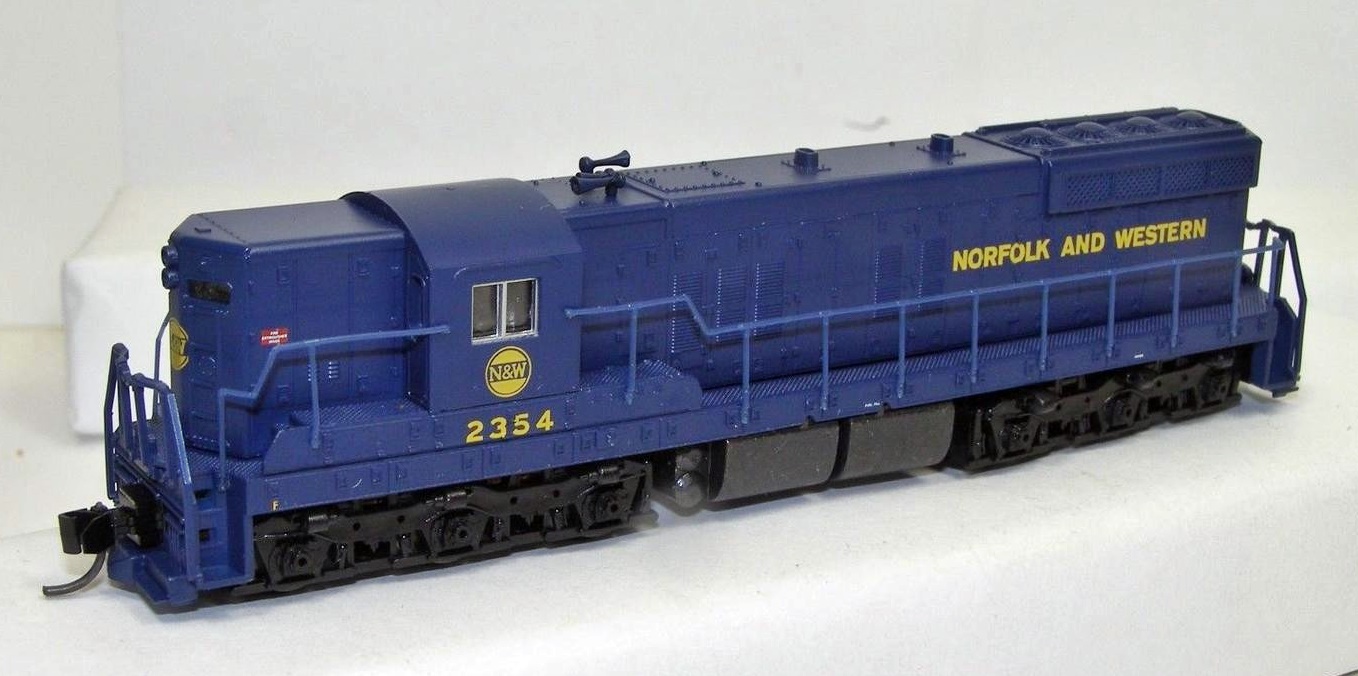
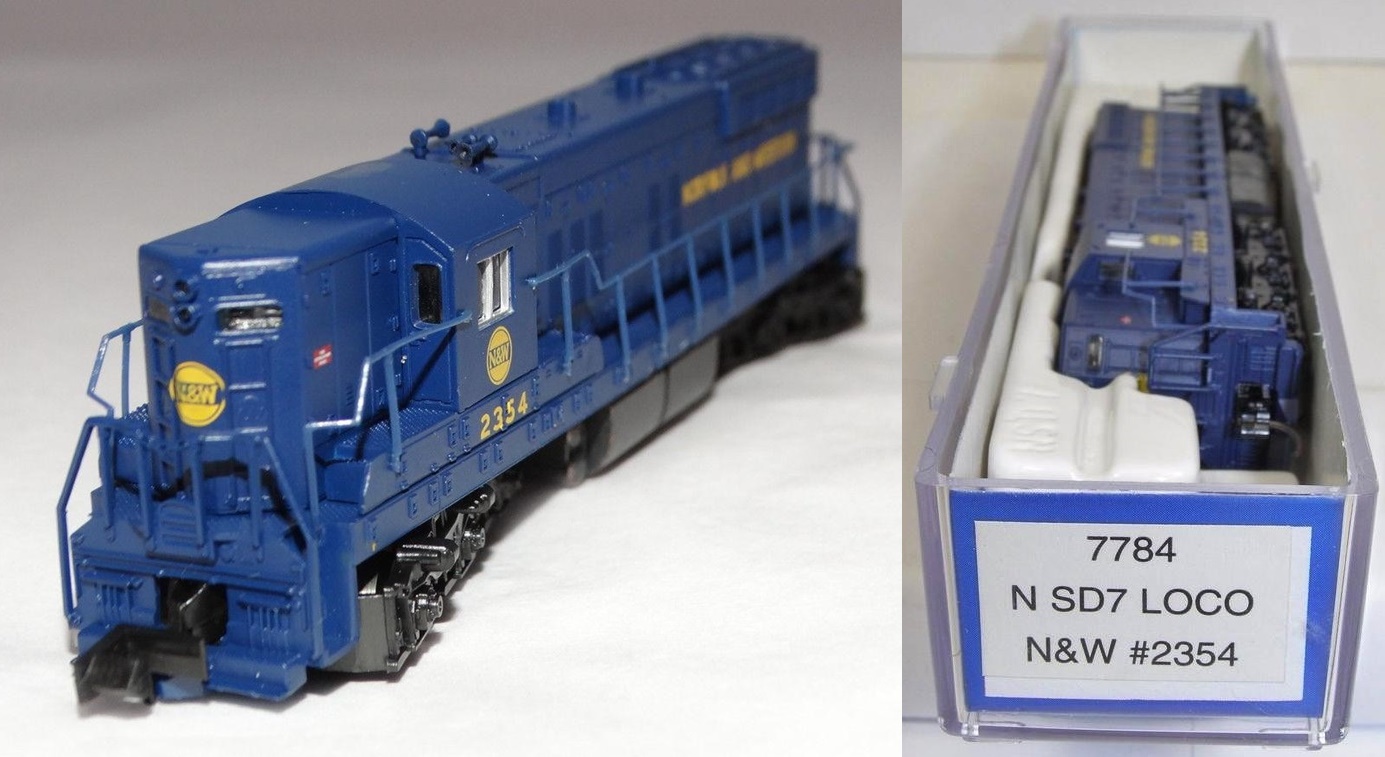
Model Information: Life-Like introduced this model in 1996. This model was one of several pretty good quality locomotives created by Life-Like in the 1990s. The model uses a dual-flywheel design, but the chassis is NOT a split-frame. Running quality is fairly good, but a DCC install is likely fairly challenging. Lighting is NOT directional. Due to the simpler design, Life-Like was able to offer these models at a lower price point than Atlas or Kato. Hence they were fairly popular. Since Walther acquired Life-Like, we have yet to see a re-release. Likely the chassis is a complete throw-away, and the shell is a bit on the simplistic side for what modelers expect in the current marketplace (2017). This model was sold either as a SD7 or a SD9, as there is little visual difference between both prototypes.
DCC Information: Although not DCC-Compatible, an excellent how-to tutorial can be found here: DCC for Life-Like SD7's and SD9's'
Prototype History: An SD7 is a 6-axle road switcher diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between February 1952 and November 1953. It had an EMD 567B 16-cylinder engine producing 1,500 horsepower (1.12 MW) for its six traction motors. 188 were built for United States railroads. Starting in August 1953 a total of 26 SD7s were produced which used either the 567BC engine or the 567C engine. These units are noted on the roster below.
This was the first model in EMD's SD (Special Duty) series of locomotives, a lengthened B-B GP7 with a C-C truck arrangement. The two extra axles and traction motors are useful in heavy, low speed freight service. SD series locomotives are still being produced today, with the SD70 being the most popular example in current production, and with many SD40-2s and rebuilds to SD40-2 specifications, or SD60s still in operation.
Yesterday's Special Duty eventually became today's Standard Duty, and yesterday's General Purpose has become today's Special Purpose ("time" freight and other time-sensitive lading). True GPs were discontinued after the completion of the last GP60 in 1994. Recently intermodal and other fast freights may be hauled by 6 axles locomotives with 4 powered axles, such as the SD70Ace-P4.
Many earlier model GPs, most particularly GP40s, GP39s and GP38s, also their SD equivalents, SD40s, SD39s and SD38s have been rebuilt to Dash 2 standards for another 30 to 40 years of service.
From Wikipedia
This was the first model in EMD's SD (Special Duty) series of locomotives, a lengthened B-B GP7 with a C-C truck arrangement. The two extra axles and traction motors are useful in heavy, low speed freight service. SD series locomotives are still being produced today, with the SD70 being the most popular example in current production, and with many SD40-2s and rebuilds to SD40-2 specifications, or SD60s still in operation.
Yesterday's Special Duty eventually became today's Standard Duty, and yesterday's General Purpose has become today's Special Purpose ("time" freight and other time-sensitive lading). True GPs were discontinued after the completion of the last GP60 in 1994. Recently intermodal and other fast freights may be hauled by 6 axles locomotives with 4 powered axles, such as the SD70Ace-P4.
Many earlier model GPs, most particularly GP40s, GP39s and GP38s, also their SD equivalents, SD40s, SD39s and SD38s have been rebuilt to Dash 2 standards for another 30 to 40 years of service.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Norfolk and Western Railway (reporting mark NW), was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its 150-year existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America" even though the N&W had mostly articulated steam on its roster. During the Civil War, the N&W was the biggest railroad in the south and moved most of the products with their steam locomotives to help the South the best way they could.
NW was famous for manufacturing its own steam locomotives, which were produced at the Roanoke Shops, as well as its own hopper cars. Around 1960, NW became the last major American railroad to convert from steam locomotives to diesel motive power but didn't retire its last remaining Y class locomotives until 1964 and 1965. By 1965, steam on class I railroads was gone but steam wasn't gone on class II railroads until 1974 and class III and mining railroads retired their steam locomotives from their active roster until 1983. By 1983, steam in America on class I, II, III, and mining railroads had finally closed the chapter on America's 150 years of steam from 1830 - 1983.
In December 1959, NW merged with the Virginian Railway (reporting mark VGN), a longtime rival in the Pocahontas coal region. By 1970, other mergers with the Nickel Plate Road and Wabash formed a system that operated 7,595 miles (12,223 km) of road on 14,881 miles (23,949 km) of track from North Carolina to New York and from Virginia to Iowa.
In 1980, NW teamed up with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier and created the Norfolk Southern Corporation holding company by merging its business operations with the business operations of the Southern Railway. The NW and the Southern Railway continued as separate railroads now under one holding company.
On December 31, 1990, the Southern Railway was renamed "Norfolk Southern Railway" to reflect the Norfolk Southern Corporation and on the same day, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway gained full control of the Norfolk and Western Railway with the Norfolk and Western being transferred from the holding company to the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, this began the final years of Norfolk and Western which was absorbed into the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway seven years later in 1997 (1990 to 1997 the Norfolk and Western continued operating by using paper operations).
In 1997 during the Conrail battle with CSX, Norfolk Southern Corporation's principal railroad, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway into their rail system, ending the existence of the Norfolk and Western Railway and having the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway becoming the only railroad in the entire Norfolk Southern system after that.
NW was famous for manufacturing its own steam locomotives, which were produced at the Roanoke Shops, as well as its own hopper cars. Around 1960, NW became the last major American railroad to convert from steam locomotives to diesel motive power but didn't retire its last remaining Y class locomotives until 1964 and 1965. By 1965, steam on class I railroads was gone but steam wasn't gone on class II railroads until 1974 and class III and mining railroads retired their steam locomotives from their active roster until 1983. By 1983, steam in America on class I, II, III, and mining railroads had finally closed the chapter on America's 150 years of steam from 1830 - 1983.
In December 1959, NW merged with the Virginian Railway (reporting mark VGN), a longtime rival in the Pocahontas coal region. By 1970, other mergers with the Nickel Plate Road and Wabash formed a system that operated 7,595 miles (12,223 km) of road on 14,881 miles (23,949 km) of track from North Carolina to New York and from Virginia to Iowa.
In 1980, NW teamed up with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier and created the Norfolk Southern Corporation holding company by merging its business operations with the business operations of the Southern Railway. The NW and the Southern Railway continued as separate railroads now under one holding company.
On December 31, 1990, the Southern Railway was renamed "Norfolk Southern Railway" to reflect the Norfolk Southern Corporation and on the same day, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway gained full control of the Norfolk and Western Railway with the Norfolk and Western being transferred from the holding company to the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, this began the final years of Norfolk and Western which was absorbed into the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway seven years later in 1997 (1990 to 1997 the Norfolk and Western continued operating by using paper operations).
In 1997 during the Conrail battle with CSX, Norfolk Southern Corporation's principal railroad, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway into their rail system, ending the existence of the Norfolk and Western Railway and having the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway becoming the only railroad in the entire Norfolk Southern system after that.
Brand/Importer Information:  Life-Like Products LLC (now Life-Like Toy and Hobby division of Wm. K. Walthers) was a manufacturer of model railroad products and was based in Baltimore, Maryland.
Life-Like Products LLC (now Life-Like Toy and Hobby division of Wm. K. Walthers) was a manufacturer of model railroad products and was based in Baltimore, Maryland.
It was founded in the 1950s by a company that pioneered extruded foam ice chests under the Lifoam trademark. Because ice chests are a summer seasonal item, the company needed a way to keep the factory operating year round. As model railroading was becoming popular in the post-war years, they saw this as an opportunity and so manufactured extruded foam tunnels for model trains. Over the years, Life-Like expanded into other scenery items, finally manufacturing rolling stock beginning in the late 1960s. At some point in the early 1970s, Life-Like purchased Varney Inc. and began to produce the former Varney line as its own.
The Canadian distributor for Life-Like products, Canadian Hobbycraft, saw a missing segment in market for Canadian model prototypes, and started producing a few Canadian models that were later, with a few modifications, offered in the US market with US roadnames.
In 2005, the company, now known as Lifoam Industries, LLC, decided to concentrate on their core products of extruded foam and sold their model railroad operations to Wm. K. Walthers.
In June 2018, Atlas and Walthers announced to have reached an agreement under which all Walthers N scale rolling stock tooling, including the former Life-Like tooling, will be purchased by Atlas.
Read more on Wikipedia and The Train Collectors Association.

It was founded in the 1950s by a company that pioneered extruded foam ice chests under the Lifoam trademark. Because ice chests are a summer seasonal item, the company needed a way to keep the factory operating year round. As model railroading was becoming popular in the post-war years, they saw this as an opportunity and so manufactured extruded foam tunnels for model trains. Over the years, Life-Like expanded into other scenery items, finally manufacturing rolling stock beginning in the late 1960s. At some point in the early 1970s, Life-Like purchased Varney Inc. and began to produce the former Varney line as its own.
The Canadian distributor for Life-Like products, Canadian Hobbycraft, saw a missing segment in market for Canadian model prototypes, and started producing a few Canadian models that were later, with a few modifications, offered in the US market with US roadnames.
In 2005, the company, now known as Lifoam Industries, LLC, decided to concentrate on their core products of extruded foam and sold their model railroad operations to Wm. K. Walthers.
In June 2018, Atlas and Walthers announced to have reached an agreement under which all Walthers N scale rolling stock tooling, including the former Life-Like tooling, will be purchased by Atlas.
Read more on Wikipedia and The Train Collectors Association.
Item created by: gdm on 2016-10-25 19:36:43. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-12-11 09:36:23
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.