Model Information: Atlas introduced its Fairbanks Morse Trainmaster model in late 2000. It is a modern mechanism with a split-frame, directional lighting, dual-flywheels, chemically blackened wheels and is drop-in decoder friendly. It has some great shell detail such as painted safety rails and etched metal grills.
DCC Information: Early versions accept a drop-in decoder.
Recent versions 'Silver Series, Sound Ready' accept ESU E24 decoders. The DC version is pre-equipped with a speaker.
Recent versions 'Silver Series, Sound Ready' accept ESU E24 decoders. The DC version is pre-equipped with a speaker.
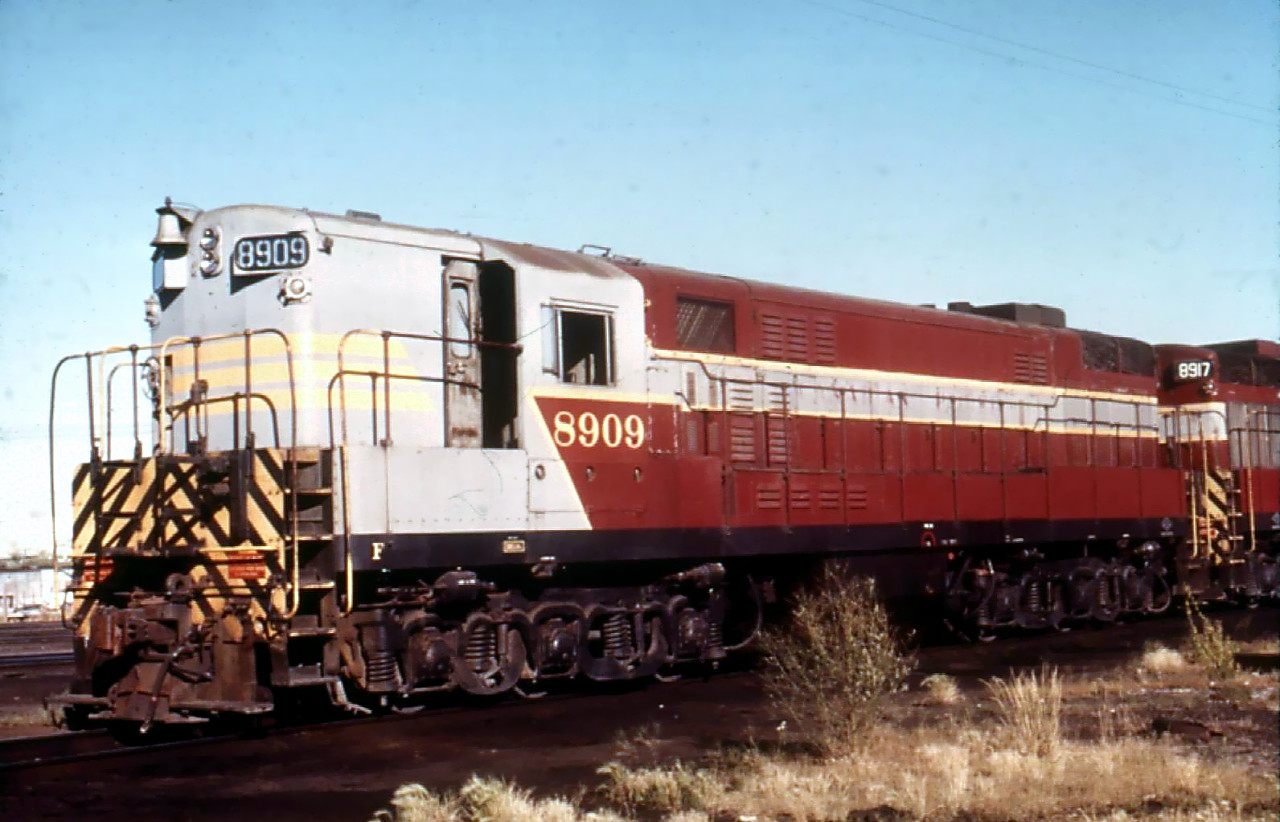
Prototype History: The H-24-66 was a diesel-electric railway locomotive model produced by Fairbanks-Morse and its Canadian licensee, the Canadian Locomotive Company. These six-axle hood unit road switchers, nicknamed Train Masters, were deployed in the United States and Canada during the 1950s. Each locomotive produced 2,400 horsepower (1.8 MW). They were the successor to the ultimately unsuccessful Consolidated line of cab units produced by F-M and CLC in the 1950s. In common with other F-M locomotives, the Train Master units employed an opposed piston-design prime mover. The official model designation was H-24-66 and rode on a pair of drop equalized three-axle "Trimount" trucks giving it an C-C wheel arrangement.
Touted by Fairbanks-Morse as "...the most useful locomotive ever built..." upon its introduction in 1953, the 2,400 horsepower (1.8 MW) H-24-66 Train Master was the most powerful single-engine diesel locomotive available, legendary for its pulling power and rapid acceleration. While some railroads saw advantages in the Train Master's greater power, the perception on the part of others that the unit had too much horsepower (coupled with the difficulties inherent in maintaining the opposed-piston engine, inadequacies in the electrical system, and a higher-than-normal consumption of cooling water) contributed to poor marketplace acceptance of the Train Masters. Perhaps it was simply ahead of its time, as no competitor offered a locomotive with an equal horsepower rating until the ALCO RSD-7 entered production in January, 1954 (As an aside, the EMD SD24 did not arrive on the scene until July, 1958, and GE did not introduce their U25C until September, 1963). Both F-M and CLC ultimately left the locomotive business.
From Wikipedia
Touted by Fairbanks-Morse as "...the most useful locomotive ever built..." upon its introduction in 1953, the 2,400 horsepower (1.8 MW) H-24-66 Train Master was the most powerful single-engine diesel locomotive available, legendary for its pulling power and rapid acceleration. While some railroads saw advantages in the Train Master's greater power, the perception on the part of others that the unit had too much horsepower (coupled with the difficulties inherent in maintaining the opposed-piston engine, inadequacies in the electrical system, and a higher-than-normal consumption of cooling water) contributed to poor marketplace acceptance of the Train Masters. Perhaps it was simply ahead of its time, as no competitor offered a locomotive with an equal horsepower rating until the ALCO RSD-7 entered production in January, 1954 (As an aside, the EMD SD24 did not arrive on the scene until July, 1958, and GE did not introduce their U25C until September, 1963). Both F-M and CLC ultimately left the locomotive business.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-02-17 11:16:43
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.