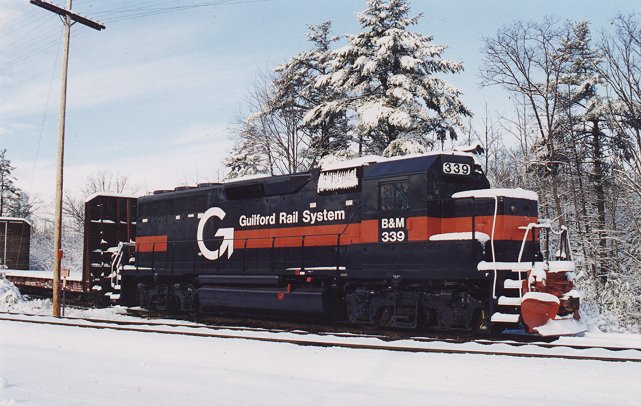
Specific Item Information: MASTER MODEL FEATURES:
• Long Hood Styles: CN (single light w/o number boards)
• 3,000 Gallon Fuel Tank
• Will have properly operating ditch lights
• Snow Shields
• Round or Square Sand Fill Hatches
• Cab-Mounted Bell
• Three-Chime Air Horn Mounted on Cab or Long Hood
• Etched Metal Sunshades (user installed)
• Factory-installed AccuMate® magnetic knuckle couplers
• Blackened metal wheels
• Scale Speed™ motor
• Atlas Master® Gold version features ESU LokSound Decoder
• Silver Series includes factory installed speaker for easy upgrade to sound
• Silver Sound Ready™
• Atlas Silver Sound Ready models are equipped with a speaker for easy conversion to sound with the addition of a decoder.
SOUND FUNCTIONALITY FEATURES (GOLD MODELS ONLY):
• Over 20 sound effects are available, including engine start-up and shutdown, prime mover sounds through all eight notches, bell, air horn, air compressor, dynamic brakes and more.
• Equipped with ESU’s Exclusive "Full Throttle" features for ultimate realism in prototype running.
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:
• Supports all DCC-programming modes
• DCC includes RailCom and RailComPlus, with 14, 28 or 128 speed steps and with 2-digit and 4-digit addressing.
• Flexible mapping of function keys F0 to F28.
• A total of 6 DCC function outputs are available, and all can be function mapped (disable, brightness, light effects) individually
• Follows all NMRA DCC standards and recommended practices.
• Long Hood Styles: CN (single light w/o number boards)
• 3,000 Gallon Fuel Tank
• Will have properly operating ditch lights
• Snow Shields
• Round or Square Sand Fill Hatches
• Cab-Mounted Bell
• Three-Chime Air Horn Mounted on Cab or Long Hood
• Etched Metal Sunshades (user installed)
• Factory-installed AccuMate® magnetic knuckle couplers
• Blackened metal wheels
• Scale Speed™ motor
• Atlas Master® Gold version features ESU LokSound Decoder
• Silver Series includes factory installed speaker for easy upgrade to sound
• Silver Sound Ready™
• Atlas Silver Sound Ready models are equipped with a speaker for easy conversion to sound with the addition of a decoder.
SOUND FUNCTIONALITY FEATURES (GOLD MODELS ONLY):
• Over 20 sound effects are available, including engine start-up and shutdown, prime mover sounds through all eight notches, bell, air horn, air compressor, dynamic brakes and more.
• Equipped with ESU’s Exclusive "Full Throttle" features for ultimate realism in prototype running.
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:
• Supports all DCC-programming modes
• DCC includes RailCom and RailComPlus, with 14, 28 or 128 speed steps and with 2-digit and 4-digit addressing.
• Flexible mapping of function keys F0 to F28.
• A total of 6 DCC function outputs are available, and all can be function mapped (disable, brightness, light effects) individually
• Follows all NMRA DCC standards and recommended practices.
Series Information:
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:Early Gold Series equipped with ESU’s Exclusive "Full Throttle" features for ultimate realism in prototype running.
Over 20 sound effects are available, including engine start-up and shutdown, prime mover sounds through all eight notches, bell, air horn, air compressor, dynamic brakes and more.
There are up to 16 user-selectable horns, 2 user-selectable bells, and 2 user-selectable synchronized brake squeals.
2024 Releases feature Soundtraxx Tsunami Decoder NMRA 21-pin plug.
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:
- Supports all DCC-programming modes
- DCC includes RailCom and RailComPlus, with 14, 28 or 128 speed steps and with 2-digit and 4-digit addressing.
- Flexible mapping of function keys F0 to F28.
- A total of 6 DCC function outputs are available, and all can be function mapped (disable, brightness, light effects) individually
- Follows all NMRA DCC standards and recommended practices.
Model Information: In 1973 Canadian National (CN) designed the safety cab, also known as the comfort cab, which featured a full-width nose that was intended to improve crew safety in the event of a collision. The first CN locomotives to feature this cab were GMDD GP38-2s and MLW M420s. GO Transit ordered the first safety cab equipped GP40-2s in 1973 with a three-unit order. CN then ordered their first safety cab GP40-2s from GMDD in 1974. Using CN’s locomotive classification system, these locomotives were assigned the designation GF-430 (General Motors, Freight, 4-axle, 3000hp). Letters are added after this designation to denote the separate orders for a given model.
The terminology "early" and "late" is used when referring to various road names on this run. "Late" CN and former CN units feature ditch lights, snow shields and have their air horn relocated to the top of the long hood.
The terminology "early" and "late" is used when referring to various road names on this run. "Late" CN and former CN units feature ditch lights, snow shields and have their air horn relocated to the top of the long hood.
Prototype History: The GP40 is a 4-axle diesel-electric road-switcher locomotive built by General Motors, Electro-Motive Division between November 1965 and December 1971. It has an EMD 645E3 16-cylinder engine generating 3,000 hp (2,240 kW).
The GP40 is 3 feet (0.914 m) longer than its EMD 567D3A-engined predecessor, the GP35, and distinguished visually by its three 48-inch radiator fans at the rear of the long hood, while the GP35 has two large fans and a smaller one in between. It was built on a 55 ft (16.76 m) frame; the GP35 was built on a 52 ft (15.85 m) frame - as was the GP7, 9, 18, and 30. The difference in length can be seen in the GP40's ten handrail stanchions compared to the GP35's nine.
1,187 GP40s were built for 28 U.S. railroads; 16 were built for one Canadian carrier, Canadian National; and 18 were built for two Mexican carriers, Ferrocarril Chihuahua al Pacifico and Ferrocarriles Nacional de Mexico. 60 units were built with high-short-hoods and dual control stands for Norfolk & Western Railway. Two passenger versions, the GP40P and GP40TC, were also built, but on longer frames to accommodate steam generators and HEP equipment.
On January 1, 1972, the GP40 was discontinued and replaced by the GP40-2, which has a modular electrical system and a few minor exterior changes.
From Wikipedia
A Guilford/Pan Am (MEC) train headed by a high-nose GP40 ex-NW followed by two SD40M-2 (rebuilt SD45)
The GP40 is 3 feet (0.914 m) longer than its EMD 567D3A-engined predecessor, the GP35, and distinguished visually by its three 48-inch radiator fans at the rear of the long hood, while the GP35 has two large fans and a smaller one in between. It was built on a 55 ft (16.76 m) frame; the GP35 was built on a 52 ft (15.85 m) frame - as was the GP7, 9, 18, and 30. The difference in length can be seen in the GP40's ten handrail stanchions compared to the GP35's nine.
1,187 GP40s were built for 28 U.S. railroads; 16 were built for one Canadian carrier, Canadian National; and 18 were built for two Mexican carriers, Ferrocarril Chihuahua al Pacifico and Ferrocarriles Nacional de Mexico. 60 units were built with high-short-hoods and dual control stands for Norfolk & Western Railway. Two passenger versions, the GP40P and GP40TC, were also built, but on longer frames to accommodate steam generators and HEP equipment.
On January 1, 1972, the GP40 was discontinued and replaced by the GP40-2, which has a modular electrical system and a few minor exterior changes.
From Wikipedia
A Guilford/Pan Am (MEC) train headed by a high-nose GP40 ex-NW followed by two SD40M-2 (rebuilt SD45)
Road Name History: The Canadian National Railway Company (reporting mark CN) is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec that serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad". CN is a public company with 24,000 employees. It had a market capitalization of 32 billion CAD in 2011. CN was government-owned, having been a Canadian Crown corporation from its founding to its privatization in 1995. Bill Gates was, in 2011, the largest single shareholder of CN stock.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
CN is the largest railway in Canada, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, and is currently Canada's only transcontinental railway company, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia. Its range once reached across the island of Newfoundland until 1988, when the Newfoundland Railway was abandoned.
Following CN's purchase of Illinois Central (IC) and a number of smaller US railways, it also has extensive trackage in the central United States along the Mississippi River valley from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Today, CN owns about 20,400 route miles (32,831 km) of track in 8 provinces (the only two not served by CN are Newfoundland & Labrador and Prince Edward Island), as well as a 70-mile (113 km) stretch of track (see Mackenzie Northern Railway) into the Northwest Territories to Hay River on the southern shore of Great Slave Lake; it is the northernmost rail line anywhere within the North American Rail Network, as far north as Anchorage, Alaska (although the Alaska Railroad goes further north than this, it is isolated from the rest of the rail network).
The railway was referred to as the Canadian National Railways (CNR) between 1918 and 1960, and as Canadian National/Canadien National (CN) from 1960 to the present.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Manufacturer Information: 'Atlas Model Railroad' represents the New Jersey manufacturing facility for Atlas brand model railroad products. Atlas also imported European made models in their early years and those items will be noted as having manufacturers set appropriately. In the 1990s Atlas moved all their toolings to China.
Item created by: CMK on 2020-01-22 09:23:44. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-12-02 09:34:59
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.