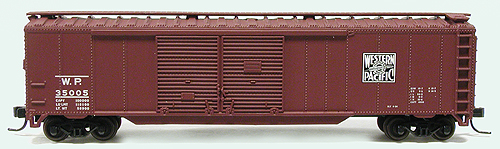
Specific Item Information: Built 4-54
Model Information: The first release of this body style was made by Roco in Austria for Atlas in 1967. Later, in 1971, Atlas moved the tooling from Austria to New Jersey and produced their own second release out of their own factory. I presume that Atlas owned the tooling because unlike other Roco models, this one did not later appear as an import by other brands such as Aurora, Minitrix or Model Power. Sometime in the 1990s Atlas again moved the production to China. As of the 2006 run, this model moved to the Atlas Trainman lower-grade range, reflecting its age.
Prototype History: The 50-foot boxcar made its first appearance in the 1930s and steadily grew in popularity over the years, which further improved redundancies by allowing for even more space within a given car. Today, the 50-footer remains the common boxcar size. After the second world war ended, and steel became once again readily available, steel became the go-to choice for construction of boxcars. Pullman Standard and ACF were some of the most prolific builders of these cars.
Double Doors were frequently an option for most of the major North American railcar manufacturers in the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s. These cars were slightly more expensive to produce and maintain, but for many applications allowed faster loading and unloading times.
Double Doors were frequently an option for most of the major North American railcar manufacturers in the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s. These cars were slightly more expensive to produce and maintain, but for many applications allowed faster loading and unloading times.
Road Name History:  The Western Pacific Railroad (reporting mark WP) was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was formed in 1903 as an attempt to break the near-monopoly the Southern Pacific Railroad had on rail service into northern California. WP's Feather River Route directly competed with SP's portion of the Overland Route for rail traffic between Salt Lake City/Ogden, Utah and Oakland, California for nearly 80 years. In 1983 the Western Pacific was acquired by the Union Pacific Railroad. The Western Pacific was one of the original operators of the California Zephyr.
The Western Pacific Railroad (reporting mark WP) was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was formed in 1903 as an attempt to break the near-monopoly the Southern Pacific Railroad had on rail service into northern California. WP's Feather River Route directly competed with SP's portion of the Overland Route for rail traffic between Salt Lake City/Ogden, Utah and Oakland, California for nearly 80 years. In 1983 the Western Pacific was acquired by the Union Pacific Railroad. The Western Pacific was one of the original operators of the California Zephyr.
The original Western Pacific Railroad was established in 1865 to build the westernmost portion of the Transcontinental Railroad between San Jose, California (later Oakland, California), and Sacramento, California. This company was absorbed into the Central Pacific Railroad in 1870.
The second company to use the name Western Pacific Railroad was founded in 1903. Under the direction of George Jay Gould I, the Western Pacific was founded to provide a standard gauge track connection to the Pacific Coast for his aspiring Gould transcontinental system. The construction was financed by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, a company in the Gould system, which lost access to California due to the attempted acquisition of the Southern Pacific Railroad by the Rio Grande's main rival, the Union Pacific Railroad. The Western Pacific Railroad acquired the Alameda and San Joaquin Railroad and began construction on what would become the Feather River Route. In 1909 it became the last major railroad completed into California. It used 85-lb rail on untreated ties, with no tie plates except on curves over one degree; in 1935 more than half of the main line still had its original rail, most of it having carried 150 million gross tons.
The Western Pacific was acquired in 1983 by Union Pacific Corporation, which in 1996 would purchase its long-time rival, the Southern Pacific Railroad. In July 2005 Union Pacific unveiled a brand new EMD SD70ACe locomotive, Union Pacific 1983, painted as an homage to the Western Pacific.

The original Western Pacific Railroad was established in 1865 to build the westernmost portion of the Transcontinental Railroad between San Jose, California (later Oakland, California), and Sacramento, California. This company was absorbed into the Central Pacific Railroad in 1870.
The second company to use the name Western Pacific Railroad was founded in 1903. Under the direction of George Jay Gould I, the Western Pacific was founded to provide a standard gauge track connection to the Pacific Coast for his aspiring Gould transcontinental system. The construction was financed by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, a company in the Gould system, which lost access to California due to the attempted acquisition of the Southern Pacific Railroad by the Rio Grande's main rival, the Union Pacific Railroad. The Western Pacific Railroad acquired the Alameda and San Joaquin Railroad and began construction on what would become the Feather River Route. In 1909 it became the last major railroad completed into California. It used 85-lb rail on untreated ties, with no tie plates except on curves over one degree; in 1935 more than half of the main line still had its original rail, most of it having carried 150 million gross tons.
The Western Pacific was acquired in 1983 by Union Pacific Corporation, which in 1996 would purchase its long-time rival, the Southern Pacific Railroad. In July 2005 Union Pacific unveiled a brand new EMD SD70ACe locomotive, Union Pacific 1983, painted as an homage to the Western Pacific.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: Emily on 2016-11-18 18:30:09
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.