USS Mississippi
| General Type | Ship |
| Unit Type | Battleship |
| Cost | 44 |
| Set | First Strike |
| Manufacturer | Forumini |
| Available | 1941 |
| Set ID | 31 |
| Game Class Limits | New Mexico |
| Class Size | 3 |
| Country | United States (Details) |
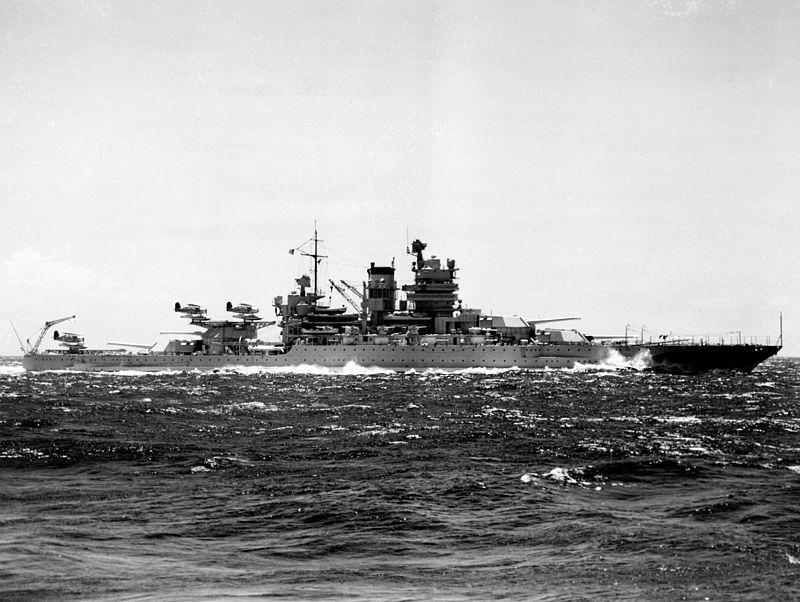
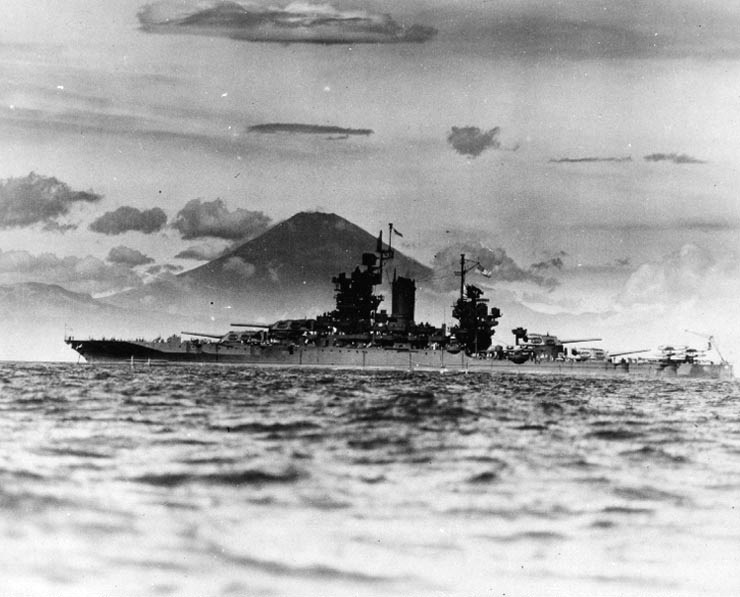
| Prototype | USS Mississippi (BB-41) (Details) |
| Class | New Mexico (Details) |
| Armor | 8 |
| Vital | 14 |
| Hull Points | 5 |
| Speed | 139 |
| Primary | 15/15/14/11 |
| Secondary | 5/5/4/0 |
| AA | 7/0/-/- |
| Special Ability | Last Salvo |
| Special Ability | Extended Range 4 |
| Special Ability | Torpedo Defense 1 |
| Game Rarity | X |
Click to see the details
market
Click to see the details
history
Prototype:
USS Mississippi (BB-41/AG-128), the second of three members of the New Mexico class, was the third ship of the United States Navy named in honor of the 20th state. The ship was built at the Newport News Shipbuilding Company of Newport News, Virginia, from her keel laying in April 1915, her launching in January 1917, and her commissioning in December that year. She was armed with a battery of twelve 14-inch (356 mm) guns in four three-gun turrets, and was protected by heavy armor plate, with her main belt armor being 13.5 inches (343 mm) thick.
The ship remained in North American waters during World War I, conducting training exercises to work up the crew. Throughout the 1920s and 1930s, the ship served in the Pacific Fleet. In May 1941, with World War II and the Battle of the Atlantic raging, Mississippi and her two sister ships were transferred to the Atlantic Fleet to help protect American shipping through the Neutrality Patrols. Two days after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Mississippi departed the Atlantic to return to the Pacific Fleet; throughout her participation in World War II, she supported amphibious operations in the Pacific. She shelled Japanese forces during the Gilbert and Marshall Islands and the Philippines campaigns and the invasions of Peleliu and Okinawa. The Japanese fleet attacked American forces during the Philippines campaign, and in the ensuing Battle of Leyte Gulf, Mississippi took part in the Battle of Surigao Strait, the last battleship engagement in history.
After the war, Mississippi was converted into a gunnery training ship, and was also used to test new weapons systems. These included the RIM-2 Terrier missile and the AUM-N-2 Petrel missile. She was eventually decommissioned in 1956 and sold to ship breakers in November that year.
The ship remained in North American waters during World War I, conducting training exercises to work up the crew. Throughout the 1920s and 1930s, the ship served in the Pacific Fleet. In May 1941, with World War II and the Battle of the Atlantic raging, Mississippi and her two sister ships were transferred to the Atlantic Fleet to help protect American shipping through the Neutrality Patrols. Two days after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Mississippi departed the Atlantic to return to the Pacific Fleet; throughout her participation in World War II, she supported amphibious operations in the Pacific. She shelled Japanese forces during the Gilbert and Marshall Islands and the Philippines campaigns and the invasions of Peleliu and Okinawa. The Japanese fleet attacked American forces during the Philippines campaign, and in the ensuing Battle of Leyte Gulf, Mississippi took part in the Battle of Surigao Strait, the last battleship engagement in history.
After the war, Mississippi was converted into a gunnery training ship, and was also used to test new weapons systems. These included the RIM-2 Terrier missile and the AUM-N-2 Petrel missile. She was eventually decommissioned in 1956 and sold to ship breakers in November that year.
Class History:
The New Mexico-class battleships of the United States Navy, all three of whose construction began in 1915, were improvements on the design introduced three years earlier with the Nevada class.
The twelve-gun main battery of the preceding Pennsylvania class was retained, but with longer 14-inch (356 mm)/50 caliber guns in improved triple turrets. Hull design was also upgraded with a 'clipper' bow for better seakeeping and a sleeker look. One ship, New Mexico, was fitted with turbo-electric propulsion.
Though eight secondary batteries were located in extremely wet bow and stern positions and were soon removed, the rest of the ships' 5-inch (127 mm)/51 caliber guns were mounted in the superstructure, a great improvement over earlier U.S. Navy battleships' arrangements.
The twelve-gun main battery of the preceding Pennsylvania class was retained, but with longer 14-inch (356 mm)/50 caliber guns in improved triple turrets. Hull design was also upgraded with a 'clipper' bow for better seakeeping and a sleeker look. One ship, New Mexico, was fitted with turbo-electric propulsion.
Though eight secondary batteries were located in extremely wet bow and stern positions and were soon removed, the rest of the ships' 5-inch (127 mm)/51 caliber guns were mounted in the superstructure, a great improvement over earlier U.S. Navy battleships' arrangements.
Country:
The U.S. is a country of 50 states covering a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. Major Atlantic Coast cities are New York, a global finance and culture center, and capital Washington, DC. Midwestern metropolis Chicago is known for influential architecture and on the west coast, Los Angeles' Hollywood is famed for filmmaking.
Item created by: Lethe
on 2015-05-31 17:46:30
Last edited by: gdm on 2019-07-19 19:06:04
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
Last edited by: gdm on 2019-07-19 19:06:04
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.