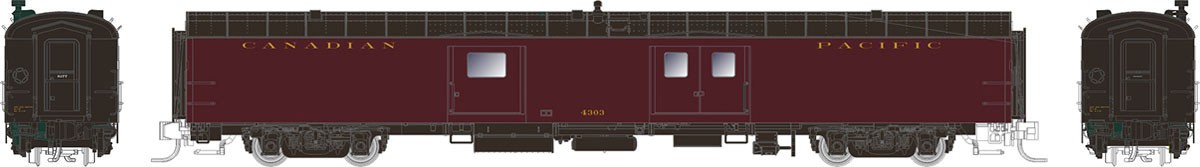
Specific Item Information: Road Numbers: 15338 & 15412
Model Information: This model represents the standard 1937 AAR 40´ Box Car. It is offered with Murphy raised panel roof, both Youngstown and Superior doors and the most common 4-5 Dreadnaught ends. AZL also offer the correct choice of wooden and etched steel running boards. This enables AZL to offer a very prototypical Box Car.
Some small notes on freight cars in general. Trucks used to be bolted together and that was outlawed by A.R.A. / A.A.R. for good reasons. A maintenance nightmare since they could come apart. Replaced by solid frame trucks they also saw a change as A.A.R. made roller bearings mandatory in the early 1950s.
Other developmental changes effected the running boards. They were probably all wooden to start with. Wood was more slippery than steel, so wood was banned in 1944. In the 1950s running boards and side ladders were outlawed as well. That is why the 1930´s Box Cars lived long with updates through their operational lives. By 1970 these Box Cars could not be found on Class 1 railroads any longer.
Some small notes on freight cars in general. Trucks used to be bolted together and that was outlawed by A.R.A. / A.A.R. for good reasons. A maintenance nightmare since they could come apart. Replaced by solid frame trucks they also saw a change as A.A.R. made roller bearings mandatory in the early 1950s.
Other developmental changes effected the running boards. They were probably all wooden to start with. Wood was more slippery than steel, so wood was banned in 1944. In the 1950s running boards and side ladders were outlawed as well. That is why the 1930´s Box Cars lived long with updates through their operational lives. By 1970 these Box Cars could not be found on Class 1 railroads any longer.
Prototype History: The Association of American Railroads had been establishing design standards for freight cars since the early part of the century. Each new design standard meant higher capacity, lighter, more durable cars. The 1937 standard 40' box car featured an interior height of 10'. Just prior to America's entry into the war, there was a push for an even larger interior height for the AAR standard. The first cars that would eventually be termed 1944 AAR, were actually built in 1941 but the war delayed its declaration as the standard. The new taller cars required a new design of end. Corrugated metal ends had been used since the days when wood side cars dominated for a very good reason, shifting loads would burst through wooden ends during sudden starts and stops! These corrugated panels were stamped in two sections, split horizontally down the middle. The 1937 standard had 5 ribs on one half and 4 ribs on the other -- creating what is called a 5-4 Dreadnaught end. The slightly taller 1944 model required something a little different. The lower panel has 4 ribs while the upper panel has 3 then a space and a final rectangular rib at the top. Called a 4-3-1 (or R-3-4) Improved Dreadnaught end, this design would dominate new box car construction for years.
Road Name History:  The New York, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad (reporting mark NKP), abbreviated NYC&St.L, was a railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. Commonly referred to as the Nickel Plate Road, the railroad served a large area, including trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois and Missouri. Its primary connections included Buffalo, Chicago, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Indianapolis, St. Louis, and Toledo.
The New York, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad (reporting mark NKP), abbreviated NYC&St.L, was a railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. Commonly referred to as the Nickel Plate Road, the railroad served a large area, including trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois and Missouri. Its primary connections included Buffalo, Chicago, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Indianapolis, St. Louis, and Toledo.
The Nickel Plate Railroad was constructed in 1881 along the South Shore of the Great Lakes connecting Buffalo and Chicago to compete with the Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway. In 1964 the Nickel Plate Road and several other mid-western carriers were merged into the larger Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W). The goal of the N&W expansion was to form a more competitive and successful system serving 14 states and the Canadian province of Ontario on more than 7,000 miles (11,000 km) of railroad. The profitable N&W was itself combined with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier, to form Norfolk Southern Corporation (NS) in 1982.
At the end of 1960 NKP operated 2,170 miles (3,490 km) of road on 4,009 miles (6,452 km) of track, not including the 25 miles (40 km) of Lorain & West Virginia. That year it reported 9758 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 41 million passenger-miles.
The Nickel Plate Historical and Technical Society works to preserve the memory of the Nickel Plate Road.
From WIkipedia

The Nickel Plate Railroad was constructed in 1881 along the South Shore of the Great Lakes connecting Buffalo and Chicago to compete with the Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway. In 1964 the Nickel Plate Road and several other mid-western carriers were merged into the larger Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W). The goal of the N&W expansion was to form a more competitive and successful system serving 14 states and the Canadian province of Ontario on more than 7,000 miles (11,000 km) of railroad. The profitable N&W was itself combined with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier, to form Norfolk Southern Corporation (NS) in 1982.
At the end of 1960 NKP operated 2,170 miles (3,490 km) of road on 4,009 miles (6,452 km) of track, not including the 25 miles (40 km) of Lorain & West Virginia. That year it reported 9758 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 41 million passenger-miles.
The Nickel Plate Historical and Technical Society works to preserve the memory of the Nickel Plate Road.
From WIkipedia
Brand/Importer Information: AZL is the leader in North American Z scale locomotives and rolling stock. Since 2000, AZL has released a vast variety of freight, passenger and locomotives. AZL continues to push the boundaries of Z scale with amazing details and incredible performance. No matter if you are looking to run steam, or the most modern diesels, AZL has something for you.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-06-22 17:38:25. Last edited by CNW400 on 2021-06-23 10:44:42
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.