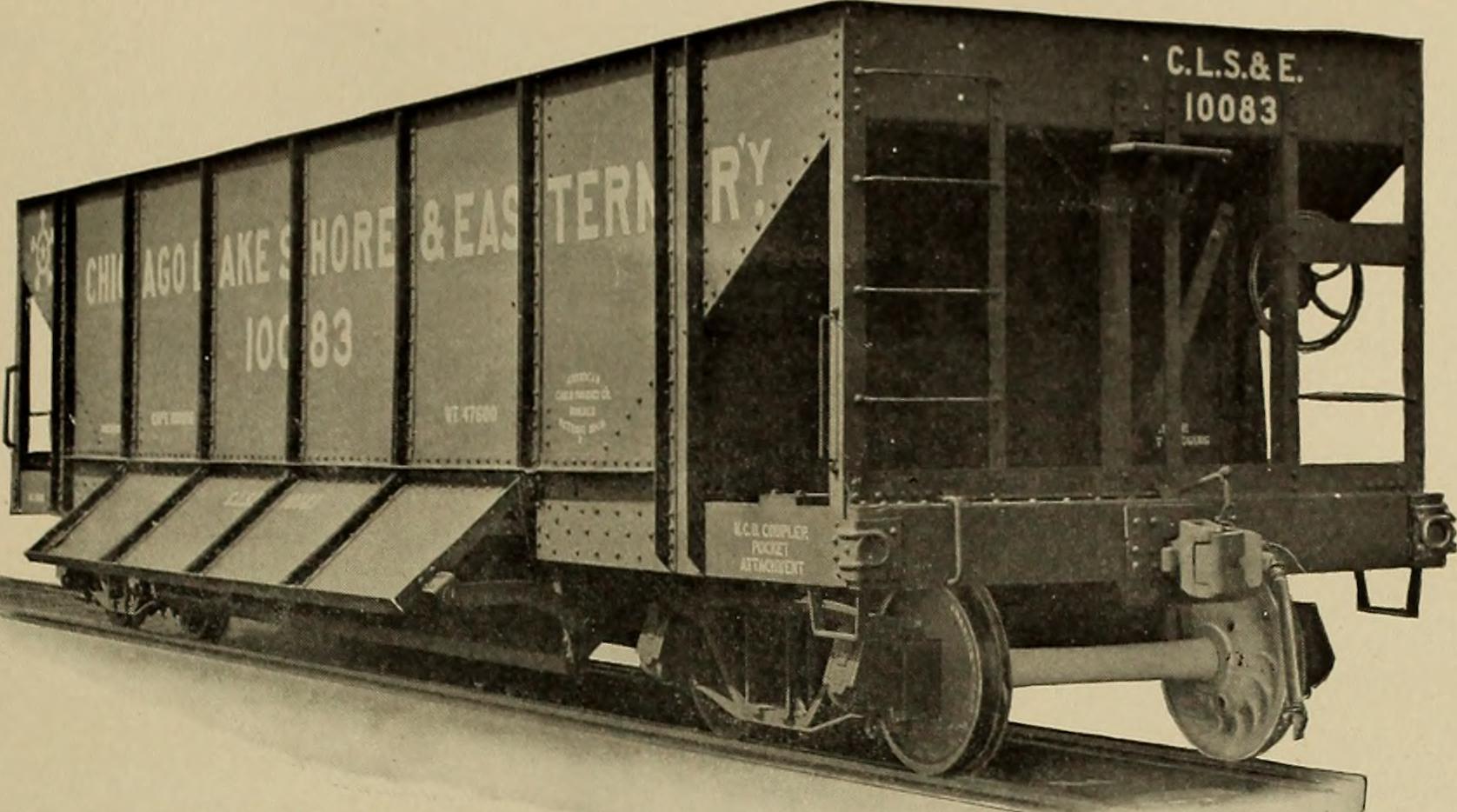
Company History: The CLS&E was established in 1897 to merge the Calumet & Blue Island Railroad with the Chicago Lake Shore & Eastern Railway Company of Indiana. It ran from Pine Junction, Indiana 8 miles to Clarke Junction, then to Illinois Steel’s South Works in South Chicago. In 1898, an 8 mile connection was built between the CLS&E and their sister road Elgin Joliet & Eastern. Operations of the EJ&E and CLS&E were combined at that point. In 1906, the line was extended to a new steel mill in Gary, Indiana. In 1908, the line west of Indiana Harbor was abandoned. The following year, the EJ&E leased the CLS&E. The CLS&E was merged into the Elgin Joliet & Eastern in 1938.
Successor/Parent History: The EJ&E dates from 1888. For most of its history, it was owned by US Steel whose Gary Works is near the east end of the line. Another company owns the mill now.
The EJ&E traces a wide arc around the Chicago area between 30 and 40 miles from the city center from Waukegan on the north, around Walker and Joliet, then east as far as Porter, Indiana. Because of this, the EJ&E was known for years as “The Chicago Outer Belt.” It also had the nickname, “The J”.
EJ&E’s two biggest missions have been moving steel and acting as a transfer road for all of Chicago’s Class 1’s and shortlines. As a result, the line was heavily trafficked with 100 locomotives required to serve just 230 route miles. In addition, EJ&E had over 10,000 freight cars, a huge fleet for a line that size.
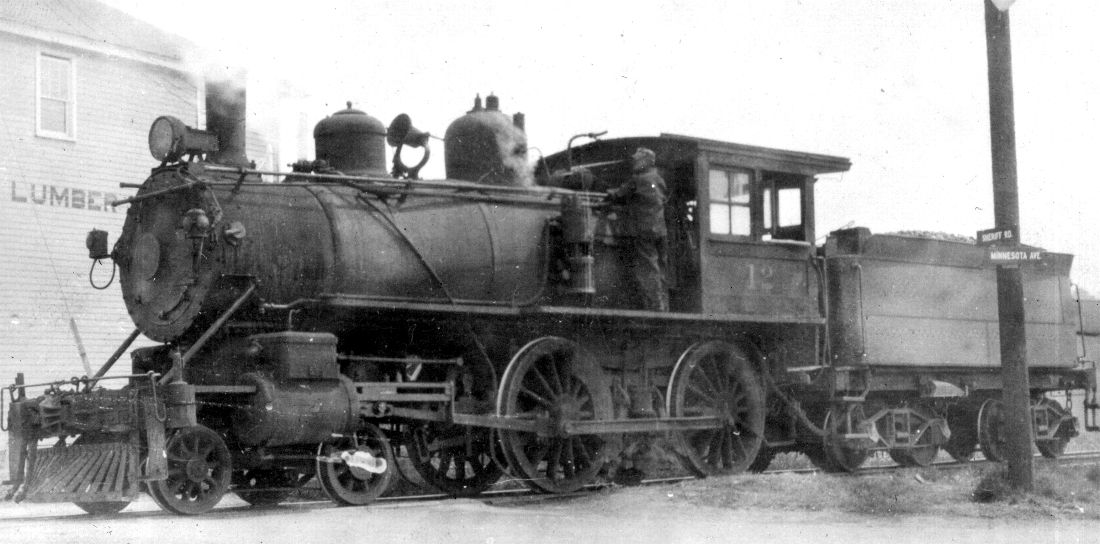
In the early diesel days, EJ&E stuck mostly with Baldwin and EMD with a few Alco RS2’s thrown in. The J had more Baldwin center cab transfer engines (DT 6-6-2000) than anyone else, in fact more than just about everyone else combined. Ballasted EMD SD7’s painted in green over orange were also used in transfer service. EMD NW2’s were the primary switchers. In 1970, the Baldwins were replaced by EMD SD38-2’s, delivered with dual controls to they could just as easily run long hood forward. By that time, EJ&E had gone to solid orange with silver trucks and fuel tanks with various striping and logo placement variations over the years. They would also toy with gold and yellow and green and yellow schemes.
In 2009 the Elgin Joliet & Eastern was acquired by Canadian National in order to link their former Wisconsin Central, Illinois Central, Chicago Central & Pacific, and Grand Trunk Western lines. These lines approached the city from different directions and had required trackage rights and terminal roads to reach each other so acquiring the EJ&E was a logical move.
The EJ&E traces a wide arc around the Chicago area between 30 and 40 miles from the city center from Waukegan on the north, around Walker and Joliet, then east as far as Porter, Indiana. Because of this, the EJ&E was known for years as “The Chicago Outer Belt.” It also had the nickname, “The J”.
EJ&E’s two biggest missions have been moving steel and acting as a transfer road for all of Chicago’s Class 1’s and shortlines. As a result, the line was heavily trafficked with 100 locomotives required to serve just 230 route miles. In addition, EJ&E had over 10,000 freight cars, a huge fleet for a line that size.
In the early diesel days, EJ&E stuck mostly with Baldwin and EMD with a few Alco RS2’s thrown in. The J had more Baldwin center cab transfer engines (DT 6-6-2000) than anyone else, in fact more than just about everyone else combined. Ballasted EMD SD7’s painted in green over orange were also used in transfer service. EMD NW2’s were the primary switchers. In 1970, the Baldwins were replaced by EMD SD38-2’s, delivered with dual controls to they could just as easily run long hood forward. By that time, EJ&E had gone to solid orange with silver trucks and fuel tanks with various striping and logo placement variations over the years. They would also toy with gold and yellow and green and yellow schemes.
In 2009 the Elgin Joliet & Eastern was acquired by Canadian National in order to link their former Wisconsin Central, Illinois Central, Chicago Central & Pacific, and Grand Trunk Western lines. These lines approached the city from different directions and had required trackage rights and terminal roads to reach each other so acquiring the EJ&E was a logical move.
Brief History: The U.S. is a country of 50 states covering a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. Major Atlantic Coast cities are New York, a global finance and culture center, and capital Washington, DC. Midwestern metropolis Chicago is known for influential architecture and on the west coast, Los Angeles' Hollywood is famed for filmmaking.
Item created by: Lethe on 2024-01-03 09:44:20
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.