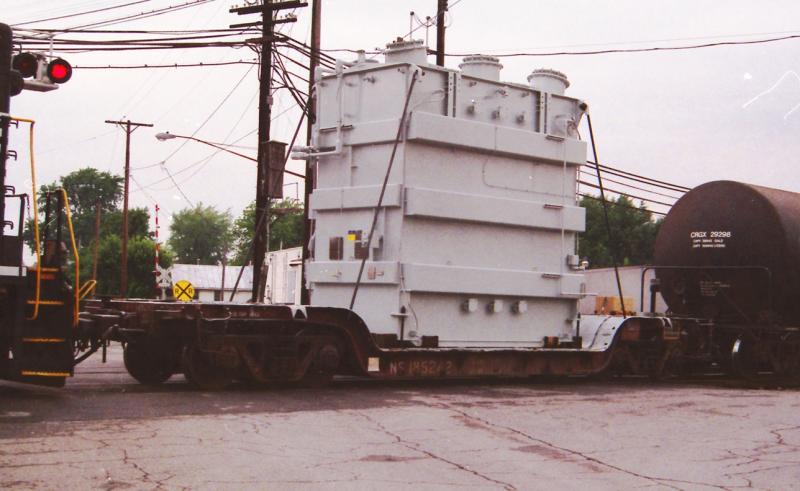
Specific Item Information: This depressed center flat car with Buckeye trucks had a 250,000-pound capacity and was 65’ in length. St. Louis Southwestern, commonly known as Cotton Belt, was founded in 1891 and became a Southern Pacific subsidiary in 1932, before eventually fully merging in 1992. It is now a heritage component of Union Pacific.
Model Information: This model was first released by Micro-Trains in February of 2001. It is somewhat different from most MTL toolings in that 1) Most of the body is die-cast metal as opposed to injection-molded plastic and 2) The car runs on 3-Axle freight trucks (Buckeye). Some releases of this model come with loads. Typically these loads need to be assembled and/or painted by the customer. The loads typically represent large and/or heavy items that would be too cumbersome or heavy to be transported by a traditional 50' fishbelly flatcar. Examples of these loads are include: heavy transformers, pipes, girders and large vehicles. The depressed center was specifically designed to make sure the load would be able to make it through standard-height tunnels. Although most fo the body is made from a die-cast metal frame, the ends of the main platform are made from plastic which snaps on to the metal underframe.
Prototype History: A flatcar (US) (also flat car (US) or flat wagon (UIC)) is a piece of railroad (US) or railway (non-US) rolling stock that consists of an open, flat deck mounted on a pair of trucks (US) or bogies (UK), one at each end containing four or six wheels. Occasionally, flat cars designed to carry extra heavy or extra large loads are mounted on a pair (or rarely, more) of bogeys under each end . The deck of the car can be wood or steel, and the sides of the deck can include pockets for stakes or tie-down points to secure loads. Flatcars designed for carrying machinery have sliding chain assemblies recessed in the deck.
Depressed center flat cars are of a special construction having the portion of floor extending between trucks depressed to provide necessary overhead clearance for lading. When large and heavy loads need to be moved long distances railroads are often the best choice for the job. These loads are often tall enough that they wouldn't pass safely under bridges or other obstacles if carried on conventional flat cars. To provide extra clearance, railroads use heavy-duty, depressed center flat cars. The lower center deck provides several inches of extra clearance, and since the cargo does not have to be lifted as high, loading and unloading is easier.
Depressed center flat cars are of a special construction having the portion of floor extending between trucks depressed to provide necessary overhead clearance for lading. When large and heavy loads need to be moved long distances railroads are often the best choice for the job. These loads are often tall enough that they wouldn't pass safely under bridges or other obstacles if carried on conventional flat cars. To provide extra clearance, railroads use heavy-duty, depressed center flat cars. The lower center deck provides several inches of extra clearance, and since the cargo does not have to be lifted as high, loading and unloading is easier.
Road Name History: The St. Louis Southwestern Railway (reporting mark SSW), known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply Cotton Belt, is a former US Class I railroad which operated between St. Louis, Missouri, and various points in the states of Arkansas and Texas from 1891 to 1992.
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
The Cotton Belt was one of the lines comprising the railroad empire acquired by financier Jay Gould in the last quarter of the 19th century; according to the Handbook of Texas, By 1890 Gould owned the Missouri Pacific, the Texas and Pacific, the St. Louis Southwestern, and the International-Great Northern, one-half of the mileage in the Southwest.
The railroad was organized on January 15, 1891, although it had its origins in a series of short lines founded in Tyler, Texas, in 1870 that connected northeastern Texas to Arkansas and southeastern Missouri. Construction of the original Tyler Tap Railroad began in the summer of 1875.
On October 18, 1903, the Cotton Belt gained trackage rights via the Thebes Bridge and the Missouri Pacific Railroad along the eastern shore of the Mississippi River to reach East St. Louis, Illinois, and then used Terminal Railroad Association trackage rights into St. Louis. The Cotton Belt also operated a yard and a locomotive servicing facility in East St. Louis, just east of Valley Junction, and south of Alton and Southern Railroad's Gateway Yard, and north of Kansas City Southern's East St. Louis Yard. They also had a freight station in downtown St. Louis. Union Pacific Railroad now operates the yard (still named "Cotton Belt Yard"), but the engine servicing facilities have been demolished.
The Cotton Belt and subsidiary St. Louis Southwestern Railway of Texas together operated 1,607 miles of road in 1945; 1,555 miles in 1965; and 2,115 miles in 1981 after taking over the Rock Island's Golden State Route. In 1925 SSW and SSW of Texas reported a total of 1474 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 75 million passenger-miles; in 1970 it carried 8650 million ton-miles and no passengers.
The Southern Pacific Company gained Interstate Commerce Commission approval to control the Cotton Belt system on April 14, 1932, but continued to operate it as a separate company until 1992, when the SP consolidated the Cotton Belt's operations into the parent company. Cotton Belt diesel locomotives from 1959 on were painted in Southern Pacific's "bloody nose" scheme - dark gray locomotive body with a red "winged" nose. "Cotton Belt" was painted on the sides and in later years the letters "SSW" were painted on the nose.
In 1996 the Union Pacific Railroad finished the acquisition that was effectively begun almost a century before with the purchase of the Southern Pacific by UP in 1901, until divestiture was ordered in 1913. The merged company retains the name "Union Pacific" for all railroad operations. Many former SSW locomotives are used by Union Pacific today, although few still sport unmodified "Cotton Belt" paint. Most of the remaining units have been repainted into the UP scheme, while others wear patched SSW paint with a UP shield logo and new numbers applied over the SSW number.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Micro-Trains is the brand name used by both Kadee Quality Products and Micro-Trains Line. For a history of the relationship between the brand and the two companies, please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide.
Manufacturer Information:  Micro-Trains Line split off from Kadee Quality Products in 1990. Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
Micro-Trains Line split off from Kadee Quality Products in 1990. Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
Micro-Trains Line Co. split off from Kadee in 1990 to form a completely independent company. For this reason, products from this company can appear with labels from both enterprises. Due to the nature of production idiosyncrasies and various random factors, the rolling stock from Micro-Trains can have all sorts of interesting variations in both their packaging as well as the products themselves. When acquiring an MTL product it is very important to understand these important production variations that can greatly enhance (or decrease) the value of your purchase.
Please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide

Micro-Trains Line Co. split off from Kadee in 1990 to form a completely independent company. For this reason, products from this company can appear with labels from both enterprises. Due to the nature of production idiosyncrasies and various random factors, the rolling stock from Micro-Trains can have all sorts of interesting variations in both their packaging as well as the products themselves. When acquiring an MTL product it is very important to understand these important production variations that can greatly enhance (or decrease) the value of your purchase.
Please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide
Item created by: CMK on 2023-09-02 04:47:59. Last edited by grothe77 on 2023-09-18 10:59:45
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.