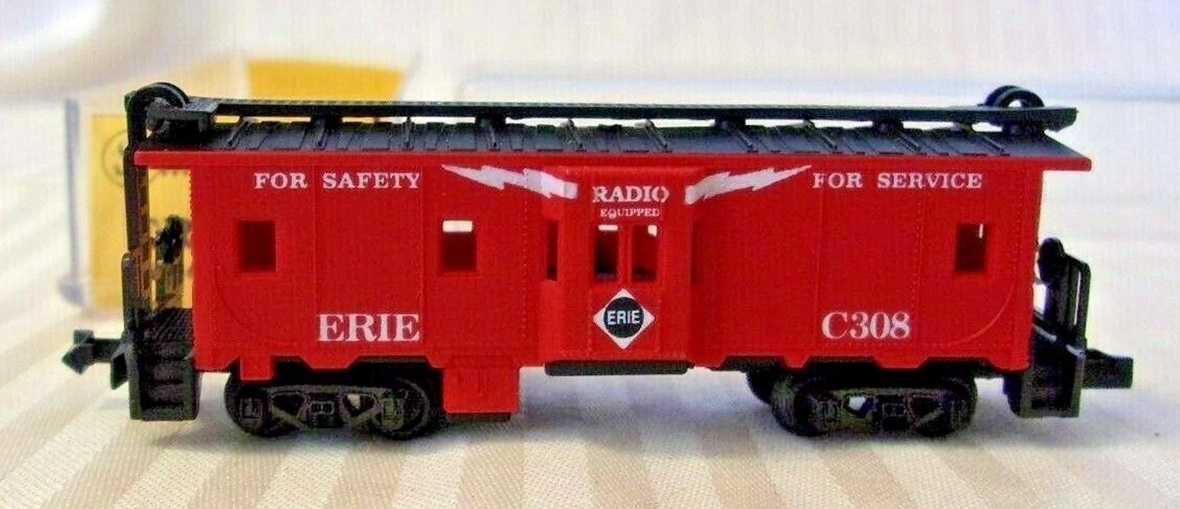
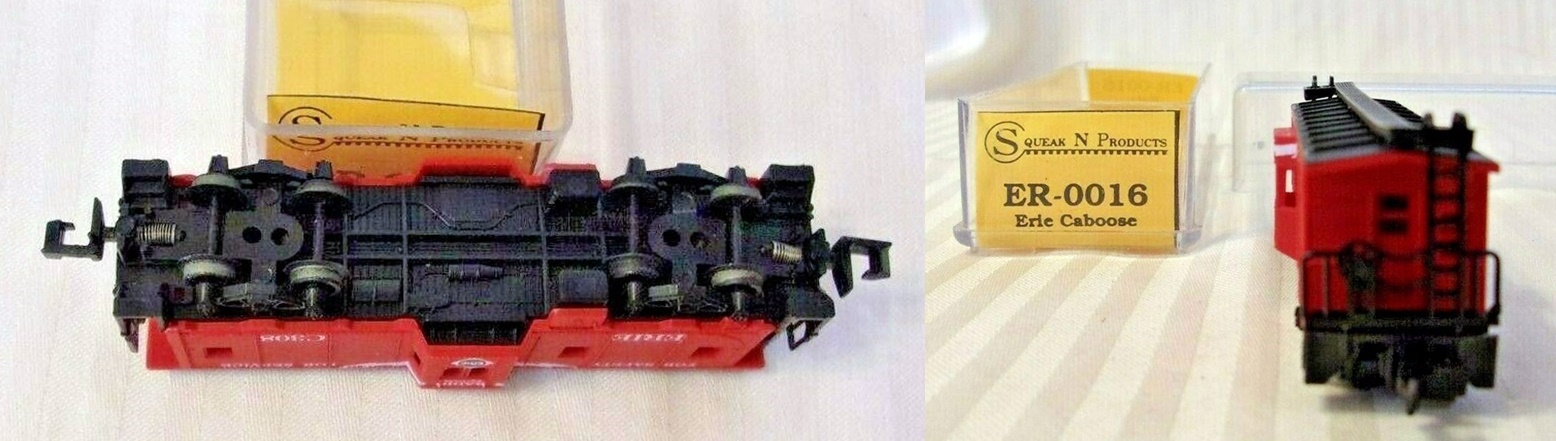
Model Information: This Model Power body style was released in the 1990s and is a Chinese knock-off of Lima's Bay Window model from the 1960s and 1970s. The only noticeable difference is that the window bays are part of the body mold, whereas with the Lima body, they were separately attached.
Prototype History: In a bay window caboose, the crew monitoring the train sits in the middle of the car in a section of wall that projects from the side of the caboose. The windows set into these extended walls resemble architectural bay windows, so the caboose type is called a bay window caboose. This type afforded a better view of the side of the train and eliminated the falling hazard of the cupola. The bay window gained favor with many railroads because it eliminated the need for additional clearances in tunnels and overpasses. On the west coast, the Milwaukee Road and the Northern Pacifc Railway used these cars, converting over 900 roof top cabooses to bay window cabooses in the late 1930's. Milwaukee Road rib-side window cabooses are preserved at New Libson, Wisconsin, the Illinois Railway Museum, the Mt. Rainer Scenic Railroad, and Cedarburg, Wisconsin.
When the shift was made from wooden to steel caboose construction, a new type of caboose also arrived. The new caboose design replaced the traditional roof-mounted “cupola” with “bay-windows” attached to the sides of the caboose. As freight cars grew taller, the effectiveness of cupolas as practical observation points was diminished. This was especially true on lines that suffered from low clearances and were incapable of making cupolas high enough to see over the top of the tallest freight cars. Cabooses were prone to rough handling, and many a trainman was knocked out of his perch in the cupola and injured when he fell. The new caboose design was safer as well as more effective.
When the shift was made from wooden to steel caboose construction, a new type of caboose also arrived. The new caboose design replaced the traditional roof-mounted “cupola” with “bay-windows” attached to the sides of the caboose. As freight cars grew taller, the effectiveness of cupolas as practical observation points was diminished. This was especially true on lines that suffered from low clearances and were incapable of making cupolas high enough to see over the top of the tallest freight cars. Cabooses were prone to rough handling, and many a trainman was knocked out of his perch in the cupola and injured when he fell. The new caboose design was safer as well as more effective.
Road Name History: The Erie (the second railroad by that name) was formed in 1895 from the reorganization of the New York Lake Erie & Western which had cobbled together a Jersey City (across the Hudson from New York City) to Chicago route from the original Erie, the Chicago & Atlantic, Atlantic & Great Western and a few smaller lines. The route had been built to 6’ gauge and had been standard gauged in 1880.
The New York – Chicago main was all double track with big rail. However, the mainline managed to miss every major city along the way. Binghamton, New York and Akron, Ohio were the biggest cities on the mainline between New York and Chicago. Buffalo, Rochester, Youngstown, Cleveland, Dayton, and Cincinnati were all at the end of branches from the mainline. Some said that “you could forget how much unpopulated land there was in the Northeast until you rode the Erie.”
Erie and its predecessors were early victims of “robber barons” that saddled the company with debt that it would carry for over 100 years. The companies went bankrupt 3 times in the 19th Century and once during the Depression (in 1938, after most other lines ironically.) Erie promoted exclusively from within and management was rife with nepotism. It was called “Weary Erie”, and “The Scarlet Woman of Wall Street.”
Erie’s steam fleet was varied although not terribly modern. The Erie passed through Pennsylvania’s anthracite region so camelback locomotives were part of the mix. In fact Erie had the largest camelbacks ever built – 0-8-8-0’s delivered in 1908. Erie was also one of only two roads to employ Triplexes, in this case with the 2-8-8-8-2 wheel arrangement. Their most modern steam consisted of heavy Berkshires delivered in 1929 when the company was under the influence of the Van Sweringen brothers who also controlled Nickel Plate, C&O, Pere Marquette and Hocking Valley. As a result, they dieselized fairly early primarily with EMD, and Alco road and passenger units and switchers from nearly every builder. Like future dance partner DL&W, Erie road switchers were setup for long-hood-forward operation.
Other than heavy commuter operations in New Jersey, passenger operations paled in comparison to other eastern trunk lines. Erie concentrated on freight. From about 1947 until 1955, the Erie was fairly healthy, although still paying way too much for debt service. They even paid dividends for much of this period. Quartets of F units dragged freights over 185 cars long across New York’s scenic Southern Tier. Erie’s big clearances (due to the original 6’ track gauge) made Erie the go-to road for highly lucrative over-size loads. The Erie was much loved by communities along the line.
The mid-to-late 50s presented one disaster after another. Twin hurricanes damaged track (although not as bad as neighbor DL&W who really took it in the teeth), then strikes in the cement and steel industries cut traffic dramatically. Labor trouble in the tire center of Akron (where Erie was a major carrier) led to much of the tire industry leaving the area. Erie’s net income fell in half the next year and then they began to lose money. Combining parallel routes and Jersey Shore terminals with the Lackawanna helped but not enough. In 1960, The Erie merged with the Delaware Lackawanna & Western. Here are Erie’s stats in their final year: 2,215 route miles (about the same length as competitors Nickel Plate and Wabash); 484 diesels; 535 passenger cars; 20,028 freight cars.
The New York – Chicago main was all double track with big rail. However, the mainline managed to miss every major city along the way. Binghamton, New York and Akron, Ohio were the biggest cities on the mainline between New York and Chicago. Buffalo, Rochester, Youngstown, Cleveland, Dayton, and Cincinnati were all at the end of branches from the mainline. Some said that “you could forget how much unpopulated land there was in the Northeast until you rode the Erie.”
Erie and its predecessors were early victims of “robber barons” that saddled the company with debt that it would carry for over 100 years. The companies went bankrupt 3 times in the 19th Century and once during the Depression (in 1938, after most other lines ironically.) Erie promoted exclusively from within and management was rife with nepotism. It was called “Weary Erie”, and “The Scarlet Woman of Wall Street.”
Erie’s steam fleet was varied although not terribly modern. The Erie passed through Pennsylvania’s anthracite region so camelback locomotives were part of the mix. In fact Erie had the largest camelbacks ever built – 0-8-8-0’s delivered in 1908. Erie was also one of only two roads to employ Triplexes, in this case with the 2-8-8-8-2 wheel arrangement. Their most modern steam consisted of heavy Berkshires delivered in 1929 when the company was under the influence of the Van Sweringen brothers who also controlled Nickel Plate, C&O, Pere Marquette and Hocking Valley. As a result, they dieselized fairly early primarily with EMD, and Alco road and passenger units and switchers from nearly every builder. Like future dance partner DL&W, Erie road switchers were setup for long-hood-forward operation.
Other than heavy commuter operations in New Jersey, passenger operations paled in comparison to other eastern trunk lines. Erie concentrated on freight. From about 1947 until 1955, the Erie was fairly healthy, although still paying way too much for debt service. They even paid dividends for much of this period. Quartets of F units dragged freights over 185 cars long across New York’s scenic Southern Tier. Erie’s big clearances (due to the original 6’ track gauge) made Erie the go-to road for highly lucrative over-size loads. The Erie was much loved by communities along the line.
The mid-to-late 50s presented one disaster after another. Twin hurricanes damaged track (although not as bad as neighbor DL&W who really took it in the teeth), then strikes in the cement and steel industries cut traffic dramatically. Labor trouble in the tire center of Akron (where Erie was a major carrier) led to much of the tire industry leaving the area. Erie’s net income fell in half the next year and then they began to lose money. Combining parallel routes and Jersey Shore terminals with the Lackawanna helped but not enough. In 1960, The Erie merged with the Delaware Lackawanna & Western. Here are Erie’s stats in their final year: 2,215 route miles (about the same length as competitors Nickel Plate and Wabash); 484 diesels; 535 passenger cars; 20,028 freight cars.
Brand/Importer Information: Squeak N Products was started in 1989. The company specializes in N scale models and concentrates on Northeast roadnames, especially the "Squeak" or NYS & W.
Squeak N Products assigns an incremental stock number to its models, preceded by two letters representing the road letters. As a convention, in this database, we will use the number as the main stock number and will indicate the full stock number as secondary number.
Note: There was not a product #0013.
Squeak N Products assigns an incremental stock number to its models, preceded by two letters representing the road letters. As a convention, in this database, we will use the number as the main stock number and will indicate the full stock number as secondary number.
Note: There was not a product #0013.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2021-02-21 05:39:23
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.