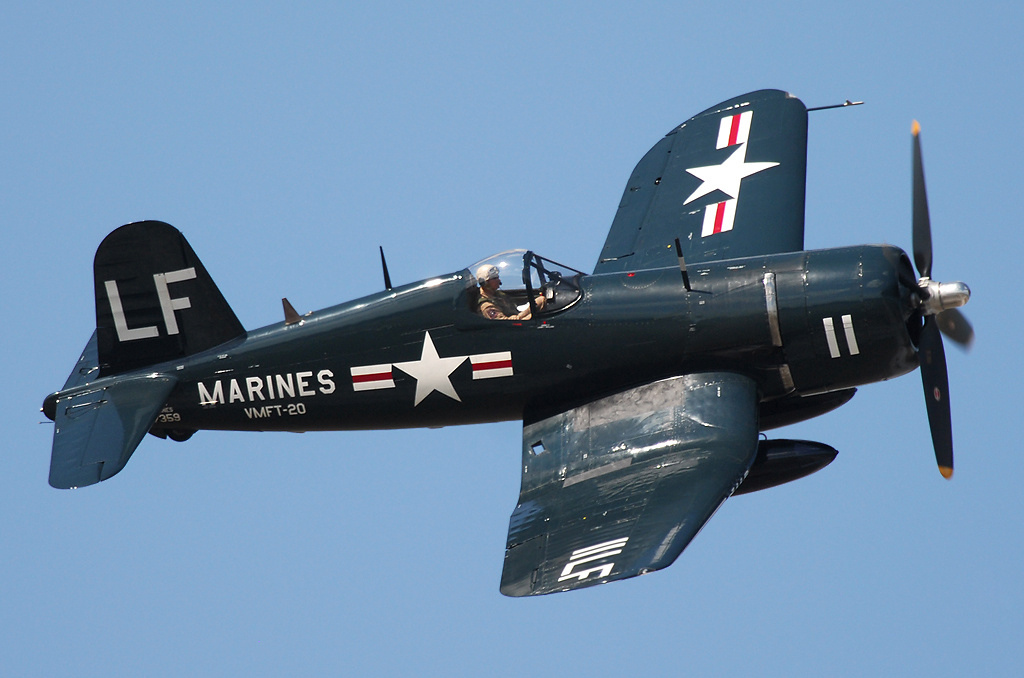
Aircraft History: The Vought F4U Corsair is an American fighter aircraft that saw service primarily in World War II and the Korean War. Designed and initially manufactured by Chance Vought, the Corsair was soon in great demand; additional production contracts were given to Goodyear, whose Corsairs were designated FG, and Brewster, designated F3A.
The Corsair was designed and operated as a carrier-based aircraft, and entered service in large numbers with the U.S. Navy in late 1944 and early 1945. It quickly became one of the most capable carrier-based fighter-bombers of World War II. Some Japanese pilots regarded it as the most formidable American fighter of World War II, and its naval aviators achieved an 11:1 kill ratio. Yet early problems with carrier landings and logistics allowed it to be eclipsed as the dominant carrier-based fighter by the Grumman F6F Hellcat, powered by the same Double Wasp engine first flown on the Corsair's first prototype in 1940.
Instead, the Corsair came to and retained prominence in its area of greatest deployment: land-based use by the U.S. Marines. The Corsair served almost exclusively as a fighter-bomber throughout the Korean War and during the French colonial wars in Indochina and Algeria.[7] In addition to its use by the U.S. and British, the Corsair was also used by the Royal New Zealand Air Force, French Naval Aviation, and other air forces until the 1960s. From the first prototype delivery to the U.S. Navy in 1940, to final delivery in 1953 to the French, 12,571 F4U Corsairs were manufactured[8] in 16 separate models. Its 1942–53 production run was the longest of any U.S. piston-engined fighter.
The Corsair was designed and operated as a carrier-based aircraft, and entered service in large numbers with the U.S. Navy in late 1944 and early 1945. It quickly became one of the most capable carrier-based fighter-bombers of World War II. Some Japanese pilots regarded it as the most formidable American fighter of World War II, and its naval aviators achieved an 11:1 kill ratio. Yet early problems with carrier landings and logistics allowed it to be eclipsed as the dominant carrier-based fighter by the Grumman F6F Hellcat, powered by the same Double Wasp engine first flown on the Corsair's first prototype in 1940.
Instead, the Corsair came to and retained prominence in its area of greatest deployment: land-based use by the U.S. Marines. The Corsair served almost exclusively as a fighter-bomber throughout the Korean War and during the French colonial wars in Indochina and Algeria.[7] In addition to its use by the U.S. and British, the Corsair was also used by the Royal New Zealand Air Force, French Naval Aviation, and other air forces until the 1960s. From the first prototype delivery to the U.S. Navy in 1940, to final delivery in 1953 to the French, 12,571 F4U Corsairs were manufactured[8] in 16 separate models. Its 1942–53 production run was the longest of any U.S. piston-engined fighter.
Manufacturer: Vought is the name of several related American aerospace firms. These have included, in the past, Lewis and Vought Corporation, Chance Vought, Vought-Sikorsky, LTV Aerospace (part of Ling-Temco-Vought), Vought Aircraft Companies, and the current Vought Aircraft Industries. The first incarnation of Vought was established by Chance M. Vought and Birdseye Lewis in 1917. In 1928, it was acquired by United Aircraft and Transport Corporation, which a few years later became United Aircraft Corporation; this was the first of many reorganizations and buyouts. During the 1920s and 1930s, Vought Aircraft and Chance Vought specialized in carrier-based aircraft for the United States Navy, by far its biggest customer. Chance Vought produced thousands of planes during World War II, including the F4U Corsair. Vought became independent again in 1954, and was purchased by Ling-Temco-Vought in 1961. The company designed and produced a variety of planes and missiles throughout the Cold War. Vought was sold from LTV and owned in various degrees by the Carlyle Group and Northrop Grumman in the early 1990s. It was then fully bought by Carlyle, renamed Vought Aircraft Industries, with headquarters in Dallas, Texas. In June 2010, the Carlyle Group sold Vought to the Triumph Group.
Country: The U.S. is a country of 50 states covering a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. Major Atlantic Coast cities are New York, a global finance and culture center, and capital Washington, DC. Midwestern metropolis Chicago is known for influential architecture and on the west coast, Los Angeles' Hollywood is famed for filmmaking.
Item created by: Lethe on 2015-05-31 17:46:30. Last edited by gdm on 2020-12-10 15:04:08
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.